| Hypoglossal nucleus | |
|---|---|
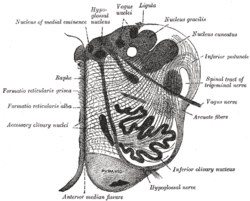 Section of the medulla oblongata. (Hypoglossal nucleus visible top left.) | |
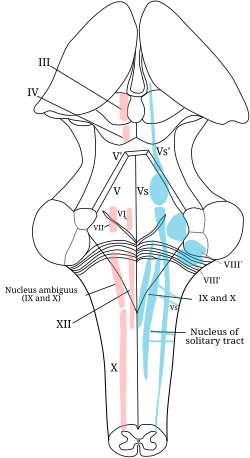 The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue. (XII labeled at bottom left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus nervi hypoglossi |
| NeuroNames | 757 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2644 |
| TA | A14.1.04.227 |
| FMA | 54505 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
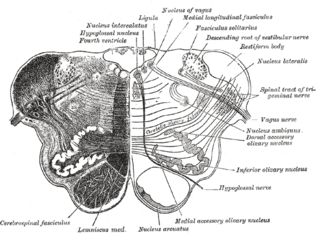
The hypoglossal nucleus is a cranial nerve nucleus, found within the medulla. Being a motor nucleus, it is close to the midline. In the open medulla, it is visible as what is known as the hypoglossal trigone , a raised area (medial to the vagal trigone) protruding slightly into the fourth ventricle.
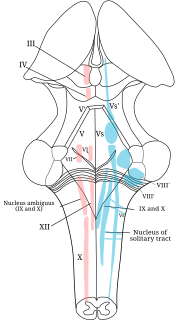
A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neurons in the brain stem that is associated with one or more cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei. Lesions occurring at these nuclei can lead to effects resembling those seen by the severing of nerve(s) they are associated with. All the nuclei except that of the trochlear nerve supply nerves of the same side of the body.

The medulla oblongata is a long stem-like structure which makes up part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep wake cycle.

In the upper part of the medulla oblongata, the hypoglossal nucleus approaches the rhomboid fossa, where it lies close to the middle line, under an eminence named the hypoglossal trigone. It is a slight elevation in the floor of the inferior recess of the fourth ventricle, beneath which is the nucleus of origin of the twelfth cranial nerve.
Contents
The hypoglossal nucleus is located between the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the midline of the medulla. Axons from the hypoglossal nucleus pass anteriorly through the medulla forming the hypoglossal nerve which exits between the pyramid and olive in a groove called the anterolateral sulcus.

The dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve is a cranial nerve nucleus for the vagus nerve in the medulla that lies ventral to the floor of the fourth ventricle. It mostly serves parasympathetic vagal functions in the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and other thoracic and abdominal vagal innervations. The cell bodies for the preganglionic parasympathetic vagal neurons that innervate the heart reside in the nucleus ambiguus.

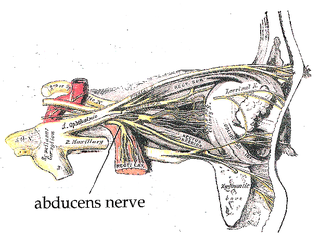
The hypoglossal nerve is the twelfth cranial nerve, and innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue, except for the palatoglossus which is innervated by the vagus nerve. It is a nerve with a solely motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, passes through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue. There are two hypoglossal nerves in the body: one on the left, and one on the right.

The medullary pyramids are paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts – known together as the pyramidal tracts. The lower limit of the pyramids is marked when the fibers cross (decussate).