The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The great auricular nerve is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the head. It originates from the second and third cervical (spinal) nerves (C2-C3) of the cervical plexus. It provides sensory innervation to the skin over the parotid gland and the mastoid process, parts of the outer ear, and to the parotid gland and its fascia.

The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.

The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face, brain and neck.
Superficial muscular aponeurotic system (SMAS) is a thin yet tough unitary tissue plane of the face formed by facial fasciae, subcutis connective tissue, and facial muscles. Its composition varies, containing muscle fibres in some areas, and fibrous or fibroaponeurotic tissue in others. It connects to the dermis via vertical septa. It does not attach to bone. In most areas, a distinct plane can be defined deep to the SMAS.

The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.

In anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication. Found only in mammals, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter. The most obvious muscle of mastication is the masseter muscle, since it is the most superficial and one of the strongest.

The platysma muscle is a superficial muscle of the human neck that overlaps the sternocleidomastoid. It covers the anterior surface of the neck superficially. When it contracts, it produces a slight wrinkling of the neck, and a "bowstring" effect on either side of the neck.

In human anatomy, the superficial temporal artery is a major artery of the head. It arises from the external carotid artery when it splits into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.

Anatomists use the term triangles of the neck to describe the divisions created by the major muscles in the region.
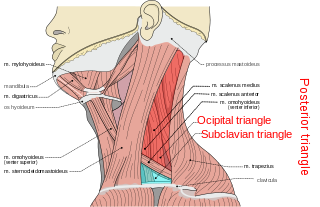
The posterior triangle is a region of the neck.

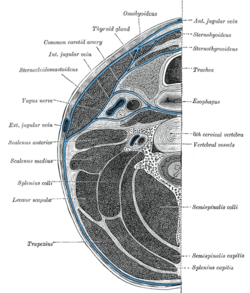
The deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.

The temporal fascia is a fascia of the head that covers the temporalis muscle and structures situated superior to the zygomatic arch.

The masseteric fascia and parotideomasseteric fascia are fascias of the head varyingly described depending upon the source consulted. They may or may not be described as one and the same structure.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.
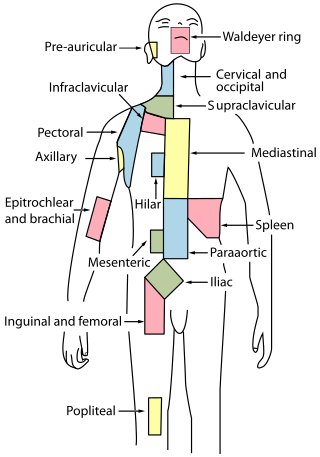
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflammation.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
The parotid fascia is a tough fascia enclosing the parotid gland. It has a superficial layer and a deep layer.