
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.

The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

The lesser occipital nerve is a cutaneous spinal nerve of the cervical plexus. It arises from second cervical (spinal) nerve (C2). It innervates the skin of the back of the upper neck and of the scalp posterior to the ear.

The great auricular nerve is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the head. It originates from the second and third cervical (spinal) nerves (C2-C3) of the cervical plexus. It provides sensory innervation to the skin over the parotid gland and the mastoid process, parts of the outer ear, and to the parotid gland and its fascia.

The digastric muscle is a bilaterally paired suprahyoid muscle located under the jaw. Its posterior belly is attached to the mastoid notch of temporal bone, and its anterior belly is attached to the digastric fossa of mandible; the two bellies are united by an intermediate tendon which is held in a loop that attaches to the hyoid bone. The anterior belly is innervated via the mandibular nerve, and the posterior belly is innervated via the facial nerve. It may act to depress the mandible or elevate the hyoid bone.
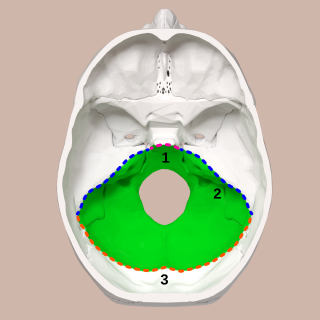
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid bones, temporal bones, and occipital bone. It lodges the cerebellum, and parts of the brainstem.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.

The stylohyoid muscle is one of the suprahyoid muscles. Its originates from the styloid process of the temporal bone; it inserts onto hyoid bone. It is innervated by a branch of the facial nerve. It acts draw the hyoid bone upwards and backwards.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.

The zygomatic nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve. It arises in the pterygopalatine fossa and enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure before dividing into its two terminal branches: the zygomaticotemporal nerve and zygomaticofacial nerve.

The posterior auricular artery is a small artery that arises from the external carotid artery. It ascends along the side of the head. It supplies several muscles of the neck and several structures of the head.

The mental nerve is a sensory nerve of the face. It is a branch of the posterior trunk of the inferior alveolar nerve, itself a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensation to the front of the chin and the lower lip, as well as the gums of the anterior mandibular (lower) teeth. It can be blocked with local anaesthesia for procedures on the chin, lower lip, and mucous membrane of the inner cheek. Problems with the nerve cause chin numbness.

The retromandibular vein is a major vein of the face. It is formed within the parotid gland by the confluence of the maxillary vein, and superficial temporal vein. It descends in the gland and splits into two branches upon emerging from the gland. Its anterior branch then joins the (anterior) facial vein forming the common facial vein, while its posterior branch joins the posterior auricular vein forming the external jugular vein.
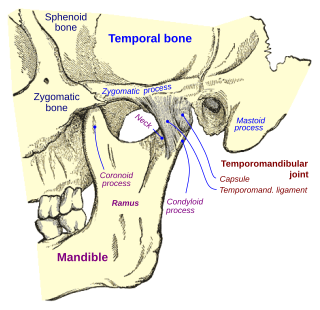
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, the mastoid part articulates with two other bones.

The posterior ethmoidal nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1)). It provides sensory innervation to the sphenoid sinus and ethmoid sinus, and part of the dura mater in the anterior cranial fossa.

The zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (malar branches) are nerves of the face. They run across the zygomatic bone to the lateral angle of the orbit. Here, they supply the orbicularis oculi muscle, and join with filaments from the lacrimal nerve and the zygomaticofacial branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).

The cervical branch of the facial nerve is a nerve in the neck. It is a branch of the facial nerve (VII). It supplies the platysma muscle, among other functions.

The posterior auricular muscle is a muscle behind the auricle of the outer ear. It arises from the mastoid part of the temporal bone, and inserts into the lower part of the cranial surface of the auricle of the outer ear. It draws the auricle backwards, usually a very slight effect.

The superior auricular muscle is a muscle above the auricle of the outer ear. It originates from the epicranial aponeurosis, and inserts into the upper part of the medial surface of the auricle. It draws the auricle upwards.

The anterior auricular muscle, the smallest of the three auricular muscles, is thin and fan-shaped, and its fibers are pale and indistinct. It arises from the lateral edge of the epicranial aponeurosis, and its fibers converge to be inserted into a projection on the front of the helix.



















