| Olivary body | |
|---|---|
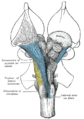
 The medulla, showing the olives lying adjacent to the pyramids. | |
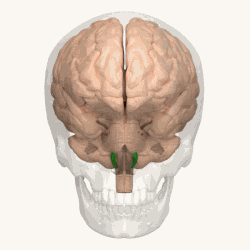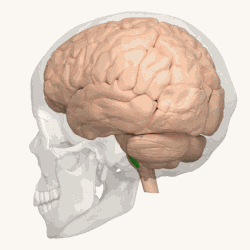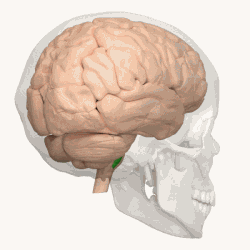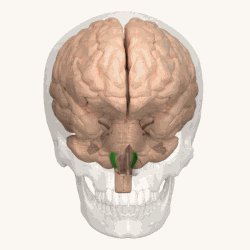 Animation shows the location of the olives in green. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Medulla |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | oliva |
| MeSH | D009847 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The olivary bodies or simply olives (Latin oliva and olivae, singular and plural, respectively) are a pair of prominent oval structures on either side of the medullary pyramids in the medulla, the lower portion of the brainstem. They contain the olivary nuclei.