
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

The solitary nucleus is a series of sensory nuclei forming a vertical column of grey matter in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. It receives general visceral and/or special visceral inputs from the facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve and vagus nerve ; it receives and relays stimuli related to taste and visceral sensation. It sends outputs to various parts of the brain, such as the hypothalamus, thalamus, and reticular formation. Neuron cell bodies of the SN are roughly somatotopically arranged along its length according to function.

Glomus cells are the cell type mainly located in the carotid bodies and aortic bodies. Glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors which sense the oxygen, carbon dioxide and pH levels of the blood. When there is a decrease in the blood's pH, a decrease in oxygen (pO2), or an increase in carbon dioxide (pCO2), the carotid bodies and the aortic bodies signal the dorsal respiratory group in the medulla oblongata to increase the volume and rate of breathing. The glomus cells have a high metabolic rate and good blood perfusion and thus are sensitive to changes in arterial blood gas tension. Glomus type II cells are sustentacular cells having a similar supportive function to glial cells.

A pseudounipolar neuron is a type of neuron which has one extension from its cell body. This type of neuron contains an axon that has split into two branches. A single process arises from the cell body and then divides into an axon and a dendrite. They develop embryologically as bipolar in shape, and are thus termed pseudounipolar instead of unipolar.
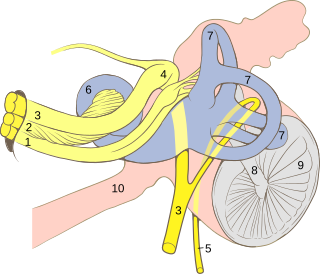
The geniculate ganglion is a collection of pseudounipolar sensory neurons of the facial nerve located in the facial canal of the head. It receives fibers from the facial nerve. It sends fibers that supply the lacrimal glands, submandibular glands, sublingual glands, tongue, palate, pharynx, external auditory meatus, stapedius muscle, posterior belly of the digastric muscle, stylohyoid muscle, and muscles of facial expression.

The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is the upper-most and largest of the cervical sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk. It probably formed by the union of four sympathetic ganglia of the cervical spinal nerves C1–C4. It is the only ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system that innervates the head and neck. The SCG innervates numerous structures of the head and neck.

The superior ganglion of the vagus nerve is a sensory ganglion of the peripheral nervous system. It is located within the jugular foramen, where the vagus nerve exits the skull. It is smaller than and proximal to the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve.

The tympanic nerve is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve found near the ear. It gives sensation to the middle ear, the Eustachian tube, the parotid gland, and mastoid air cells. It gives parasympathetic to supply to the parotid gland via the otic ganglion and the auriculotemporal nerve.

The superior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve is a sensory ganglion of the peripheral nervous system. It is located within the jugular foramen where the glossopharyngeal nerve exits the skull. It is smaller than and superior to the inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve.

The nerve of the pterygoid canal is formed by the union of the (parasympathetic) greater petrosal nerve and (sympathetic) deep petrosal nerve within the cartilaginous substance filling the foramen lacerum. From the foramen lacerum, the nerve of the pterygoid canal passes through the pterygoid canal to reach the pterygopalatine fossa, ending at the pterygopalatine ganglion.

The inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve is one of the two sensory ganglia of each vagus nerve. It contains neuron cell bodies of general visceral afferent fibers and special visceral afferent fibers. It is situated within the jugular fossa just below the skull. It is situated just below the superior ganglion of vagus nerve.

The intermediate nerve, nervus intermedius, nerve of Wrisberg or Glossopalatine nerve is the part of the facial nerve located between the motor component of the facial nerve and the vestibulocochlear nerve. It contains the sensory and parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve. Upon reaching the facial canal, it joins with the motor root of the facial nerve at the geniculate ganglion. Alex Alfieri postulates that the intermediate nerve should be considered as a separate cranial nerve and not a part of the facial nerve.
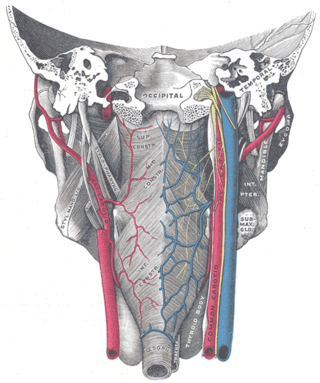
The pharyngeal plexus is a nerve plexus located upon the outer surface of the pharynx. It contains a motor component, a sensory component, and sympathetic component.

The salivatory nuclei are two parasympathetic general visceral efferent cranial nerve nuclei - the superior salivatory nucleus and the inferior salivatory nucleus - that innervate the salivary glands. Both are located in the pontine tegmentum of the brainstem.

The gustatory nucleus is the rostral part of the solitary nucleus located in the medulla. The gustatory nucleus is associated with the sense of taste and has two sections, the rostral and lateral regions. A close association between the gustatory nucleus and visceral information exists for this function in the gustatory system, assisting in homeostasis - via the identification of food that might be possibly poisonous or harmful for the body. There are many gustatory nuclei in the brain stem. Each of these nuclei corresponds to three cranial nerves, the facial nerve (VII), the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), and the vagus nerve (X) and GABA is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter involved in its functionality. All visceral afferents in the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves first arrive in the nucleus of the solitary tract and information from the gustatory system can then be relayed to the thalamus and cortex.

The following diagram is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the human nervous system:

The ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. Three types of axons enter the ciliary ganglion but only the preganglionic parasympathetic axons synapse there. The entering axons are arranged into three roots of the ciliary ganglion, which join enter the posterior surface of the ganglion.













