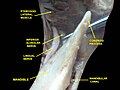
| Mandibular canal | |
|---|---|
 The permanent teeth, viewed from the right. The external layer of bone has been partly removed and the maxillary sinus has been opened. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | canalis mandibulae |
| MeSH | D000088263 |
| TA98 | A02.1.15.030 |
| TA2 | 867 |
| FMA | 59473 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |

In human anatomy, the mandibular canal is a canal within the mandible that contains the inferior alveolar nerve, inferior alveolar artery, and inferior alveolar vein. It runs obliquely downward and forward in the ramus, and then horizontally forward in the body, where it is placed under the alveoli and communicates with them by small openings.
Contents
On arriving at the incisor teeth, it turns back to communicate with the mental foramen, giving off a small canal known as the mandibular incisive canal, which run to the cavities containing the incisor teeth. [1] It carries branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and artery.
The mandibular canal is continuous with two foramina: the mental foramen which opens in the mental region of the mandible and carried the distal fibres of the inferior alveolar nerve as the mental nerve; and the mandibular foramen on medial aspect of ramus, into which the mandibular nerve enters to become the inferior alveolar nerve. The mandibular canal often runs close to the apices of the third molar tooth, and the inferior alveolar nerve can become damaged during removal of this tooth, causing sensory disturbance in the distribution of the nerve. This is sometimes the case for the second or first molar teeth, and care must be taken during removal or root canal treatment in such cases to prevent nerve injury or extrusion of root canal filling materials. [2]