
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The maxilla in vertebrates is the upper fixed bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible, which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended.

In anatomy, the palatine bones are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxillae, they comprise the hard palate.

The vomer is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms the inferior part of the nasal septum in humans, with the superior part formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The name is derived from the Latin word for a ploughshare and the shape of the bone.
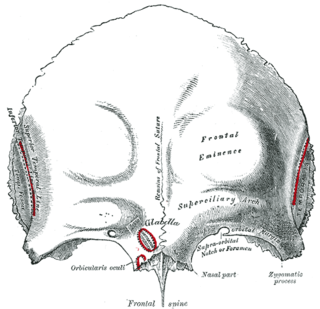
The orbital or horizontal part of the frontal bone consists of two thin triangular plates, the orbital plates, which form the vaults of the orbits, and are separated from one another by a median gap, the ethmoidal notch.
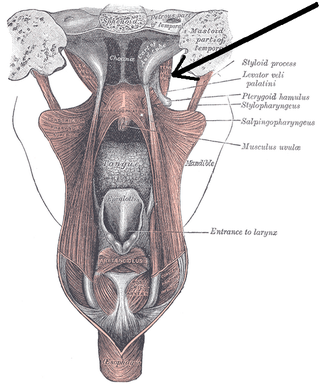
The tensor veli palatini muscle is a thin, triangular muscle of the head that tenses the soft palate and opens the Eustachian tube to equalise pressure in the middle ear.

The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid, one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone, positioned in the skull behind each eye. There is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.
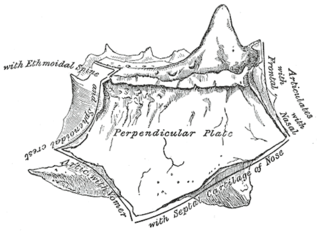
The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone is a thin, flattened lamina, polygonal in form, which descends from the under surface of the cribriform plate, and assists in forming the septum of the nose; it is generally deflected a little to one or other side. The anterior border articulates with the spine of the frontal bone and the crest of the nasal bones.

The sphenoidal process of palatine bone is a thin, superomedially directed plate of bone. It is smaller and more inferior compared to the orbital process of palatine bone.

The perpendicular plate of palatine bone is the vertical part of the palatine bone, and is thin, of an oblong form, and presents two surfaces and four borders.

The horizontal plate of palatine bone is a quadrilateral part of the palatine bone, and has two surfaces and four borders.

The frontal process of the maxilla is a strong plate, which projects upward, medialward, and backward from the maxilla, forming part of the lateral boundary of the nose.
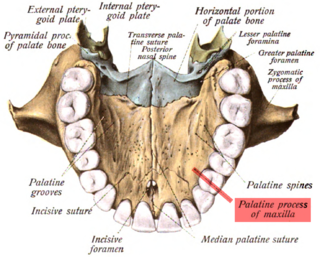
In human anatomy of the mouth, the palatine process of maxilla, is a thick, horizontal process of the maxilla. It forms the anterior three quarters of the hard palate, the horizontal plate of the palatine bone making up the rest.

The body of the sphenoid bone, more or less cubical in shape, is hollowed out in its interior to form two large cavities, the sphenoidal sinuses, which are separated from each other by a septum.

The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
This glossary explains technical terms commonly employed in the description of dinosaur body fossils. Besides dinosaur-specific terms, it covers terms with wider usage, when these are of central importance in the study of dinosaurs or when their discussion in the context of dinosaurs is beneficial. The glossary does not cover ichnological and bone histological terms, nor does it cover measurements.


















