
The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face, brain and neck.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (which is in turn a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal nerve.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.

The lingual nerve carries sensory innervation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It contains fibres from both the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) and from the facial nerve (CN VII). The fibres from the trigeminal nerve are for touch, pain and temperature (general sensation), and the ones from the facial nerve are for taste (special sensation).

The supratrochlear nerve is a branch of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) from the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the forehead and the upper eyelid.
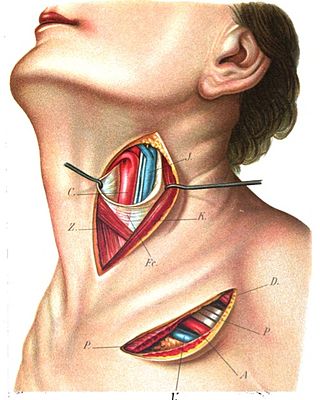
The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.

The supraclavicular nerve is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the cervical plexus that arises from the third and fourth cervical (spinal) nerves. It emerges from beneath the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, then split into multiple branches. Together, these innervate the skin over the shoulder.

The transverse cervical nerve is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the cervical plexus that arises from the second and third cervical spinal nerves (C2-C3). It curves around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, then pierces the fascia of the neck before dividing into two branches. It provides sensory innervation to the front of the neck.

The mylohyoid nerve is a mixed nerve of the head. It is a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve. It provides motor innervation the mylohyoid muscle, and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. It provides sensory innervation to part of the submental area, and sometimes also the mandibular (lower) molar teeth, requiring local anaesthesia for some oral procedures.

The marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve arises from the facial nerve in the parotid gland at the parotid plexus. It passes anterior-ward deep to the platysma and depressor anguli oris muscles. It provides motor innervation to muscles of the lower lip and chin: the depressor labii inferioris muscle, depressor anguli oris muscle, and mentalis muscle. It communicates with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar nerve.

The buccal branches of the facial nerve, are of larger size than the rest of the branches, pass horizontally forward to be distributed below the orbit and around the mouth.

The posterior auricular nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the facial nerve. It communicates with branches from the vagus nerve, the great auricular nerve, and the lesser occipital nerve. Its auricular branch supplies the posterior auricular muscle, the intrinsic muscles of the auricle, and gives sensation to the auricle. Its occipital branch supplies the occipitalis muscle.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The temporal branches of the facial nerve crosses the zygomatic arch to the temporal region, supplying the auriculares anterior and superior, and joining with the zygomaticotemporal branch of the maxillary nerve, and with the auriculotemporal branch of the mandibular nerve.

The zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (malar branches) are nerves of the face. They run across the zygomatic bone to the lateral angle of the orbit. Here, they supply the orbicularis oculi muscle, and join with filaments from the lacrimal nerve and the zygomaticofacial branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).

The digastric branch of facial nerve provides motor innervation to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. It branches from the facial nerve near to the stylomastoid foramen as the CN VII exits the facial canal. It commonly arises in common with the stylohyoid branch of facial nerve.

The facial muscles are a group of striated skeletal muscles supplied by the facial nerve that, among other things, control facial expression. These muscles are also called mimetic muscles. They are only found in mammals, although they derive from neural crest cells found in all vertebrates. They are the only muscles that attach to the dermis.

The parotid plexus or plexus parotideus is the branch point of the facial nerve (extratemporal) after it leaves the stylomastoid foramen. This division takes place within the parotid gland.
















