The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.
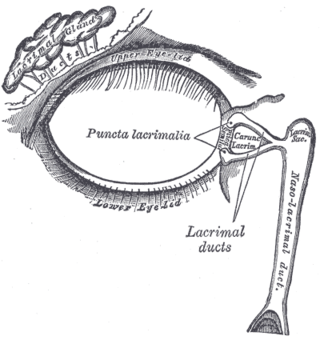
The lacrimal glands are paired exocrine glands, one for each eye, found in most terrestrial vertebrates and some marine mammals, that secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film. In humans, they are situated in the upper lateral region of each orbit, in the lacrimal fossa of the orbit formed by the frontal bone. Inflammation of the lacrimal glands is called dacryoadenitis. The lacrimal gland produces tears which are secreted by the lacrimal ducts, and flow over the ocular surface, and then into canals that connect to the lacrimal sac. From that sac, the tears drain through the lacrimal duct into the nose.

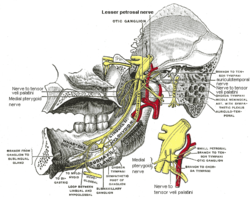
The otic ganglion is a small parasympathetic ganglion located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve. It is functionally associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve and innervates the parotid gland for salivation.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.
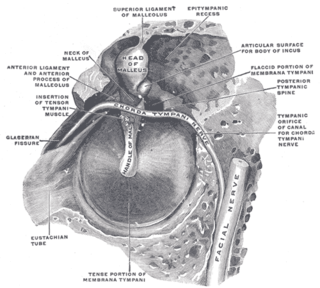
Chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve that carries gustatory (taste) sensory innervation from the front of the tongue and parasympathetic (secretomotor) innervation to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands.

The greater petrosal nerve is a nerve of the head mainly containing pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres which ultimately synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion.
Petrosal nerve may refer to:

The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word petrosus, meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body. In other mammals, it is a separate bone, the petrosal bone.

The submandibular ganglion is part of the human autonomic nervous system. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck..

The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The tympanic nerve is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve passing through the petrous part of the temporal bone to reach the middle ear. It provides sensory innervation for the middle ear, the Eustachian tube, the parotid gland, and mastoid cells. It also carries parasympathetic fibers destined for the parotid gland.

The superior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve is a sensory ganglion of the peripheral nervous system. It is located within the jugular foramen where the glossopharyngeal nerve exits the skull. It is smaller than and superior to the inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve.

Parasympathetic ganglia are the autonomic ganglia of the parasympathetic nervous system. Most are small terminal ganglia or intramural ganglia, so named because they lie near or within (respectively) the organs they innervate. The exceptions are the four paired parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck.

The nerve of the pterygoid canal is formed by the union of the (parasympathetic) greater petrosal nerve and (sympathetic) deep petrosal nerve within the cartilaginous substance filling the foramen lacerum. From the foramen lacerum, the nerve of the pterygoid canal passes through the pterygoid canal to reach the pterygopalatine fossa, ending at the pterygopalatine ganglion.
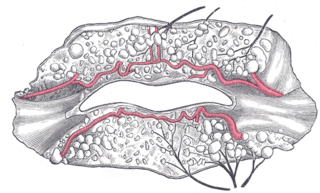
The labial glands are minor salivary glands situated between the mucous membrane and the orbicularis oris around the orifice of the mouth.

The salivatory nuclei are two general visceral efferent nuclei located in the caudal pons, dorsal and lateral to the facial nucleus. Their neurons give rise to preganglionic parasympathetic nerve fibers in the control of salivation. The superior salivatory nucleus supplies fibers to the intermediate nerve (part of the facial nerve. The inferior salivatory nucleus supplies fibers to the glossopharyngeal nerve. The nuclei may also be involved in parasympathetic control of head vasculature.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The hiatus for lesser petrosal nerve is a hiatus in the petrous part of the temporal bone which transmits the lesser petrosal nerve. It is located posterior to the groove for the superior petrosal sinus and posterolateral to the jugular foramen.