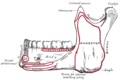
| Depressor labii | |
|---|---|
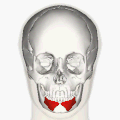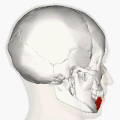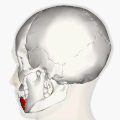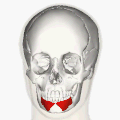
 Muscles of the head, face, and neck. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Oblique line of the mandible, between the symphysis and the mental foramen |
| Insertion | Integument of the lower lip, orbicularis oris fibers, its fellow of the opposite side |
| Nerve | Marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve |
| Actions | Depression of the lower lip |
| Antagonist | Orbicularis oris muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus depressor labii inferioris |
| TA98 | A04.1.03.033 |
| TA2 | 2083 |
| FMA | 46816 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The depressor labii inferioris (or quadratus labii inferioris) is a facial muscle. It helps to lower the bottom lip.