Related Research Articles

The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiovascular center, the respiratory center, vomiting and vasomotor centers, responsible for the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'.
Articles related to anatomy include:

In anatomy, the extrapyramidal system is a part of the motor system network causing involuntary actions. The system is called extrapyramidal to distinguish it from the tracts of the motor cortex that reach their targets by traveling through the pyramids of the medulla. The pyramidal tracts may directly innervate motor neurons of the spinal cord or brainstem, whereas the extrapyramidal system centers on the modulation and regulation of anterior (ventral) horn cells.
The internal capsule is a paired white matter structure, as a two-way tract, carrying ascending and descending fibers, to and from the cerebral cortex. The internal capsule is situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the subcortical basal ganglia. As it courses it separates the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.

The pyramidal tracts include both the corticobulbar tract and the corticospinal tract. These are aggregations of efferent nerve fibers from the upper motor neurons that travel from the cerebral cortex and terminate either in the brainstem (corticobulbar) or spinal cord (corticospinal) and are involved in the control of motor functions of the body.

The corticobulbartract is a two-neuron white matter motor pathway connecting the motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the medullary pyramids, which are part of the brainstem's medulla oblongata region, and are primarily involved in carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves, like muscles of the face, head and neck. The corticobulbar tract is one of the pyramidal tracts, the other being the corticospinal tract.

The inferior olivary nucleus (ION) is a structure found in the medulla oblongata underneath the superior olivary nucleus. In vertebrates, the ION is known to coordinate signals from the spinal cord to the cerebellum to regulate motor coordination and learning. These connections have been shown to be tightly associated, as degeneration of either the cerebellum or the ION results in degeneration of the other.

The rubrospinal tract is one of the descending tracts of the spinal cord. It is a motor control pathway that originates in the red nucleus. It is a part of the lateral indirect extrapyramidal tract.

The red nucleus or nucleus ruber is a structure in the rostral midbrain involved in motor coordination. The red nucleus is pale pink, which is believed to be due to the presence of iron in at least two different forms: hemoglobin and ferritin. The structure is located in the midbrain tegmentum next to the substantia nigra and comprises caudal magnocellular and rostral parvocellular components. The red nucleus and substantia nigra are subcortical centers of the extrapyramidal motor system.

The inferior cerebellar peduncle is formed by fibers of the restiform body that join with fibers from the much smaller juxtarestiform body. The inferior cerebellar peduncle is the smallest of the three cerebellar peduncles.

The globose nucleus is one of the deep cerebellar nuclei. It is located medial to the emboliform nucleus, and lateral to the fastigial nucleus. The globose nucleus and emboliform nucleus are known collectively as the interposed nuclei.
The interposed nucleus is the combined paired globose and emboliform nuclei, on either side of the cerebellum. It is located in the roof of the fourth ventricle, lateral to the fastigial nucleus. The emboliform nucleus is the anterior interposed nucleus, and the globose nucleus is the posterior interposed nucleus.
Abnormal posturing is an involuntary flexion or extension of the arms and legs, indicating severe brain injury. It occurs when one set of muscles becomes incapacitated while the opposing set is not, and an external stimulus such as pain causes the working set of muscles to contract. The posturing may also occur without a stimulus. Since posturing is an important indicator of the amount of damage that has occurred to the brain, it is used by medical professionals to measure the severity of a coma with the Glasgow Coma Scale and the Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale.

In the human brain, the superior cerebellar peduncle is one of the three paired cerebellar peduncles of bundled fibers that connect the cerebellum to the brainstem. The superior cerebellar peduncle connects to the midbrain. It consists mainly of efferent fibers, the cerebellothalamic tract that runs from a cerebellar hemisphere to the contralateral thalamus, and the cerebellorubral tract that runs from a cerebellar hemisphere to the red nucleus. It also contains afferent tracts, most prominent of which is the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Other afferent tracts are the ventral trigeminal tract, tectocerebellar fibers, and noradrenergic fibers from the locus coeruleus. The superior peduncle emerges from the upper and medial parts of the white matter of each cerebellar hemisphere and is placed under cover of the upper part of the cerebellum.
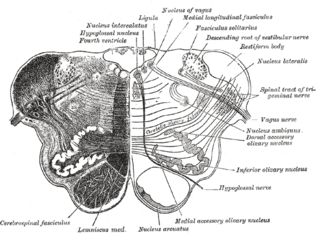
The olivocerebellar tract, also known as olivocerebellar fibers, are neural fibers which originate at the olivary nucleus and pass out through the hilum and decussate with those from the opposite olive in the raphe nucleus, then as internal arcuate fibers they pass partly through and partly around the opposite olive and enter the inferior peduncle to be distributed to the cerebellar hemisphere of the opposite side from which they arise.
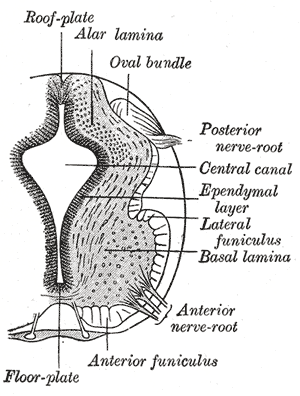
Alpha (α) motor neurons (also called alpha motoneurons), are large, multipolar lower motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle and are directly responsible for initiating their contraction. Alpha motor neurons are distinct from gamma motor neurons, which innervate intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles.
The myoclonic triangle is an important feedback circuit of the brainstem and deep cerebellar nuclei which is responsible for modulating spinal cord motor activity.

The pontocerebellar fibers are the second-order neuron fibers of the corticopontocerebellar tracts that cross to the other side of the pons and run within the middle cerebellar peduncles, from the pons to the contralateral cerebellum. They arise from the pontine nuclei as the second part of the corticopontocerebellar tract, and decussate (cross-over) in the pons before passing through the middle cerebellar peduncles to reach and terminate in the contralateral posterior lobe of the cerebellum (neocerebellum). It is part of a pathway involved in the coordination of voluntary movements.
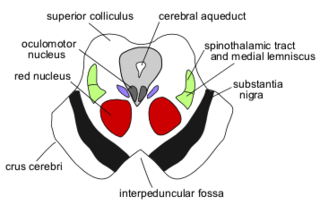
The central tegmental tract is a tract that carries ascending and descending fibers, situated in the midbrain tegmentum, and the pontine tegmentum. The tract is situated in the central portion of the reticular formation.
References
- ↑ "Rubroolivary fibers".
- ↑ Kennedy PR (December 1990). "Corticospinal, rubrospinal and rubro-olivary projections: a unifying hypothesis". Trends Neurosci. 13 (12): 474–479. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(90)90079-P. PMID 1703677. S2CID 4012758.