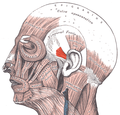
| Anterior auricular muscle | |
|---|---|
 Face and neck muscles. Anterior auricular muscle shown in red. | |
 The muscles of the auricula. Anterior auricular is at right (indicated by the red arrow). | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Temporal fascia |
| Insertion | Major helix (ear) |
| Artery | Posterior auricular artery |
| Nerve | Temporal branch of facial nerve |
| Actions | Pulls ear forward |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus auricularis anterior |
| TA98 | A04.1.03.020 |
| TA2 | 2089 |
| FMA | 46856 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The anterior auricular muscle, the smallest of the three auricular muscles, is thin and fan-shaped, and its fibers are pale and indistinct. It arises from the lateral edge of the epicranial aponeurosis, and its fibers converge to be inserted into a projection on the front of the helix.