Related Research Articles

In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, ventral projection of the thalamus where the thalamus connects with the optic nerve. There are two LGNs, one on the left and another on the right side of the thalamus. In humans, both LGNs have six layers of neurons alternating with optic fibers.

The paraventricular nucleus is a nucleus in the hypothalamus. Anatomically, it is adjacent to the third ventricle and many of its neurons project to the posterior pituitary. These projecting neurons secrete oxytocin and a smaller amount of vasopressin, otherwise the nucleus also secretes corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). CRH and TRH are secreted into the hypophyseal portal system and act on different targets neurons in the anterior pituitary. PVN is thought to mediate many diverse functions through these different hormones, including osmoregulation, appetite, and the response of the body to stress.
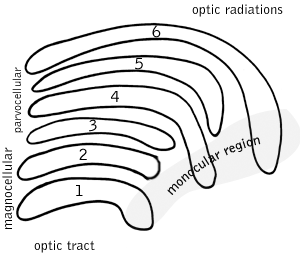
Parvocellular cells, also called P-cells, are neurons located within the parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus. "Parvus" is Latin for "small", and the name "parvocellular" refers to the small size of the cell compared to the larger magnocellular cells. Phylogenetically, parvocellular neurons are more modern than magnocellular ones.

The red nucleus or nucleus ruber is a structure in the rostral midbrain involved in motor coordination. The red nucleus is pale pink, which is believed to be due to the presence of iron in at least two different forms: hemoglobin and ferritin. The structure is located in the tegmentum of the midbrain next to the substantia nigra and comprises caudal magnocellular and rostral parvocellular components. The red nucleus and substantia nigra are subcortical centers of the extrapyramidal motor system.
A koniocellular cell is a neuron with a small cell body that is located in the koniocellular layer of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) in primates, including humans.

The nucleus raphe pallidus receives afferent connections from the periaqueductal gray, the Paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus, central nucleus of the amygdala, lateral hypothalamic area, and parvocellular reticular nucleus.

The nucleus raphe magnus is one of the seven raphe nuclei. It is situated in the pons in the brainstem, just rostral to the nucleus raphe obscurus.
Parvocellular can refer to:
The lateral reticular nucleus, of the lateral funiculus, can be divided into three subnuclei, the parvocellular, magnocellular and the subtrigeminal. As is typical of the reticular formation, none of these are very distinct subnuclei, but rather blurred distinctions between cell types and location. The lateral reticular nucleus sends all of its projections to the cerebellum.
The ventral reticular nucleus is a continuation of the parvocellular nucleus in the brainstem.
The parvocellular reticular nucleus is part of the brain located dorsolateral to the caudal pontine reticular nucleus.
The gigantocellular reticular nucleus (Gi) is a subregion of the medullary reticular formation. As the name indicates, it consists mainly of so-called giant neuronal cells.
The myoclonic triangle is an important feedback circuit of the brainstem and deep cerebellar nuclei which is responsible for modulating spinal cord motor activity.
The rubro-olivary tract is a tract which connects the inferior olive and the parvocellular red nucleus.

A midget cell is one type of retinal ganglion cell (RGC). Midget cells originate in the ganglion cell layer of the retina, and project to the parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). The axons of midget cells travel through the optic nerve and optic tract, ultimately synapsing with parvocellular cells in the LGN. These cells are known as midget retinal ganglion cells due to the small sizes of their dendritic trees and cell bodies. About 80% of RGCs are midget cells. They receive inputs from relatively few rods and cones. In many cases, they are connected to midget bipolar cells, which are linked to one cone each.
The magnocellular red nucleus is located in the rostral midbrain and is involved in motor coordination. Together with the parvocellular red nucleus, the mRN makes up the red nucleus. Due to the role it plays in motor coordination, the magnocellular red nucleus may be implicated in the characteristic symptom of restless legs syndrome (RLS). The mRN receives most of its signals from the motor cortex and the cerebellum.
Parvocellular neurosecretory cells are small neurons that produce hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in various nuclei of the hypothalamus or in closely related areas of the basal brain, mainly in the medial zone of the hypothalamus. All or most of the axons of the parvocellular neurosecretory cells project to the median eminence, at the base of the brain, where their nerve terminals release the hypothalamic hormones. These hormones are then immediately absorbed into the blood vessels of the hypothalamo-pituitary portal system, which carry them to the anterior pituitary gland, where they regulate the secretion of hormones into the systemic circulation.
Reticular nucleus may refer to:
Ventral nucleus may refer to: