
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. In the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of 7,641 islands which are broadly categorized in three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. It is the world's twelfth-most-populous country, with diverse ethnicities and cultures. Manila is the country's capital, and its most populated city is Quezon City; both are within Metro Manila.

The history of the Philippines dates from the earliest hominin activity in the archipelago at least 709,000 years ago. Homo luzonensis, a species of archaic humans, was present on the island of Luzon at least 67,000 years ago.

The Philippines is an archipelago that comprises 7,641 islands with a total land area of 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi).country]]. The eleven largest islands contain 95% of the total land area. The largest of these islands is Luzon at about 105,000 square kilometers (40,541 sq mi). The next largest island is Mindanao at about 95,000 square kilometers (36,680 sq mi). The archipelago is around 800 kilometers (500 mi) from the Asian mainland and is located between Taiwan and Borneo.

Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and north-west of mainland Australia which is part of Oceania. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia and the Indian Ocean. Apart from the British Indian Ocean Territory and two out of 26 atolls of Maldives in South Asia, Maritime Southeast Asia is the only other subregion of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere. Mainland Southeast Asia is completely in the Northern Hemisphere. East Timor and the southern portion of Indonesia are the parts of Southeast Asia that lie south of the Equator.

Luzon is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as well as Quezon City, the country's most populous city. With a population of 64 million as of 2021, it contains 52.5% of the country's total population and is the 4th most populous island in the world. It is the 15th largest island in the world by land area.

The Visayas, or the Visayan Islands, are one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, it consists of several islands, primarily surrounding the Visayan Sea, although the Visayas are also considered the northeast extremity of the entire Sulu Sea. Its inhabitants are predominantly the Visayan peoples.

The Philippine–American War, known alternatively as the Philippine Insurrection, Filipino–American War, or Tagalog Insurgency, was fought between the First Philippine Republic and the United States from February 4, 1899, until July 2, 1902. Tensions arose after the United States annexed the Philippines under the Treaty of Paris at the conclusion of the Spanish–American War rather than acknowledging the Philippines' declaration of independence, developing into the eruption of open battle. The war can be seen as a continuation of the Philippine struggle for independence that began in 1896 with the Philippine Revolution against Spanish rule.
Leyte is an island in the Visayas group of islands in the Philippines. It is eighth-largest and sixth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 2,626,970 as of 2020 census.

Palawan, officially the Province of Palawan, is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in terms of total area of 14,649.73 km2 (5,656.29 sq mi). The capital and largest city is Puerto Princesa wherein it is geographically grouped but administered independently from the province. Palawan is known as the Philippines' Last Frontier and as the Philippines' Best Island.

The Philippine Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean east of the Philippine Archipelago and the largest sea in the world, occupying an estimated surface area of 5 million square kilometers. The Philippine Sea Plate forms the floor of the sea. Its western border is the first island chain to the west, comprising the Ryukyu Islands in the northwest and Taiwan in the west. Its southwestern border comprises the Philippine islands of Luzon, Catanduanes, Samar, Leyte, and Mindanao. Its northern border comprises the Japanese islands of Honshu, Shikoku and Kyūshū. Its eastern border is the second island chain to the east, comprising the Bonin Islands and Iwo Jima in the northeast, the Mariana Islands in the due east, and Halmahera, Palau, Yap and Ulithi in the southeast. Its southern border is Indonesia's Morotai Island.

The Mariana Islands, also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fourteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east. They lie south-southeast of Japan, west-southwest of Hawaii, north of New Guinea and east of the Philippines, demarcating the Philippine Sea's eastern limit. They are found in the northern part of the western Oceanic sub-region of Micronesia, and are politically divided into two jurisdictions of the United States: the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and, at the southern end of the chain, the territory of Guam. The islands were named after the influential Spanish queen Mariana of Austria following their colonization in the 17th century.
The governor-general of the Philippines was the title of the government executive during the colonial period of the Philippines, governed by Mexico City and Madrid (1565–1898) and the United States (1898–1946), and briefly by Great Britain (1762–1764) and Japan (1942–1945). They were also the representative of the executive of the ruling power.

In the law of the United States, an insular area is a U.S.-associated jurisdiction that is not part of the 50 states or the District of Columbia. This includes fourteen U.S. territories administered under U.S. sovereignty, as well as three sovereign states each with a Compact of Free Association with the United States. The term also may be used to refer to the previous status of the Philippine Islands and the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands when it existed.

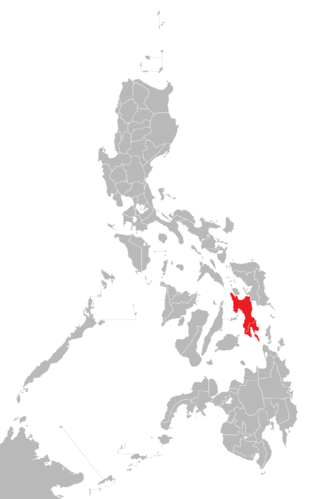
Samar is the third-largest and seventh-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 1,909,537 as of the 2020 census. It is located in the eastern Visayas, which are in the central Philippines. The island is divided into three provinces: Samar, Northern Samar, and Eastern Samar. These three provinces, along with the provinces on the nearby islands of Leyte and Biliran, are part of the Eastern Visayas region.

Filipinos are citizens or people identified with the country of the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian peoples, all typically speaking Filipino, English, or other Philippine languages. Currently, there are more than 185 ethnolinguistic groups in the Philippines each with its own language, identity, culture, tradition, and history.
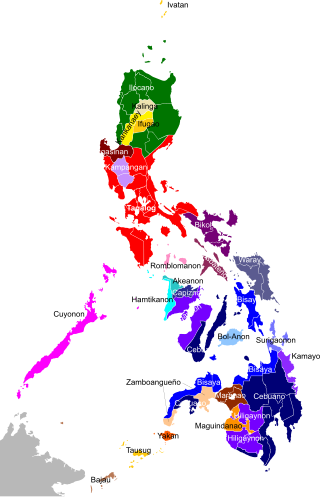
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous People groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither indigenous nor moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.

The Spanish East Indies were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1899, governed for the Spanish Crown from Mexico City and Madrid through the captaincy general which ruled Manila.

The Philippines campaign, Battle of the Philippines, Second Philippines campaign, or the Liberation of the Philippines, codenamed Operation Musketeer I, II, and III, was the American, Mexican, Australian and Filipino campaign to defeat and expel the Imperial Japanese forces occupying the Philippines during World War II.

The history of the Philippines from 1565 to 1898 is known as Spanish colonial period, during which the Philippine Islands were ruled as the Captaincy General of the Philippines within the Spanish East Indies, initially under the Viceroyalty of New Spain, based in Mexico City, until the independence of the Mexican Empire from Spain in 1821. This resulted in direct Spanish control during a period of governmental instability there. The Philippines was under direct royal governance from 1821 to 1898.

















