This article may be too technical for most readers to understand.(February 2024) |
| Sternohyoid muscle | |
|---|---|
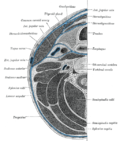
 Muscles of neck. Sternohyoideus labeled at middle, just to the right of thyroid cartilage. | |
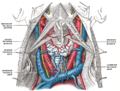
 Muscles of the neck. Lateral view. Sternohyoid muscle labeled | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Manubrium of sternum |
| Insertion | Hyoid bone |
| Artery | Superior thyroid artery |
| Nerve | C1-C3 by a branch of ansa cervicalis |
| Actions | Depresses hyoid |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus sternohyoideus |
| TA98 | A04.2.04.002 |
| TA2 | 2168 |
| FMA | 13341 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The sternohyoid muscle is a bilaterally paired, [1] long, [1] thin, [1] [2] narrow strap muscle [2] of the anterior neck. [1] It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It is innervated by the ansa cervicalis. It acts to depress the hyoid bone.
Contents
- Structure
- Origin
- Nerve supply
- Relations
- Variations
- Actions/movements
- Function
- Additional images
- References
- External links
The sternohyoid muscle is a flat muscle located on both sides of the neck, part of the infrahyoid muscle group. It originates from the medial edge of the clavicle, sternoclavicular ligament, and posterior side of the manubrium, and ascends to attach to the body of the hyoid bone. The sternohyoid muscle, along with other infrahyoid muscles, functions to depress the hyoid bone, which is important for activities such as speaking, chewing, and swallowing. Additionally, this muscle group contributes to the protection of the trachea, esophagus, blood vessels, and thyroid gland. The sternohyoid muscle also plays a minor role in head movements. [3]