
The sense of balance or equilibrioception is the perception of balance and spatial orientation. It helps prevent humans and nonhuman animals from falling over when standing or moving. Equilibrioception is the result of a number of sensory systems working together; the eyes, the inner ears, and the body's sense of where it is in space (proprioception) ideally need to be intact.

The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The brainstem is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem.

The internal capsule is a paired white matter structure, as a two-way tract, carrying ascending and descending fibers, to and from the cerebral cortex. The internal capsule is situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the subcortical basal ganglia. As it courses it separates the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.
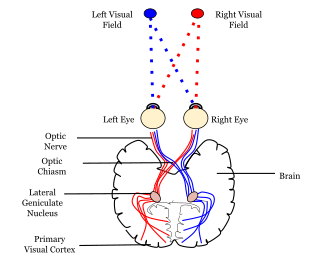
In neuroanatomy, a neural pathway is the connection formed by axons that project from neurons to make synapses onto neurons in another location, to enable neurotransmission. Neurons are connected by a single axon, or by a bundle of axons known as a nerve tract, or fasciculus. Shorter neural pathways are found within grey matter in the brain, whereas longer projections, made up of myelinated axons, constitute white matter.

The spinothalamic tract is a nerve tract in the anterolateral system in the spinal cord. This tract is an ascending sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.

The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) (also known as the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway is the major sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception from the skin and joints. It transmits this information to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus in the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in the gracile fasciculus and the cuneate fasciculus, tracts that make up the white matter dorsal columns of the spinal cord. At the level of the medulla oblongata, the fibers of the tracts decussate and are continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.
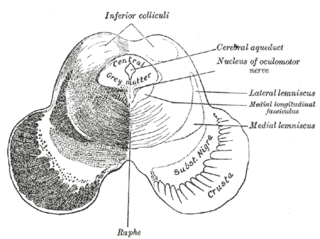
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is a prominent bundle of nerve fibres which pass within the ventral/anterior portion of periaqueductal gray of the mesencephalon (midbrain). It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement.
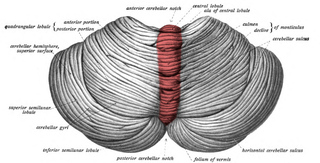
The cerebellar vermis is located in the medial, cortico-nuclear zone of the cerebellum, which is in the posterior fossa of the cranium. The primary fissure in the vermis curves ventrolaterally to the superior surface of the cerebellum, dividing it into anterior and posterior lobes. Functionally, the vermis is associated with bodily posture and locomotion. The vermis is included within the spinocerebellum and receives somatic sensory input from the head and proximal body parts via ascending spinal pathways.

The spinocerebellar tracts are nerve tracts originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. The two main tracts are the dorsal spinocerebellar tract, and the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Both of these tracts are located in the peripheral region of the lateral funiculi.

The dentate nucleus is a cluster of neurons, or nerve cells, in the central nervous system that has a dentate – tooth-like or serrated – edge. It is located within the deep white matter of each cerebellar hemisphere, and it is the largest single structure linking the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. It is the largest and most lateral, or farthest from the midline, of the four pairs of deep cerebellar nuclei, the others being the globose and emboliform nuclei, which together are referred to as the interposed nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus. The dentate nucleus is responsible for the planning, initiation and control of voluntary movements. The dorsal region of the dentate nucleus contains output channels involved in motor function, which is the movement of skeletal muscle, while the ventral region contains output channels involved in nonmotor function, such as conscious thought and visuospatial function.

The fastigial nucleus is located in each hemisphere of the cerebellum. It is one of the four deep cerebellar nuclei.

The vestibulospinal tract is a neural tract in the central nervous system. Specifically, it is a component of the extrapyramidal system and is classified as a component of the medial pathway. Like other descending motor pathways, the vestibulospinal fibers of the tract relay information from nuclei to motor neurons. The vestibular nuclei receive information through the vestibulocochlear nerve about changes in the orientation of the head. The nuclei relay motor commands through the vestibulospinal tract. The function of these motor commands is to alter muscle tone, extend, and change the position of the limbs and head with the goal of supporting posture and maintaining balance of the body and head.

The vestibular nuclei (VN) are the cranial nuclei for the vestibular nerve located in the brainstem.

The sensory decussation or decussation of the lemnisci is a decussation of axons from the gracile nucleus and cuneate nucleus, known together as the dorsal column nuclei. The dorsal column nuclei are responsible for fine touch, vibration, proprioception and two-point discrimination.
The isothalamus is a division used by some researchers in describing the thalamus.
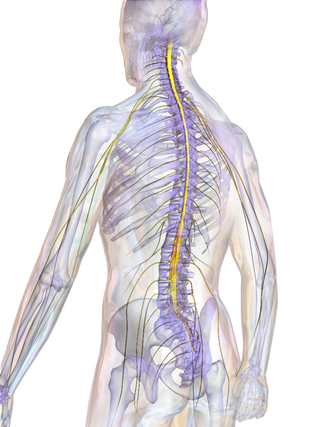
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.

The proper fasciculi, or spinospinal fasciculi, or propriospinal tracts, are groups of short fibres, ascending and descending, and crossed and uncrossed, within the spinal cord. These fibres are grouped into anterior, posterior, and lateral regions and make up a spinal pathway. Descending dorsal root collaterals are often included in the pathway.














