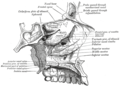
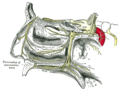
| Incisive canals | |
|---|---|
 The bony palate and alveolar arch (incisive canals labeled at upper left) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | canales incisivi |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.061 |
| TA2 | 788 |
| FMA | 59107 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The incisive canals (also: "nasopalatine canals") are two bony canals of the anterior hard palate connecting the nasal cavity and the oral cavity. An incisive canal courses through each maxilla. Below, the two incisive canals typically converge medially. [1]
Contents
Each incisive canal transmits a nasopalatine nerve, and an anastomosis of the greater palatine artery and a posterior septal branch of the sphenopalatine artery. [1]