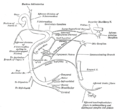
| Geniculate ganglion | |
|---|---|
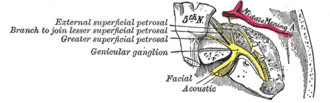 The course and connections of the facial nerve in the temporal bone. | |
 Cranial nerves VII and VIII and selected structures of the inner and middle ear. 1 Nervus vestibularis, 2 Nervus cochlearis, 3 Nervus intermediofacialis, 4 Ganglion geniculi, 5 Chorda tympani, 6 Cochlea, 7 Ductus semicirculares, 8 Malleus, 9 Membrana tympani, 10 Tuba auditiva | |
| Details | |
| Innervates | Lacrimal glands, submandibular glands, sublingual glands, tongue, palate, pharynx, external auditory meatus, stapedius muscle, posterior belly of the digastric muscle, stylohyoid muscle, muscles of facial expression |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ganglion geniculi nervi facialis |
| MeSH | D005830 |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.116 |
| TA2 | 6287 |
| FMA | 53414 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The geniculate ganglion (from Latin genu, for "knee" [1] ) is a bilaterally paired special sense ganglion [2] of the intermediate nerve component of the facial nerve (CN VII). [3] It is situated within facial canal of the head.[ citation needed ]
Contents
- Anatomy
- Structure
- Relations
- Clinical significance
- Herpes zoster oticus
- Additional images
- See also
- References
- External links
It contains cell bodies of first-order unipolar sensory neurons which convey gustatory (taste) afferents from taste receptors of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue by way of the chorda tympani, and of the palate by way of the greater petrosal nerve, From the ganglion, the proximal fibres proceed to the gustatory (i.e. superior/rostral [3] ) part of the solitary nucleus where they synapse with second-order neurons. [2]