| Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle | |
|---|---|
 | |
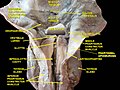
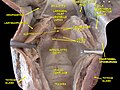
 Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves (middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle labeled as Mid. constr. at center) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Hyoid bone |
| Insertion | Pharyngeal raphe |
| Artery | Ascending pharyngeal artery |
| Nerve | Pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve |
| Actions | Swallowing |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus constrictor pharyngis medius |
| TA98 | A05.3.01.108 |
| TA2 | 2184 |
| FMA | 46622 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The middle pharyngeal constrictor is a fan-shaped muscle located in the neck. It is one of three pharyngeal constrictor muscles. It is smaller than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.
Contents
- Structure
- Origin
- Insertion
- Innervation
- Actions/movements
- Function
- Additional images
- References
- Further reading
- External links
The middle pharyngeal constrictor originates from the greater cornu and lesser cornu of the hyoid bone, and the stylohyoid ligament. It inserts onto the pharyngeal raphe. It is innervated by a branch of the vagus nerve through the pharyngeal plexus. It acts to propel a bolus downwards along the pharynx towards the esophagus, facilitating swallowing.