The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates, and it connects the knee with the ankle bones. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane or centre-line. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of the leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body next to the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

In the human skull, the zygomatic bone is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. It is situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek, part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit, and parts of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal fossa. It presents a malar and a temporal surface; four processes, and four borders.

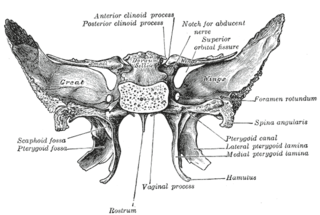
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the temporal bone and the basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended.
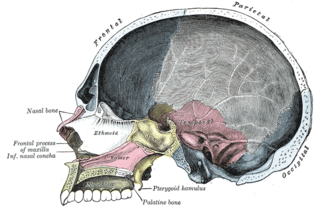
The inferior nasal concha is one of the three paired nasal conchae in the nose. It extends horizontally along the lateral wall of the nasal cavity and consists of a lamina of spongy bone, curled upon itself like a scroll,. The inferior nasal conchae are considered a pair of facial bones. As the air passes through the turbinates, the air is churned against these mucosa-lined bones in order to receive warmth, moisture and cleansing. Superior to inferior nasal concha are the middle nasal concha and superior nasal concha which arise from the cranial portion of the skull. Hence, these two are considered as a part of the cranial bones.

The medial pterygoid, is a thick, quadrilateral muscle of mastication.

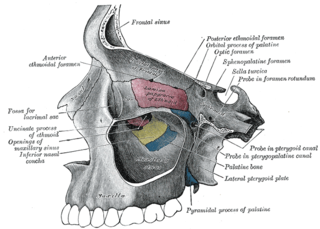
In human anatomy, the pterygopalatine fossa is a fossa in the skull. A human skull contains two pterygopalatine fossae—one on the left side, and another on the right side. Each fossa is a cone-shaped paired depression deep to the infratemporal fossa and posterior to the maxilla on each side of the skull, located between the pterygoid process and the maxillary tuberosity close to the apex of the orbit. It is the indented area medial to the pterygomaxillary fissure leading into the sphenopalatine foramen. It communicates with the nasal and oral cavities, infratemporal fossa, orbit, pharynx, and middle cranial fossa through eight foramina.

The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid, one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone; there is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.

The ethmoidal labyrinth or lateral mass of the ethmoid bone consists of a number of thin-walled cellular cavities, the ethmoid air cells, arranged in three groups, anterior, middle, and posterior, and interposed between two vertical plates of bone; the lateral plate forms part of the orbit, the medial plate forms part of the nasal cavity. In the disarticulated bone many of these cells are opened into, but when the bones are articulated, they are closed in at every part, except where they open into the nasal cavity.
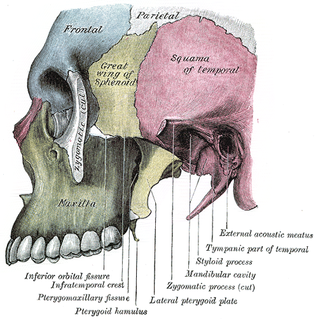
The pterygomaxillary fissure is a fissure of the human skull. It is vertical, and descends at right angles from the medial end of the inferior orbital fissure. It is a triangular interval, formed by the divergence of the maxilla from the pterygoid process of the sphenoid.

The middle cranial fossa, deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity, situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions, and it contains superficial muscles that are visible during dissection after removing skin and fascia: namely, the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid, and the medial pterygoid.

The sphenoidal process of the palatine bone is a thin, compressed plate, much smaller than the orbital, and directed upward and medialward.

The perpendicular plate of palatine bone is the vertical part of the palatine bone, and is thin, of an oblong form, and presents two surfaces and four borders.

The horizontal plate of palatine bone is a quadrilateral part of the palatine bone, and has two surfaces and four borders.

Each Zygomatic process is the part of a bone which articulates with the zygomatic bone. The three processes are:

The frontal process of maxilla is a strong plate, which projects upward, medialward, and backward from the maxilla, forming part of the lateral boundary of the nose.
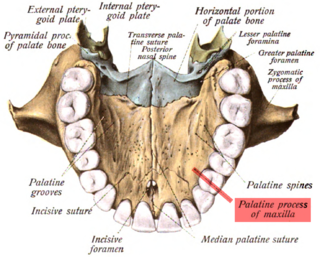
In human anatomy of the mouth, the palatine process of maxilla, is a thick, horizontal process of the maxilla. It forms the anterior three quarters of the hard palate, the horizontal plate of the palatine bone making up the rest.
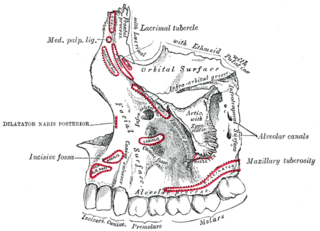
At the lower part of the infratemporal surface of the maxilla is a rounded eminence, the maxillary tuberosity, especially prominent after the growth of the wisdom tooth; it is rough on its lateral side for articulation with the pyramidal process of the palatine bone and in some cases articulates with the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid.