In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (lit. triplet nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name (trigeminal, from Latin tri- 'three' and -geminus 'twin') derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it.

The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. The internal capsule contains both ascending and descending axons, going to and coming from the cerebral cortex. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.
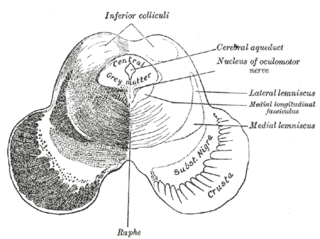
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is a prominent bundle of nerve fibres which pass within the ventral/anterior portion of periaqueductal gray of the mesencephalon (midbrain). It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement.
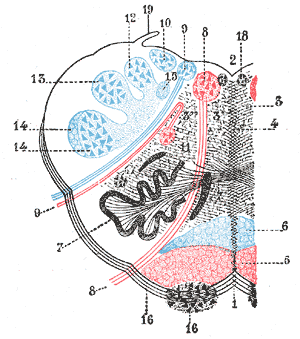
Medial medullary syndrome, also known as inferior alternating syndrome, hypoglossal alternating hemiplegia, lower alternating hemiplegia, or Dejerine syndrome, is a type of alternating hemiplegia characterized by a set of clinical features resulting from occlusion of the anterior spinal artery. This results in the infarction of medial part of the medulla oblongata.

The corticobulbartract is a two-neuron white matter motor pathway connecting the motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the medullary pyramids, which are part of the brainstem's medulla oblongata region, and are primarily involved in carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves. The corticobulbar tract is one of the pyramidal tracts, the other being the corticospinal tract.

The rubrospinal tract is a part of the nervous system. It is a part of the lateral indirect extrapyramidal tract.

The pontine nuclei are all neurons of the ventral pons collectively. Corticopontine fibres project from the primary motor cortex to the ipsilateral pontine nucleus; pontocerebellar fibers then relay the information to the contralateral cerebellum via the middle cerebellar peduncle.

The upper part of the posterior district of the medulla oblongata is occupied by the inferior cerebellar peduncle, a thick rope-like strand situated between the lower part of the fourth ventricle and the roots of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.

The paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) is a subset of neurons of the oral and caudal pontine reticular nuclei mediating horizontal gaze. It is situated in the pons adjacent to the abducens nucleus. It projects to the ipsilateral abducens nucleus, and contralateral oculomotor nucleus to mediate conjugate horizontal eye movements and saccades.

The facial motor nucleus is a collection of neurons in the brainstem that belong to the facial nerve. These lower motor neurons innervate the muscles of facial expression and the stapedius.

Cerebellar peduncles connect the cerebellum to the brain stem. There are six cerebellar peduncles in total, three on each side:

The middle cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of the brain. It connects the pons to the cerebellum, with fibres originating from the pontine nucleus and travelling to the opposite hemisphere of the cerebellar cortex. It is supplied by the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) and branches from the basilar artery. It conveys information from the cerebrum and the pons to the cerebellum.
The reticulotegmental nucleus, tegmental pontine reticular nucleus is an area within the floor of the pons, in the brain stem. This area is known to affect the cerebellum with its axonal projections.
The paramedian reticular nucleus sends its connections to the spinal cord in a mostly ipsilateral manner, although there is some decussation.

The basilar part of pons, also known as basis pontis, or basilar pons, is the ventral part of the pons in the brainstem; the dorsal part is known as the pontine tegmentum.

The pontocerebellar fibers are the second-order neuron fibers of the corticopontocerebellar tracts that cross to the other side of the pons and run within the middle cerebellar peduncles, from the pons to the contralateral cerebellum. They arise from the pontine nuclei as the second part of the corticopontocerebellar tract, and decussate (cross-over) in the pons before passing through the middle cerebellar peduncles to reach and terminate in the contralateral posterior lobe of the cerebellum (neocerebellum). It is part of a pathway involved in the coordination of voluntary movements.
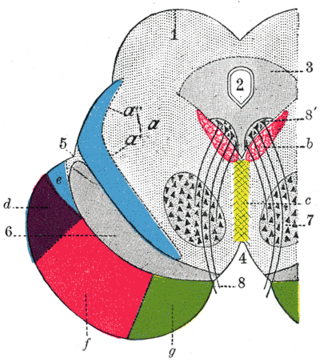
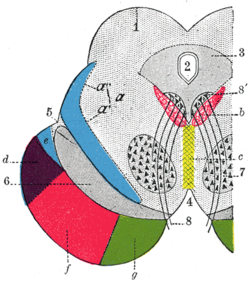
Corticopontine fibers are projections from layer V of the cerebral cortex to the pontine nuclei of the ventral pons. They represent the first link in a cortico-cerebello-cortical pathway mediating neocerebellar control of the motor cortex. The pathway is especially important for voluntary movements.

The anatomy of the cerebellum can be viewed at three levels. At the level of gross anatomy, the cerebellum consists of a tightly folded and crumpled layer of cortex, with white matter underneath, several deep nuclei embedded in the white matter, and a fluid-filled ventricle in the middle. At the intermediate level, the cerebellum and its auxiliary structures can be broken down into several hundred or thousand independently functioning modules or compartments known as microzones. At the microscopic level, each module consists of the same small set of neuronal elements, laid out with a highly stereotyped geometry.
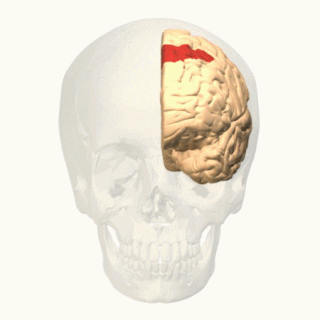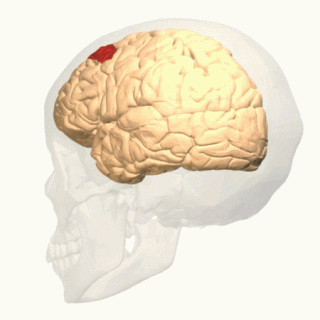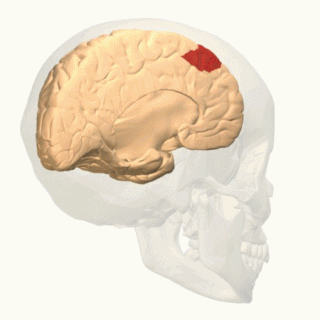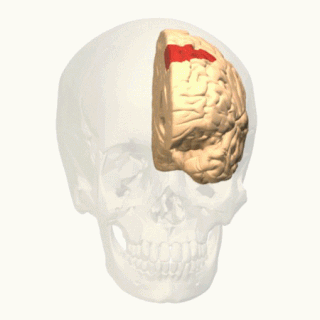
In neuroanatomy, corticomesencephalic tract is a descending nerve tract that originates in the frontal eye field and terminate in the midbrain. Its fibers mediate conjugate eye movement.