
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The sacrum, in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) between ages 18 and 30.

The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra.

The suprahyoid muscles are four muscles located above the hyoid bone in the neck. They are the digastric, stylohyoid, geniohyoid, and mylohyoid muscles. They are all pharyngeal muscles, with the exception of the geniohyoid muscle. The digastric is uniquely named for its two bellies. Its posterior belly rises from the mastoid process of the cranium and slopes downward and forward. The anterior belly arises from the digastric fossa on the inner surface of the mandibular body, which slopes downward and backward. The two bellies connect at the intermediate tendon. The intermediate tendon passes through a connective tissue loop attached to the hyoid bone. The mylohyoid muscles are thin, flat muscles that form a sling inferior to the tongue supporting the floor of the mouth. The geniohyoids are short, narrow muscles that contact each other in the midline. The stylohyoids are long, thin muscles that are nearly parallel with the posterior belly of the digastric muscle.

The digastric muscle is a bilaterally paired suprahyoid muscle located under the jaw. Its posterior belly is attached to the mastoid notch of temporal bone, and its anterior belly is attached to the digastric fossa of mandible; the two bellies are united by an intermediate tendon which is held in a loop that attaches to the hyoid bone. The anterior belly is innervated via the mandibular nerve, and the posterior belly is innervated via the facial nerve. It may act to depress the mandible or elevate the hyoid bone.

In anatomy, a process is a projection or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body. For instance, in a vertebra, a process may serve for muscle attachment and leverage, or to fit, with another vertebra. The word is also used at the microanatomic level, where cells can have processes such as cilia or pedicels. Depending on the tissue, processes may also be called by other terms, such as apophysis, tubercle, or protuberance.

The geniohyoid muscle is a narrow paired muscle situated superior to the medial border of the mylohyoid muscle. It is named for its passage from the chin to the hyoid bone.

The mylohyoid muscle or diaphragma oris is a paired muscle of the neck. It runs from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the mouth. It is named after its two attachments near the molar teeth. It forms the floor of the submental triangle. It elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue, important during swallowing and speaking.

The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. It is a fan-shaped muscle that comprises the bulk of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible; it inserts onto the hyoid bone, and the bottom of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding the tongue.

The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a quadrilateral muscle of the pharynx. It is the uppermost and thinnest of the three pharyngeal constrictors.
Genioglossus advancement (GA) is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the base of the tongue is pulled forward. It is usually to increase airway size due to deformity or a sleep breathing disorder. This procedure is frequently performed with either uvulopalatopharyngoplasty or maxillomandibular advancement surgeries.

The ischium forms the lower and back region of the hip bone.
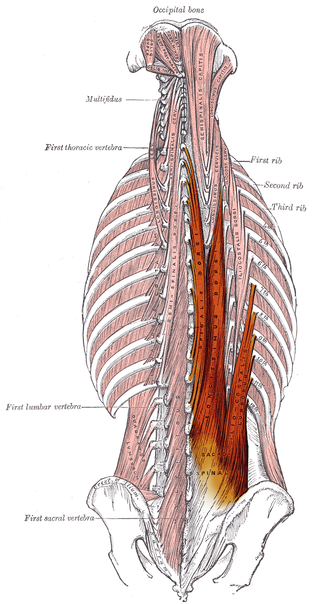
The erector spinae or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes to maintain stable posture standing or sitting.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone, positioned in the skull behind each eye. There is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.
The lumbar fascia is the lumbar portion of the thoracolumbar fascia. It consists of three fascial layers - posterior, middle, and anterior - that enclose two muscular compartments. The anterior and middle layers occur only in the lumbar region, whereas the posterior layer extends superiorly to the inferior part of the neck, and the inferiorly to the dorsal surface of the sacrum. The quadratus lumborum is contained in the anterior muscular compartment, and the erector spinae in the posterior compartment. Psoas major lies anterior to the anterior layer. Various superficial muscles of the posterior thorax and abdomen arise from the posterior layer - namely the latissimus dorsi, and serratus posterior inferior.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The sublingual space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space located below the mouth and above the mylohyoid muscle, and is part of the suprahyoid group of fascial spaces.
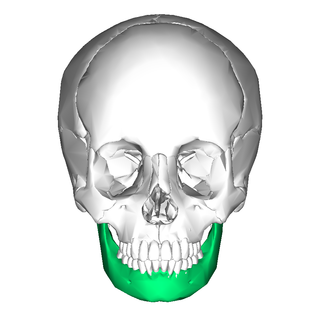
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible, lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lower – and typically more mobile – component of the mouth.

Each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species.



















