
In anatomy, the palatine bones are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxillae, they comprise the hard palate.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.

The pterygopalatine ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck,.

The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, located in the maxilla. It drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the semilunar hiatus. It is located to the side of the nasal cavity, and below the orbit.
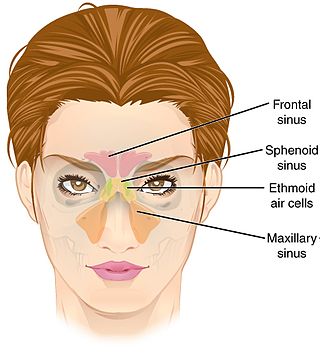
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of small air-filled cavities. The cells are located within the lateral mass (labyrinth) of each ethmoid bone and are variable in both size and number. The cells are grouped into anterior, middle, and posterior groups; the groups differ in their drainage modalities, though all ultimately drain into either the superior or the middle nasal meatus of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity.

The greater petrosal nerve is a nerve of the head mainly containing pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres which ultimately synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion. It branches from the facial nerve and is derived from the parasympathetic part of the nervus intermedius component of CN VII, with its cell bodies located in the superior salivary nucleus. In the connective tissue substance of the foramen lacerum, the greater petrosal nerve unites with the (sympathetic) deep petrosal nerve to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal which proceeds to the pterygopalatine ganglion.

In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve (V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (CN V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxilla, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face, and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.

In human anatomy, the pterygopalatine fossa is a fossa in the skull. A human skull contains two pterygopalatine fossae—one on the left side, and another on the right side. Each fossa is a cone-shaped paired depression deep to the infratemporal fossa and posterior to the maxilla on each side of the skull, located between the pterygoid process and the maxillary tuberosity close to the apex of the orbit. It is the indented area medial to the pterygomaxillary fissure leading into the sphenopalatine foramen. It communicates with the nasal and oral cavities, infratemporal fossa, orbit, pharynx, and middle cranial fossa through eight foramina.
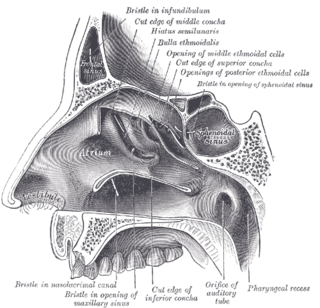
The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus occurring within the body of the sphenoid bone. It represents one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The pair of sphenoid sinuses are separated in the middle by a septum of sphenoid sinuses. Each sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity via the opening of sphenoidal sinus. The two sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape, and are usually asymmetrical.

The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid, one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.
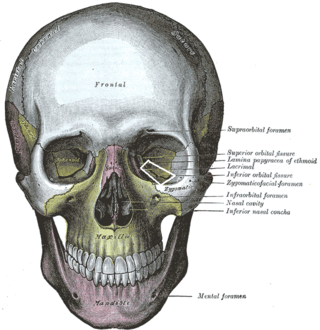
The inferior orbital fissure is a gap between the greater wing of sphenoid bone, and the maxilla. It connects the orbit (anteriorly) with the infratemporal fossa and pterygopalatine fossa (posteriorly).
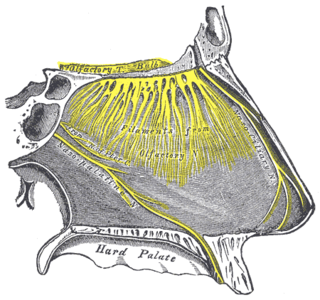
The nasopalatine nerve (also long sphenopalatine nerve) is a nerve of the head. It is a sensory branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) that passes through the pterygopalatine ganglion (without synapsing) and then through the sphenopalatine foramen to enter the nasal cavity, and finally out of the nasal cavity through the incisive canal and then the incisive fossa to enter the hard palate. It provides sensory innervation to the posteroinferior part of the nasal septum, and gingiva just posterior to the upper incisor teeth.
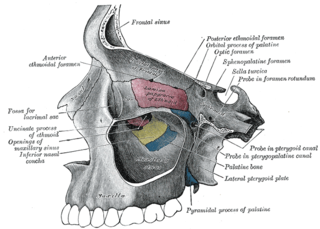
The sphenopalatine foramen is a fissure of the skull that connects the nasal cavity and the pterygopalatine fossa. It gives passage to the sphenopalatine artery, nasopalatine nerve, and the superior nasal nerve.

The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

The pharyngeal nerve is a small branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2), arising at (the posterior part of the) pterygopalatine ganglion. It passes posterior-ward through the palatovaginal canal with the pharyngeal branch of the maxillary artery.

The sphenoidal process of palatine bone is a thin, superomedially directed plate of bone. It is smaller and more inferior compared to the orbital process of palatine bone.

The perpendicular plate of palatine bone is the vertical part of the palatine bone, and is thin, of an oblong form, and presents two surfaces and four borders.

The greater palatine canal is a passage in the skull that transmits the descending palatine artery, vein, and greater and lesser palatine nerves between the pterygopalatine fossa and the oral cavity.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

















