
In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only afferent fibers, the mandibular nerve contains both afferent and efferent fibers. These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication.

The buccinator is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.
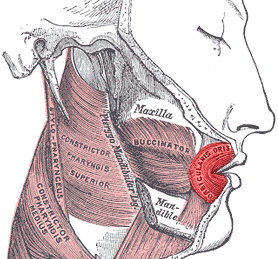
In human anatomy, the orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth. It is not a true sphincter, as was once thought, as it is actually composed of four independent quadrants that interlace and give only an appearance of circularity.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.

The zygomaticus major muscle is a muscle of the face. It arises from either zygomatic arch (cheekbone); it inserts at the corner of the mouth. It is innervated by branches of the facial nerve.

The facial artery, formerly called the external maxillary artery, is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies blood to superficial structures of the medial regions of the face.

The buccal nerve is a sensory nerve of the face arising from the mandibular nerve. It conveys sensory information from the skin of the cheek, and parts of the oral mucosa, periodontium, and gingiva.

The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (which is in turn a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal nerve.

The buccal artery is a small artery in the head. It branches off the second part of the maxillary artery and supplies the cheek and buccinator muscle.

The transverse facial artery is an artery that branches from the superficial temporal artery and runs across the face.

The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible.

The infraorbital artery is a small artery in the head that arises from the maxillary artery and passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit, then passes forward along the floor of the orbit, finally exiting the orbit through the infraorbital foramen to reach the face.

The marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve arises from the facial nerve in the parotid gland at the parotid plexus. It passes anterior-ward deep to the platysma and depressor anguli oris muscles. It provides motor innervation to muscles of the lower lip and chin: the depressor labii inferioris muscle, depressor anguli oris muscle, and mentalis muscle. It communicates with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar nerve.

The temporal branches of the facial nerve crosses the zygomatic arch to the temporal region, supplying the auriculares anterior and superior, and joining with the zygomaticotemporal branch of the maxillary nerve, and with the auriculotemporal branch of the mandibular nerve.

The zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (malar branches) are nerves of the face. They run across the zygomatic bone to the lateral angle of the orbit. Here, they supply the orbicularis oculi muscle, and join with filaments from the lacrimal nerve and the zygomaticofacial branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).

The cervical branch of the facial nerve is a nerve in the neck. It is a branch of the facial nerve (VII). It supplies the platysma muscle, among other functions.
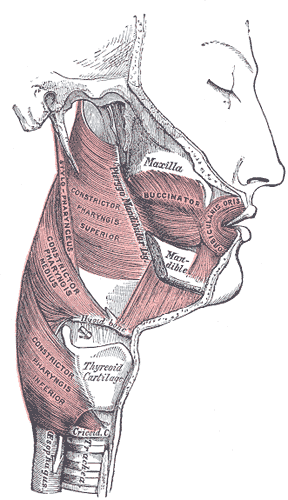
The buccal space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the cheek, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the buccinator muscle and deep to the platysma muscle and the skin. The buccal space is part of the subcutaneous space, which is continuous from head to toe.

The facial muscles are a group of striated skeletal muscles supplied by the facial nerve that, among other things, control facial expression. These muscles are also called mimetic muscles. They are only found in mammals, although they derive from neural crest cells found in all vertebrates. They are the only muscles that attach to the dermis.
Lip reconstruction may be required after trauma or surgical excision. The lips are considered the beginning of the oral cavity and are the most common site of oral cancer. Any reconstruction of the lips must include both functional and cosmetic considerations. The lips are necessary for speech, facial expression, and eating. Because of their prominent location on the face, even small abnormalities can be apparent.
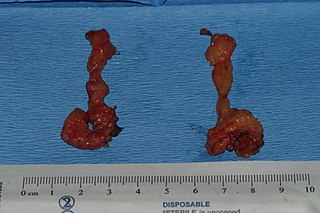
The buccal fat pad is one of several encapsulated fat masses in the cheek. It is a deep fat pad located on either side of the face between the buccinator muscle and several more superficial muscles. The inferior portion of the buccal fat pad is contained within the buccal space. It should not be confused with the malar fat pad, which is directly below the skin of the cheek. It should also not be confused with jowl fat pads. It is implicated in the formation of hollow cheeks and the nasolabial fold, but not in the formation of jowls.



















