Articles related to anatomy include:

The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra.

The external carotid artery is the major artery of the head and upper neck. It arises from the common carotid artery. It terminates by splitting into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland.

The paired submandibular glands are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In adult humans, they each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as parotid gland secretion rises to 50%. The average length of the normal adult human submandibular salivary gland is approximately 27 mm, while the average width is approximately 14.3 mm.

The digastric muscle is a bilaterally paired suprahyoid muscle located under the jaw. Its posterior belly is attached to the mastoid notch of temporal bone, and its anterior belly is attached to the digastric fossa of mandible; the two bellies are united by an intermediate tendon which is held in a loop that attaches to the hyoid bone. The anterior belly is innervated via the mandibular nerve, and the posterior belly is innervated via the facial nerve. It may act to depress the mandible or elevate the hyoid bone.

The sublingual gland is a seromucous polystomatic exocrine gland. Located underneath the oral diaphragm, the sublingual gland is the smallest and most diffuse of the three major salivary glands of the oral cavity, with the other two being the submandibular and parotid. The sublingual gland provides approximately 3-5% of the total salivary volume.

The geniohyoid muscle is a narrow paired muscle situated superior to the medial border of the mylohyoid muscle. It is named for its passage from the chin to the hyoid bone.

The mylohyoid muscle or diaphragma oris is a paired muscle of the neck. It runs from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the mouth. It is named after its two attachments near the molar teeth. It forms the floor of the submental triangle. It elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue, important during swallowing and speaking.

The facial artery, formerly called the external maxillary artery, is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies blood to superficial structures of the medial regions of the face.

The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle of the neck. Above, it attaches onto the greater cornu of the hyoid bone; below, it attaches onto the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage. It is innervated by fibres derived from the cervical spinal nerve 1 that run with the hypoglossal nerve to reach this muscle. The thyrohyoid muscle depresses the hyoid bone and elevates the larynx during swallowing. By controlling the position and shape of the larynx, it aids in making sound.

The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. It is a fan-shaped muscle that comprises the bulk of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible; it inserts onto the hyoid bone, and the bottom of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding the tongue.

The styloglossus muscle is a bilaterally paired muscle of the tongue. It originates at the styloid process of the temporal bone. It inserts onto the side of the tongue. It acts to elevate and retract the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve.
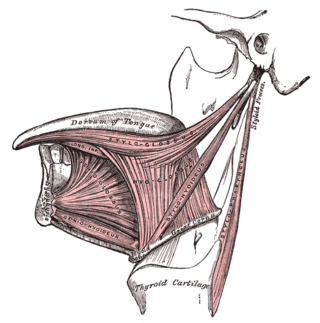
The chondroglossus muscle is a muscle of the tongue. It arises from the medial side of the lesser horn of the hyoid bone, before blending with intrinsic muscles of the tongue. It is supplied by the hypoglossal nerve.

The lingual nerve carries sensory innervation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It contains fibres from both the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) and from the facial nerve (CN VII). The fibres from the trigeminal nerve are for touch, pain and temperature (general sensation), and the ones from the facial nerve are for taste (special sensation).

The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue.

The submandibular duct is one of the salivary excretory ducts. It is about 5 cm long, and its wall is much thinner than that of the parotid duct. It drains saliva from each bilateral submandibular gland and sublingual gland to the sublingual caruncle in the floor of the mouth.

The deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The sublingual space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space located below the mouth and above the mylohyoid muscle, and is part of the suprahyoid group of fascial spaces.

The submandibular space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space, and is paired on either side, located on the superficial surface of the mylohyoid muscle between the anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric muscle. The space corresponds to the anatomic region termed the submandibular triangle, part of the anterior triangle of the neck.


























