
Suriname, officially the Republic of Suriname, is a sovereign state in northern South America. Situated slightly north of the equator within the tropics, over 90% of its territory is covered by rainforests, the highest proportion of forest cover in the world. Suriname is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, and Brazil to the south. It is the smallest country in South America by both population and territory, with around 612,985 inhabitants in an area of approximately 163,820 square kilometers. The capital and largest city is Paramaribo, home to roughly half the population.
After the creation of the Statute of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, the Royal Netherlands Army was entrusted with the defence of Suriname, while the defence of the Netherlands Antilles was the responsibility of the Royal Netherlands Navy. The army set up a separate Netherlands Armed Forces in Suriname. Upon independence in 1975, this force was turned into the Surinamese Armed Forces. On February 25, 1980, a group of 15 non-commissioned officers and one junior officer, under the leadership of sergeant major Dési Bouterse, staged a coup d'état and overthrew the Government. Subsequently, the SKM was rebranded as the National Army.

Paramaribo is the capital and largest city of Suriname, located on the banks of the Suriname River in the Paramaribo District. Paramaribo has a population of roughly 241,000 people, almost half of Suriname's population. The historic inner city of Paramaribo has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2002.

Sipaliwini is the largest district of Suriname, located in the south. Sipaliwini is the only district that does not have a regional capital, as it is directly administered by the national government in Paramaribo. Sipaliwini District includes disputed areas, with the southwestern region controlled and administered by Guyana, whereas the southeastern region is controlled by French Guiana.

The Guianas, sometimes called by the Spanish loan-word Guayanas, is a region in north-eastern South America which includes the following three territories:

The Courantyne/Corentyne/Corantijn River is a river in northern South America in Suriname and Guyana. It is the longest river in the country and creates the border between Suriname and the East Berbice-Corentyne region of Guyana.
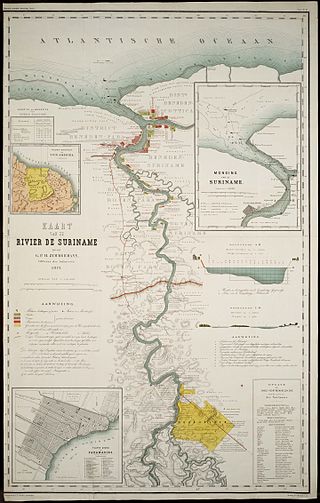
The Suriname River is 480 km long and flows through the country of Suriname. Its sources are located in the Guiana Highlands on the border between the Wilhelmina Mountains and the Eilerts de Haan Mountains. The source of the Upper Suriname River is at the confluence of the Gran Rio and Pikin Rio near the village of Goddo. The river continues shortly after the reservoir along Brokopondo as the Lower Suriname River. Than it flows Berg en Dal, the migrant communities Klaaskreek and Nieuw-Lombé, Jodensavanne, Carolina, Ornamibo and Domburg, before reaching the capital Paramaribo on the left bank and Meerzorg on the right bank. At Nieuw-Amsterdam it is joined by the Commewijne and immediately thereafter at the sandspit Braamspunt it flows into the Atlantic Ocean.
Pontoetoe was a village in the Sipaliwini District of Suriname, situated on the banks of the Paloemeu River. The village was inhabited by Wayana Amerindians.
The Aparai or Apalai are an indigenous people of Brazil, who live in Amapá and Pará states. A little community is located in French Guiana, in Antecume Pata. They were sedentary slash-and-burn farmers, necessitating periodic relocation as soil became exhausted, but also hunters and gatherers. They spoke a Carib language and in the 20th century their subsistence shifted towards craftwork as they adapted to modern Brazil and the cash economy.

The Wayana are a Carib-speaking people located in the southeastern part of the Guiana highlands, a region divided between Brazil, Suriname, and French Guiana. In 1980, when the last census took place, the Wayana numbered some 1,500 individuals, of which 150 in Brazil, among the Apalai, 400 in Suriname, and 1,000 in French Guiana, along the Maroni River. About half of them still speak their original language.
Operation Grasshopper was a project to look for natural resources in Suriname from the air. For this project, seven airstrips were constructed in the interior of Suriname from 1959 onward.
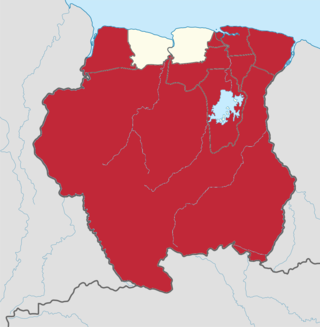
The borders of Suriname consist of land borders with three countries: Guyana, Brazil, and France. The borders with Guyana and France are in dispute, but the border with Brazil has been uncontroversial since 1906.

Indigenous peoples in Suriname, Native Surinamese, or Amerindian Surinamese, are Surinamese people who are of indigenous ancestry. They comprise approximately 3.5% of Suriname's population of 612,985.

Kasikasima, also spelt Kassikassima, is a mountain in the Sipaliwini District of Suriname. It is 718 metres (2,356 ft) high.
Medische Zending Primary Health Care Suriname, commonly known as Medische Zending or MZ is a Surinamese charitable organization offering primary healthcare to remote villages in the interior of Suriname.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Suriname was caused by Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Suriname on 13 March 2020. The case was a person who travelled from the Netherlands the previous week. On 3 April 2020, one person died. On 3 May 2020, all nine cases had recovered. On 18 May, an eleventh case was identified.

Jupta Lilian Itoewaki is a Wayana activist and politician from Suriname. Since 2018, she has been the founding president of Mulokot, an organisation representing the interests of the Wayana people. She had previously worked from 2010 with groups focused on preserving the culture and habitat of indigenous Surinamese.

Ronald "Rudi" Elwin Kappel was a Surinamese pilot. He was one of the founders of Luchtvaartbedrijf Kappel-Van Eyck which is now called Surinam Airways, the first airline in Suriname. He also helped construct the Zorg en Hoop Airport, and the Rudi Kappel Airstrip. Kappel died in an air crash near Paloemeu.













