Palatino is a family of typefaces.
Palatino may also refer to:
- Palatino Express, a passenger train, formerly called the Rome Express, operating from 1890
- Palatine Hill, also called Palatino, the centermost of the Seven Hills of Rome
Palatino is a family of typefaces.
Palatino may also refer to:

The Lupercal was a cave at the southwest foot of the Palatine Hill in Rome, located somewhere between the temple of Magna Mater and the Sant'Anastasia al Palatino. In the legend of the founding of Rome, Romulus and Remus were found there by the she-wolf who suckled them until they were rescued by the shepherd Faustulus. Luperci, the priests of Faunus, celebrated certain ceremonies of the Lupercalia at the cave, from the earliest days of the City until at least 494 AD.

The seven hills of Rome east of the river Tiber form the geographical heart of Rome, within the walls of the city.

The Aventine Hill is one of the Seven Hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the modern twelfth rione, or ward, of Rome.

The Palatine Hill, which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city and has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire." The site is now mainly a large open-air museum while the Palatine Museum houses many finds from the excavations here and from other ancient Italian sites.
Vatican Hill is a hill located across the Tiber river from the traditional seven hills of Rome, that also gave the name to Vatican City. It is the location of St. Peter's Basilica.

Pope John VII was the bishop of Rome from 1 March 705 to his death. He was an ethnic Greek, one of the Byzantine popes, but had better relations with the Lombards, who ruled much of Italy, than with Emperor Justinian II, who ruled the rest.

The Viminal Hill is the smallest of the famous Seven Hills of Rome. A finger-shape cusp pointing toward central Rome between the Quirinal Hill to the northwest and the Esquiline Hill to the southeast, it is home to the Teatro dell'Opera and the Termini Railway Station.

Campitelli is the 10th rione of Rome, identified by the initials R. X, and is located in the Municipio I.

San Sebastiano al Palatino is a church on the northeastern corner of the Palatine Hill in Rome. It is dedicated to Saint Sebastian, a late-third-century Christian martyr under the reign of Diocletian. According to legend, the church was built on the site of the saint's "first" martyrdom with arrows, which was unsuccessful.

The Oppian Hill is the southern spur of the Esquiline Hill, one of the Seven hills of Rome, Italy. It is separated from the Cispius on the north by the valley of the Suburra, and from the Caelian Hill on the south by the valley of the Colosseum. The Oppius and the Cispius together form the Esquiline plateau just inside the line of the Servian Wall.
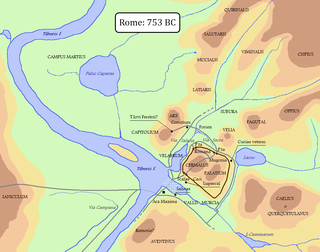
The Velia — or Velian Hill or Velian Ridge — is a saddle or spur stretching out from the middle of the north side of the Palatine Hill towards the Oppian Hill in Rome.
An episcopium is an ecclesiastical figure and their administration. The episcopium emphasizes "an essential unity between his [the bishop's] person, power and place." In medieval Italy episcopia were frequently part of a complex connected to the baptistery and cathedral.
A palatine was a high-level official attached to imperial or royal courts in Europe since Roman times.

The House of Augustus, or the Domus Augusti, is situated on the Palatine Hill in Rome, Italy. This house has been identified as the primary place of residence for the emperor Augustus.

Gaius Sextius Calvinus was a consul of the Roman Republic in 124 BC. During his consulship, he joined M. Fulvius Flaccus in waging war against the Ligures, Saluvii, and Vocontii in Transalpine Gaul. He continued as proconsul in Gaul for 123–122. He had held office as praetor no later than 127.

The Farnese Gardens, or "Gardens of Farnese upon the Palatine", are a garden in Rome, central Italy, created in 1550 on the northern portion of Palatine Hill, by Cardinal Alessandro Farnese. They were the first private botanical gardens in Europe; the first botanical gardens of any kind in Europe were started by Italian universities in the mid-16th century, only a short time before.

The Casa Romuli, also known as the tugurium Romuli, was the reputed dwelling place of the legendary founder and first king of Rome, Romulus. It was situated on the south-western corner of the Palatine hill, where it slopes down towards the Circus Maximus, near the so-called "Steps of Cacus". It was a traditional single-roomed peasants' hut of the Latins, with straw roof and wattle-and-daub walls, such as are reproduced in miniature in the distinctive funerary urns of the so-called Latial culture.

Ponte Palatino, also known as Ponte Inglese, is a bridge that links Lungotevere Aventino to Lungotevere Ripa in Rome (Italy), in the Rioni Ripa and Trastevere.

The Palatine Museum is a museum located on the Palatine Hill in Rome. Founded in the second half of the 19th century, it houses sculptures, fragments of frescoes, and archaeological material discovered on the hill.

Villa Mills, formerly known as Villa Mattei al Palatino, was a villa in Rome located above the Palatine Hill between Via di San Bonaventura and Via dei Cerchi, in the Campitelli. The structure was built over the Domus Augustana and the Domus Flavia. It was demolished at the beginning of the twentieth century to allow excavations of the archaeological site.