
The Ca' d'Oro or Palazzo Santa Sofia is a palace on the Grand Canal in Venice, northern Italy. One of the older palaces in the city, its name means "golden house" due to the gilt and polychrome external decorations which once adorned its walls. Since 1927, it has been used as a museum, as the Galleria Giorgio Franchetti.

Palazzo Barbarigo is a palace situated facing the Grand Canal of Venice, Italy. It is not to be confused with the Palazzo Barbarigo Minotto and Palazzo Barbarigo della Terrazza, both also on the Grand Canal, and other palazzi, and several villas, once owned by the Barbarigo family.

The Palazzo Vecchio is the town hall of Florence, Italy. It overlooks the Piazza della Signoria, which holds a copy of Michelangelo's David statue, and the gallery of statues in the adjacent Loggia dei Lanzi.

Stanford Memorial Church is located on the Main Quad at the center of the Stanford University campus in Stanford, California, United States. It was built during the American Renaissance by Jane Stanford as a memorial to her husband Leland. Designed by architect Charles A. Coolidge, a student of Henry Hobson Richardson, the church has been called "the University's architectural crown jewel".

Rustication is a range of masonry techniques used in classical architecture giving visible surfaces a finish texture that contrasts with smooth, squared-block masonry called ashlar. The visible face of each individual block is cut back around the edges to make its size and placing very clear. In addition the central part of the face of each block may be given a deliberately rough or patterned surface.

Villa del Poggio Imperiale is a predominantly neoclassical former grand ducal villa in Arcetri, just to the south of Florence in Tuscany, Central Italy. Beginning as a villa of the Baroncelli of Florence, it was seized by the Medici, became the home of a Medici princess, and a lavish retreat for a Grand Duchess with imperial pretensions. Later given to Napoleon's sister, it was reclaimed by the hereditary rulers of Tuscany before being finally converted to a prestigious girls' school. During its long history, it has often been at the centre of Italy's turbulent history, and has been rebuilt and redesigned many times.

The Palazzo della Civiltà Italiana, also known as the Palazzo della Civiltà del Lavoro, or in everyday speech as the Colosseo Quadrato, is a building in the EUR district in Rome. It was designed in 1938 by three Italian architects: Giovanni Guerrini, Ernesto La Padula, and Mario Romano. The building is an example of Italian Rationalism and fascist architecture with neoclassical design, representing romanità, a philosophy which encompasses the past, present, and future all in one. The enormity of the structure is meant to reflect the fascist regime's new course in Italian history. The design of the building draws inspiration from the Colosseum with rows of arches. According to legend, the structure's six vertical and nine horizontal arches are correlated to the number of letters in the Italian dictator Benito Mussolini's name.

Gothic architecture appeared in the prosperous independent city-states of Italy in the 12th century, at the same time as it appeared in Northern Europe. In fact, unlike in other regions of Europe, it did not replace Romanesque architecture, and Italian architects were not very influenced by it. However, each city developed its own particular variations of the style.

The Palazzo Dario is a palace located between the Palazzo Barbaro Wolkoff and the narrow Rio delle Torreselle on the Grand Canal in the sestiere of Dorsoduro, of the city of Venice, Italy. The palace was built in the Venetian Gothic style and was renovated in Renaissance style.

The Palazzo Mancini is a palazzo in Rome, Italy. From 1737 to 1793 it was the second home of the French Academy in Rome. It is located on Via del Corso, about a block north of Piazza Venezia.

The Palazzo di Propaganda Fide is a palace located in Rome, designed by Gian Lorenzo Bernini, then Francesco Borromini. Since 1626, it has housed the Congregation for the Evangelization of Peoples and since 1929 is an extraterritorial property of the Holy See. The complex includes a dormitory and chapel as well.

Palazzo Gondi is a palace in Florence, Italy, located a block from Piazza della Signoria. It was built in 1490 under design by Giuliano da Sangallo, who was inspired by other major works of stately buildings in the city, such as Palazzo Medici and Palazzo Strozzi. Among the elements borrowed from these earlier works are the cube-shape set around a central courtyard, the ashlar sloping on each of three floors, and the arched windows.
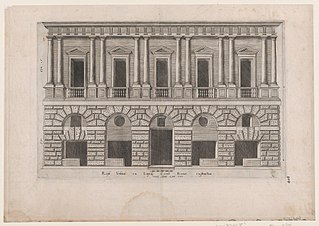
Palazzo Caprini was a Renaissance palazzo in Rome, Italy, in the Borgo rione between Piazza Scossacavalli and via Alessandrina. It was designed by Donato Bramante around 1510, or a few years before.

The Palazzo dei Consoli is a Gothic architecture, civic building in the historic center of Gubbio, region of Umbria, Italy. Construction took place during 1332–1349 under design by Angelo da Orvieto; the palace was built on a large platform built against the hillside and looming over the town below.

The Broletto or Broletto Palace of Brescia has for centuries housed the civic government offices of this city found in the region of Lombardy, Italy. The term Broletto refers to a buildings equivalent to the town hall or town assembly.

The Palazzo Curti Valmarana is a Renaissance-style palace located in the Grand Canal of Venice, Italy. It is nestled between Palazzo Querini Benzon and Palazzo Corner Spinelli in the San Marco district. Directly across the canal, it faces Palazzo Querini Dubois.

Palazzo Savorgnan is a palace in Venice, Italy, located in the Cannaregio district and overlooking Canale di Cannaregio, to the right of Palazzo Priuli Manfrin.

Palazzo Contarini Fasan is a small Gothic palace in Venice, Italy, located in the San Marco district and overlooking the Grand Canal. The palazzo is also called the House of Desdemona.

The Collegio Ghislieri was a building in Rome, seat of the eponymous charitable institution, important for architectural and historical reasons.

Palazzo Sacchetti is a palazzo in Rome, important for historical and artistic reasons.




















