The middle kingdoms of India were the political entities in the Indian subcontinent from 230 BCE to 1206 CE. The period begins after the decline of the Maurya Empire and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, starting with Simuka, from 230 BCE. The "middle" period lasted for almost 1436 years and ended in 1206 CE, with the rise of the Delhi Sultanate, founded in 1206, and the end of the Later Cholas.

The Gupta script was used for writing Sanskrit and is associated with the Gupta Empire of the Indian subcontinent, which was a period of material prosperity and great religious and scientific developments. The Gupta script was descended from Brāhmī and gave rise to the Śāradā and Siddhaṃ scripts. These scripts in turn gave rise to many of the most important Indic scripts, including Devanāgarī, the Gurmukhī script for Punjabi, the Odia script, the Bengali-Assamese script and the Tibetan script.

The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The Pallavas played a crucial role in shaping in particular southern Indian history and heritage. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahana Empire, whom they had formerly served as feudatories.

Simhavishnu also known as Avanisimha son of Simhavarman III and one of the Pallava kings of India, was responsible for the revival of the Pallavan dynasty. He was the first Pallava monarch whose domain extended beyond Kanchipuram (Kanchi) in the South. He was portrayed as a great conqueror in Mattavilasa Prahasana, a drama written by his son Mahendravarman I.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient India:

The Salankayana dynasty of ancient India ruled a part of Andhra region in India from 300 to 440 CE. Their territory was located between the Godavari and the Krishna rivers. Their capital was located at Vengi, modern Pedavegi near Eluru in West Godavari district of Andhra Pradesh.

The region of Tamil Nadu in the southeast of modern India, shows evidence of having had continuous human habitation from 15,000 BCE to 10,000 BCE. Throughout its history, spanning the early Upper Paleolithic age to modern times, this region has coexisted with various external cultures.

The Pallava script or Pallava Grantha is a Brahmic script named after the Pallava dynasty of Southern India (Tamilakam) and is attested to since the 4th century CE. In India, the Pallava script evolved from Tamil-Brahmi. The Grantha script originated from the Pallava script. Pallava also spread to Southeast Asia and evolved into scripts such as Balinese, Baybayin, Javanese, Kawi, Khmer, Lanna, Lao, Mon–Burmese, New Tai Lue, Sundanese, and Thai.
The Kadamba script is the first writing system devised specifically for writing Kannada and it was later adopted to write Telugu language.The Kadamba script is also known as Pre-Old-Kannada script.
Villavar was a tribe of hunters lived in Tamilakam, the southern part of ancient India. The word villavar derives from the Tamil word for bow (vil). The villavars lived in hill tracts and forests. Chera kings used the title villavan Kulasekhara Alwar the founder of the later Chera dynasty called himself "Villavar Kon", king of Villavars, in a Tamil work written by him known as Perumal Thirumozhi.

Mahendravadi is a historical ancient 6th Century Pallava Dynasty Town during Mahendra Varman 1, in Nemili taluk, Tamil Nadu, in northern Tamil Nadu of India.
Varman is the traditional suffix of Pallava dynasty that is generally translated as "shield" or "protector", and was adopted by Khmer royal lineages.
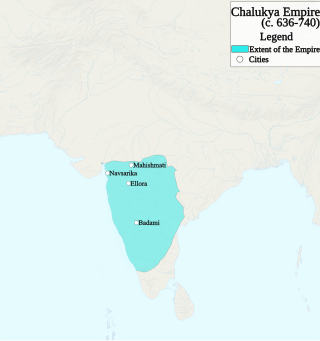
The Chalukya dynasty was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakeshin II. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century. These Western Chalukyas ruled from Kalyani until the end of the 12th century.
Rai Bahadur Valaiyattur Venkayya was an Indian epigraphist and historian. He served as the Chief Epigraphist to the Government of India from 1908 to 1912.
Standardisation of Tamil script includes various attempts in the past as well as ongoing attempts to uniformalise the Tamil script.
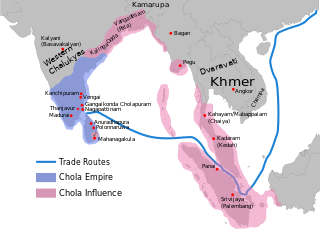
Tamils maintained a good relationship with the Chinese, with evidence of trade relations going back to 2nd century BC.
Mahendravarman is a royal title bestowed on rulers of Hindu kingdoms:

Tamil dynasties are the kingdoms who ruled over present day Tamil Nadu, Sri Lanka, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and Odisha. These include the Pallavas, the Pandyas, the Cholas and the Cheras.