
In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only afferent fibers, the mandibular nerve contains both afferent and efferent fibers. These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.

The buccal nerve is a sensory nerve of the face arising from the mandibular nerve. It conveys sensory information from the skin of the cheek, and parts of the oral mucosa, periodontium, and gingiva.

The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (which is in turn a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal nerve.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.

The internal auditory meatus is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear.

The lingual nerve carries sensory innervation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It contains fibres from both the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) and from the facial nerve (CN VII). The fibres from the trigeminal nerve are for touch, pain and temperature (general sensation), and the ones from the facial nerve are for taste (special sensation).

The mylohyoid nerve is a mixed nerve of the head. It is a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve. It provides motor innervation the mylohyoid muscle, and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. It provides sensory innervation to part of the submental area, and sometimes also the mandibular (lower) molar teeth, requiring local anaesthesia for some oral procedures.
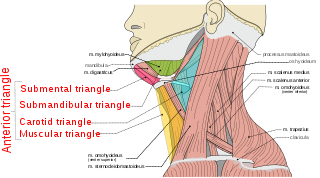
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck.

The marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve arises from the facial nerve in the parotid gland at the parotid plexus. It passes anterior-ward deep to the platysma and depressor anguli oris muscles. It provides motor innervation to muscles of the lower lip and chin: the depressor labii inferioris muscle, depressor anguli oris muscle, and mentalis muscle. It communicates with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar nerve.

The buccal branches of the facial nerve, are of larger size than the rest of the branches, pass horizontally forward to be distributed below the orbit and around the mouth.

The posterior auricular nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the facial nerve. It communicates with branches from the vagus nerve, the great auricular nerve, and the lesser occipital nerve. Its auricular branch supplies the posterior auricular muscle, the intrinsic muscles of the auricle, and gives sensation to the auricle. Its occipital branch supplies the occipitalis muscle.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The temporal branches of the facial nerve crosses the zygomatic arch to the temporal region, supplying the auriculares anterior and superior, and joining with the zygomaticotemporal branch of the maxillary nerve, and with the auriculotemporal branch of the mandibular nerve.

The zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (malar branches) are nerves of the face. They run across the zygomatic bone to the lateral angle of the orbit. Here, they supply the orbicularis oculi muscle, and join with filaments from the lacrimal nerve and the zygomaticofacial branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).

The cervical branch of the facial nerve is a nerve in the neck. It is a branch of the facial nerve (VII). It supplies the platysma muscle, among other functions.
The nerve to the stapedius is a branch of the facial nerve which innervates the stapedius muscle. It arises from the CN VII within the facial canal, opposite the pyramidal eminence. It passes through a small canal in this eminence to reach the stapedius muscle.

The stylohyoid branch of facial nerve provides motor innervation to the stylohyoid muscle. It frequently arises from the facial nerve in common with the digastric branch of facial nerve.

The lesser palatine nerves (posterior palatine nerve) are branches of the maxillary nerve (CN V2). They descends through the greater palatine canal alongside the greater palatine nerve, and emerge (separately) through the lesser palatine foramen to pass posteriorward. They supply the soft palate, tonsil, and uvula.












