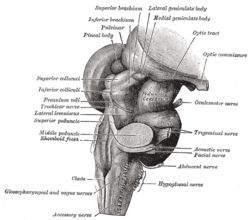
The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
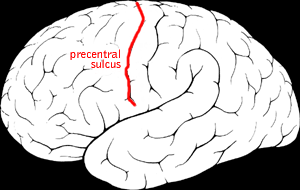
The precentral sulcus is a part of the human brain that lies parallel to, and in front of, the central sulcus. A sulcus is one of the prominent grooves on the surface of the human brain.

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

The calcarine sulcus is an anatomical landmark located at the caudal end of the medial surface of the brain of humans and other primates. Its name comes from the Latin "calcar" meaning "spur". It is very deep, and known as a complete sulcus.

The great cardiac vein is a vein of the heart. It begins at the apex of the heart and ascends along the anterior interventricular sulcus before joining the oblique vein of the left atrium to form the coronary sinus upon the posterior surface of the heart.
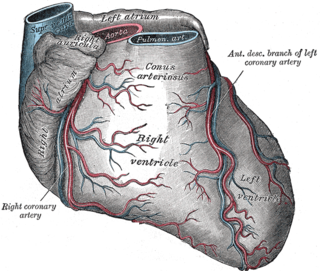
The coronary sulcus is a groove on the surface of the heart at the base of right auricle that separates the atria from the ventricles. The structure contains the trunks of the nutrient vessels of the heart, and is deficient in front, where it is crossed by the root of the pulmonary trunk. On the posterior surface of the heart, the coronary sulcus contains the coronary sinus. The right coronary artery, circumflex branch of left coronary artery, and small cardiac vein all travel along parts of the coronary sulcus.

The circumflex branch of left coronary artery is a branch of the left coronary artery. It winds around the left side of the heart along the atrioventricular groove. It supplies the posterolateral portion of the left ventricle.
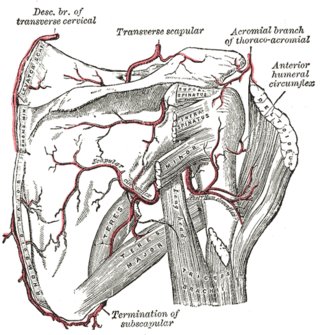
The anterior humeral circumflex artery is an artery in the arm. It is one of two circumflexing arteries that branch from the axillary artery, the other being the posterior humeral circumflex artery. The anterior humeral circumflex artery is considerably smaller than the posterior and arises nearly opposite to it, from the lateral side of the axillary artery.

The anterior interventricular sulcus is one of two grooves separating the ventricles of the heart. They can also be known as paraconal interventricular groove or subsinosal interventricular groove respectively. It is situated on the sternocostal surface of the heart, close to the left margin of the heart. It extends between the coronary sulcus, and the apex of the heart; upon reaching the diaphragmatic surface of the heart, it ends at the notch of cardiac apex. It contains the anterior interventricular branch of the left coronary artery, and great cardiac vein.

The posterior interventricular sulcus or posterior longitudinal sulcus is one of the two grooves separating the ventricles of the heart. They can be known as subsinosal interventricular groove or paraconal interventricular groove respectively. It is located on the diaphragmatic surface of the heart near the right margin. It extends between the coronary sulcus and the apex of the heart. It contains the posterior interventricular artery and middle cardiac vein.

The collateral fissure is a large sulcus on the tentorial surface of the cerebral hemisphere and extends from near the occipital pole to within a short distance of the temporal pole. It is also known as the medial occipitotemporal sulcus.

The chiasmatic groove is a transverse groove upon the superior aspect of the body of sphenoid bone within the middle cranial fossa. It is bounded anteriorly by the sphenoidal limbus, and posteriorly by the tuberculum sellae. The opening of each optic canal is placed at either lateral end of the chiasmatic sulcus. The optic chiasm is situated superior and quite posterior to the chiasmatic groove.

The posterior median sulcus of medulla oblongata is a narrow groove; and exists only in the closed part of the medulla oblongata; it becomes gradually shallower from below upward, and finally ends about the middle of the medulla oblongata, where the central canal expands into the cavity of the fourth ventricle.

In the occipital lobe, the lateral occipital sulcus, where present, divides the lateral, or middle occipital gyrus into a superior and an inferior part, which are then continuous in front with the parietal and temporal lobes. The anterior portion is often incomplete, but in some individuals it may encounter the superior temporal sulcus whilst the posterior portion originates from the middle of the curved lunate sulcus, or from a curved portion of the transverse occipital sulcus if absent.

In neuroanatomy, the marginal sulcus is a sulcus (crevice) that may be considered the termination of the cingulate sulcus. It separates the paracentral lobule anteriorly and the precuneus posteriorly.

The intercondylar fossa of femur is a deep notch between the rear surfaces of the medial and lateral epicondyle of the femur, two protrusions on the distal end of the femur that joins the knee. On the front of the femur, the condyles are but much less prominent and are separated from one another by a smooth shallow articular depression called the patellar surface because it articulates with the posterior surface of the patella (kneecap).
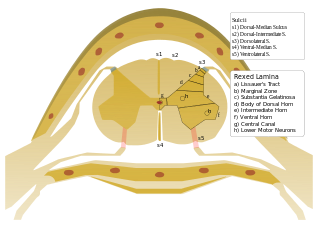
On either side of the posterior median sulcus of the spinal cord, and at a short distance from it, the posterior nerve roots are attached along a vertical furrow named the posterolateral sulcus. The portion of the medulla spinalis which lies between this and the posterior median sulcus is named the posterior funiculus.
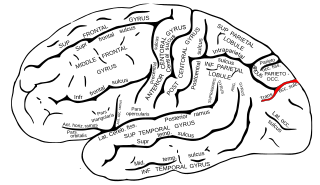
The transverse occipital sulcus is a sulcus in the occipital lobe.

The middle cerebral veins - the superficial middle cerebral vein and the deep middle cerebral vein - are two veins running along the lateral sulcus. The superficial middle cerebral vein is also known as the superficial Sylvian vein, and the deep middle cerebral vein is also known as the deep Sylvian vein. The lateral sulcus is also known as the Sylvian fissure.

The inferior or orbital surface of the frontal lobe is concave, and rests on the orbital plate of the frontal bone. It is divided into four orbital gyri by a well-marked H-shaped orbital sulcus. These are named, from their position, the medial, anterior, lateral, and posterior, orbital gyri. The medial orbital gyrus presents a well-marked antero-posterior sulcus, the olfactory sulcus, for the olfactory tract; the portion medial to this is named the straight gyrus, and is continuous with the superior frontal gyrus on the medial surface.