
Mining is the extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. The ore must be a rock or mineral that contains valuable constituent, can be extracted or mined and sold for profit. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water.

Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest, and cultural value. On Earth, it includes sunlight, atmosphere, water, land, all minerals along with all vegetation, and wildlife.

The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe is one of the five regional commissions under the jurisdiction of the United Nations Economic and Social Council. It was established in order to promote economic cooperation and integration among its member states.

The African Peer Review Mechanism (APRM) is a mutually agreed instrument voluntarily acceded to by the member states of the African Union (AU) as a self-monitoring mechanism. The APRM was launched on 9 March 2003 by the NEPAD Heads of State and Government Implementation Committee (HSGIC) in Abuja, Nigeria (NEPAD/HSGIC/03-2003/APRM/MOU, Assembly Decision 198, Decision 527 and Decision Ext/Assembly/AU/Dec.1-4 ;
There are several classification systems for the economic evaluation of mineral deposits worldwide. The most commonly used schemes base on the International Reporting Template, developed by the CRIRSCO – Committee for Mineral Reserves International Reporting Standards, like the Australian Joint Ore Reserves Committee – JORC Code 2012, the Pan-European Reserves & Resources Reporting Committee' – PERC Reporting Standard from 2021, the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum – CIM classification and the South African Code for the Reporting of Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves (SAMREC). A more detailed description of the historical development concerning reporting about mineral deposits can be found on the PERC web site. In 1997, the United Nations Framework Classification for Resources (UNFC) was development by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). The Pan African Resource Reporting Code (PARC) is based on UNFC.
Recognition of prior learning (RPL), prior learning assessment (PLA), or prior learning assessment and recognition (PLAR) describes a process used by regulatory bodies, adult learning centres, career development practitioners, military organizations, human resources professionals, employers, training institutions, colleges and universities around the world to evaluate skills and knowledge acquired outside the classroom for the purpose of recognizing competence against a given set of standards, competencies, or learning outcomes. RPL is practiced in many countries for a variety of purposes, for example an individual's standing in a profession, trades qualifications, academic achievement, recruitment, performance management, career and succession planning.
National Instrument 43-101Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects is a securities regulatory instrument that governs how companies can disclose mining-related information in Canada. Its rules aim to prevent companies from sharing inaccurate or misleading information about their mineral assets with prospective investors and the public. It is overseen and enforced by the Canadian Securities Administrators.
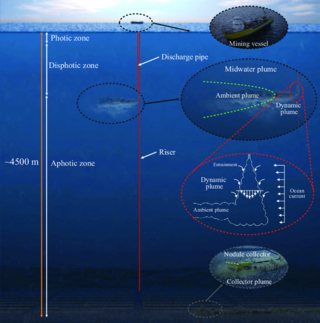
Deep sea mining is the extraction of minerals from the seabed of the deep sea. The main ores of commercial interest are polymetallic nodules, which are found at depths of 4–6 km (2.5–3.7 mi) primarily on the abyssal plain. The Clarion–Clipperton zone (CCZ) alone contains over 21 billion metric tons of these nodules, with minerals such as copper, nickel, and cobalt making up 2.5% of their weight. It is estimated that the global ocean floor holds more than 120 million tons of cobalt, five times the amount found in terrestrial reserves.
Nii Allotey Odunton, a mining engineer from Ghana, was the Secretary-General of the International Seabed Authority, serving consecutive four-year terms starting in 2009 and ending in 2017.
The International Cyanide Management Code for the Manufacture, Transport and Use of Cyanide in the Production of Gold, commonly referred to as the Cyanide Code, is a voluntary program designed to assist the global gold and silver mining industries and the producers and transporters of cyanide used in gold and silver mining in improving cyanide management practices and to publicly demonstrate their compliance with the Cyanide Code through an independent and transparent process. The Cyanide Code is intended to reduce the potential exposure of workers and communities to harmful concentrations of cyanide‚ limit releases of cyanide to the environment‚ and enhance response actions in the event of an exposure or release.

A McKelvey diagram or McKelvey box is a visual representation used to describe a natural resource such as a mineral or fossil fuel, based on the geologic certainty of its presence and its economic potential for recovery. The diagram is used to estimate the uncertainty and risk associated with availability of a natural resource. As geological assurance of a resource's occurrence decreases, risk increases. As economic recoverability of a resource decreases, risk also increases.

The International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD) is an independent think tank founded in 1990 working to shape and inform international policy on sustainable development governance. The institute has three offices in Canada - Winnipeg, Ottawa, and Toronto, and one office in Geneva, Switzerland. It has over 150 staff and associates working in over 30 countries.

The mining industry of Togo is centred mainly around the extraction of phosphate, ranking it 19th in world production. Other minerals extracted are diamond, gold, and limestone. More minerals identified but yet to be brought into production mode are manganese, bauxite, gypsum, iron ore, marble, rutile, and zinc. The mineral sector contributes 2.8% to the country's gross domestic product (GDP).
Mineral resource estimation is used to determine and define the ore tonnage and grade of a geological deposit, from the developed block model. There are different estimation methods used for different scenarios dependent upon the ore boundaries, geological deposit geometry, grade variability and the amount of time and money available. A typical resource estimation involves the construction of a geological and resource model with data from various sources. Depending on the nature of the information and whether the data is hard copy or computerized, the principal steps of computer resource estimation are:
- Creation, standardization and validation of the database.
- Section plotting and interactive geological modeling.
- Geostatistical analysis.
- Block modeling and block estimation.
Since 2011, the European Commission has triennially assessed a list of Critical Raw Materials (CRMs), with 14 CRMs identified in 2011, 20 in 2014, 27 in 2017 and 30 in 2020. These materials are mainly used in energy transition and digital technologies. Then, in March 2023, Commission President Ursula von der Leyen proposed the Critical Raw Materials Act, "for a regulation of the European Parliament and of the European Council establishing a framework for ensuring a secure and sustainable supply of critical raw materials". At the time, Europe depended on China for 98% of its rare-earth needs, 97% of its lithium supply and 93% of its magnesium supply.
Water-related industry in Africa provides jobs and employment opportunities in many sectors, for example agriculture, fisheries, manufacturing and industry.
The South African Mineral Reporting Codes (SAMCODES) are codified sets of standards and guidelines applicable to the South African Minerals and Petroleum Industries, drafted and overseen by the SAMCODES Standards Committee (SSC), a professional and non-governmental body. Specifically, the standards and guidelines are applicable to public reports compiled on behalf of South African Minerals and Petroleum companies for the benefit of investors. The Codes are incorporated into Section 12 of the Johannesburg Stock Exchange (JSE) Listings Rules, which detail "the criteria for the listing of, and the additional disclosure requirements for Mineral Companies and, in certain circumstances, substantial mineral assets of non-Mineral Companies" in South Africa. As such, the SSC acts in an advisory capacity to the JSE, ensuring that reports submitted for listings consideration are compliant with the SAMCODES.
United Nations Framework Classification for Resources (UNFC) is an international scheme for the classification, management and reporting of energy, mineral, and raw material resources. United Nations Economic Commission for Europe's (UNECE) Expert Group on Resource Management (EGRM) is responsible for the development promotion and further development of UNFC.

The PERCStandard for Reporting of Exploration Results, Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves sets out the minimum standards, as well as additional guidelines and recommendations for the Public Reporting of Exploration Results, Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves within Europe.
The United Nations Resource Management System (UNRMS) is a voluntary global standard for managing natural resources sustainably. It is based on the United Nations Framework Classification for Resources (UNFC). UNRMS aims to support the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by providing a comprehensive framework and methodology for resource progression, policy development, and financing.








