| Accessory cuneate nucleus | |
|---|---|
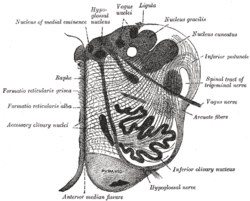 Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Accessory cuneate nucleus is not labeled, but cuneate nucleus is labeled at upper right, and the accessory cuneate nucleus would be found lateral to it.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Medulla oblongata |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus cuneatus accessorius |
| NeuroNames | 768 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2634 |
| TA | A14.1.04.209 |
| FMA | 72603 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The accessory cuneate nucleus is located lateral to the cuneate nucleus in the medulla oblongata at the level of the sensory decussation (the crossing fibers of the posterior column/medial lemniscus tract).

Standard anatomical terms of location deal unambiguously with the anatomy of animals, including humans.

The medulla oblongata is a long stem-like structure located in the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep wake cycle.

The sensory decussation or decussation of the lemniscus is a decussation or crossover of axons from the gracile nucleus and cuneate nucleus, which are responsible for fine touch, proprioception and two-point discrimination of the body. The fibres of this decussation are called the internal arcuate fibres and are found at the superior aspect of the closed medulla superior to the motor decussation. It is part of the second neuron in the posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway.
Contents
It receives input from cervical spinal nerves and transmits that information to the cerebellum. [1]
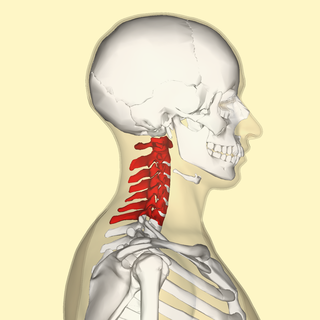
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae lie caudal of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have 7 cervical vertebrae, with the only 3 known exceptions being the manatee with 6, the two-toed sloth with 5–6, and the three-toed sloth with 9.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

The cerebellum is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as in regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans.
These fibers are called cuneocerebellar (cuneate nucleus → cerebellum) fibers.
In this function, the accessory cuneate nucleus is the upper extremity equivalent of Clarke's column. [1]

In human anatomy, the arm is the part of the upper limb between the glenohumeral joint and the elbow joint. In common usage, the arm extends to the hand. It can be divided into the upper arm, which extends from the shoulder to the elbow, the forearm which extends from the elbow to the hand, and the hand. Anatomically the shoulder girdle with bones and corresponding muscles is by definition a part of the arm. The Latin term brachium may refer to either the arm as a whole or to the upper arm on its own.