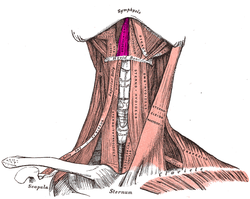
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments: vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles.

The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra.

The suprahyoid muscles are four muscles located above the hyoid bone in the neck. They are the digastric, stylohyoid, geniohyoid, and mylohyoid muscles. They are all pharyngeal muscles, with the exception of the geniohyoid muscle. The digastric is uniquely named for its two bellies. Its posterior belly rises from the mastoid process of the cranium and slopes downward and forward. The anterior belly arises from the digastric fossa on the inner surface of the mandibular body, which slopes downward and backward. The two bellies connect at the intermediate tendon. The intermediate tendon passes through a connective tissue loop attached to the hyoid bone. The mylohyoid muscles are thin, flat muscles that form a sling inferior to the tongue supporting the floor of the mouth. The geniohyoids are short, narrow muscles that contact each other in the midline. The stylohyoids are long, thin muscles that are nearly parallel with the posterior belly of the digastric muscle.

The infrahyoid muscles, or strap muscles, are a group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck. The four infrahyoid muscles are the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid and omohyoid muscles.

The omohyoid muscle is a muscle in the neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. Its inferior belly is attached to the scapula; its superior belly is attached to the hyoid bone. Its intermediate tendon is anchored to the clavicle and first rib by a fascial sling. The omohyoid is innervated by the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus. It acts to depress the hyoid bone.

The cervical plexus is a nerve plexus of the anterior rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves C1-C4. The cervical plexus provides motor innervation to some muscles of the neck, and the diaphragm; it provides sensory innervation to parts of the head, neck, and chest.

The digastric muscle is a bilaterally paired suprahyoid muscle located under the jaw. Its posterior belly is attached to the mastoid notch of temporal bone, and its anterior belly is attached to the digastric fossa of mandible; the two bellies are united by an intermediate tendon which is held in a loop that attaches to the hyoid bone. The anterior belly is innervated via the mandibular nerve, and the posterior belly is innervated via the facial nerve. It may act to depress the mandible or elevate the hyoid bone.

The mylohyoid muscle or diaphragma oris is a paired muscle of the neck. It runs from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the mouth. It is named after its two attachments near the molar teeth. It forms the floor of the submental triangle. It elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue, important during swallowing and speaking.

The stylohyoid muscle is one of the suprahyoid muscles. Its originates from the styloid process of the temporal bone; it inserts onto hyoid bone. It is innervated by a branch of the facial nerve. It acts draw the hyoid bone upwards and backwards.

The ansa cervicalis is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root and an inferior root - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated within the carotid sheath.

The sternohyoid muscle is a bilaterally paired, long, thin, narrow strap muscle of the anterior neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It is innervated by the ansa cervicalis. It acts to depress the hyoid bone.

The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle of the neck. Above, it attaches onto the greater cornu of the hyoid bone; below, it attaches onto the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage. It is innervated by fibres derived from the cervical spinal nerve 1 that run with the hypoglossal nerve to reach this muscle. The thyrohyoid muscle depresses the hyoid bone and elevates the larynx during swallowing. By controlling the position and shape of the larynx, it aids in making sound.

The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. It is a fan-shaped muscle that comprises the bulk of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible; it inserts onto the hyoid bone, and the bottom of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding the tongue.
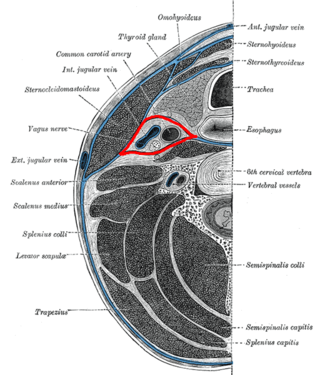
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve, and ansa cervicalis. The carotid sheath helps protects the structures contained therein.
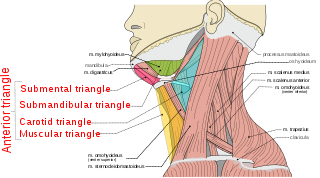
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck.

The subclavian nerve, also known as the nerve to the subclavius, is a small branch of the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It contains axons from C5 and C6. It innervates the subclavius muscle.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The inferior carotid triangle, is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid; above, by the superior belly of the omohyoid.

The cervical spinal nerve 1 (C1) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment. C1 carries predominantly motor fibres, but also a small meningeal branch that supplies sensation to parts of the dura around the foramen magnum.

The thyrohyoid branch (also: thyrohyoid branch of ansa cervicalis, or nerve to thyrohyoid (muscle)) is a motor branch derived from the cervical plexus formed by fibres of (the anterior ramus of) the cervical spinal nerve 1 (C1) (and - according to some sources - cervical spinal nerve 2 (C2) as well) that join and travel with the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII) to reach the suprahyoid region, branching away from CN XII distal to the superior root of ansa cervicalis (which is a branching other fibres of C1-C2 that had traveled with the CN XII), near the posterior border of the hyoglossus muscle. The thyrohyoid branch of ansa cervicalis innervates the thyrohyoid muscle.