Articles related to anatomy include:

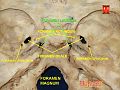
The foramen ovale is a hole in the posterior part of the sphenoid bone, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum. It is one of the larger of the several holes in the skull. It transmits the mandibular nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve.

The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended.

The occipital bone is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput. It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of the skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain.
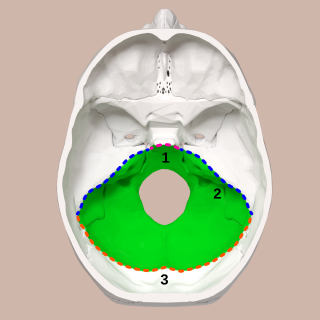
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid bones, temporal bones, and occipital bone. It lodges the cerebellum, and parts of the brainstem.

The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.

The foramen spinosum is a small open hole in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone that gives passage to the middle meningeal artery and vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve.

A jugular foramen is one of the two large foramina (openings) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed by the temporal bone and the occipital bone. It allows many structures to pass, including the inferior petrosal sinus, three cranial nerves, the sigmoid sinus, and meningeal arteries.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone, positioned in the skull behind each eye. There is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.
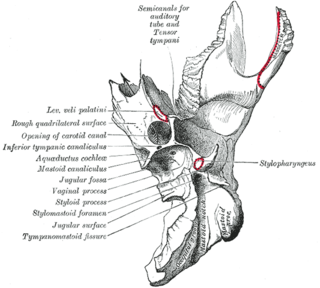
The carotid canal is a passage in the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull through which the internal carotid artery and its internal carotid (nervous) plexus pass from the neck into the cranial cavity.

The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior, the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word petrosus, meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body. In other mammals, it is a separate bone, the petrosal bone.

The basilar part of the occipital bone extends forward and upward from the foramen magnum, and presents in front an area more or less quadrilateral in outline.

The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

The nerve of the pterygoid canal is formed by the union of the (parasympathetic) greater petrosal nerve and (sympathetic) deep petrosal nerve within the cartilaginous substance filling the foramen lacerum. From the foramen lacerum, the nerve of the pterygoid canal passes through the pterygoid canal to reach the pterygopalatine fossa, ending at the pterygopalatine ganglion.

The body of the sphenoid bone, more or less cubical in shape, is hollowed out in its interior to form two large cavities, the sphenoidal sinuses, which are separated from each other by a septum.

The clivus or Blumenbach clivus is a part of the occipital bone at the base of the skull. It is a shallow depression behind the dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. It slopes gradually to the anterior part of the basilar occipital bone at its junction with the sphenoid bone. It extends to the foramen magnum. It is related to the pons and the abducens nerve.

The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy: