Related Research Articles

Kidney stone disease, also known as renal calculus disease, nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material develops in the urinary tract. Renal calculi typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small calculus may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than 5 millimeters, it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back that often radiates downward to the groin. A calculus may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a renal calculus are likely to have another within ten years.
The excretory system is a passive biological system that removes excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. The dual function of excretory systems is the elimination of the waste products of metabolism and to drain the body of used up and broken down components in a liquid and gaseous state. In humans and other amniotes, most of these substances leave the body as urine and to some degree exhalation, mammals also expel them through sweating.

The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lined with urothelial cells, a form of transitional epithelium, and feature an extra layer of smooth muscle in the lower third to aid in peristalsis. The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone. Stenosis is when a ureter is narrowed, due to for example chronic inflammation. Congenital abnormalities that affect the ureters can include the development of two ureters on the same side or abnormally placed ureters. Additionally, reflux of urine from the bladder back up the ureters is a condition commonly seen in children.
Potter sequence is the atypical physical appearance of a baby due to oligohydramnios experienced when in the uterus. It includes clubbed feet, pulmonary hypoplasia and cranial anomalies related to the oligohydramnios. Oligohydramnios is the decrease in amniotic fluid volume sufficient to cause deformations in morphogenesis of the baby.

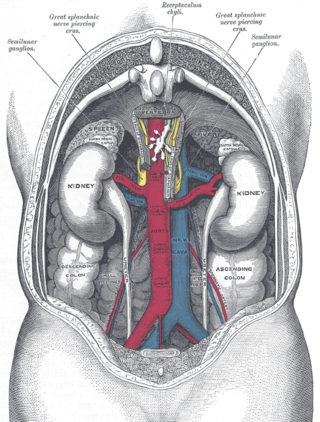
The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.

A nephrectomy is the surgical removal of a kidney, performed to treat a number of kidney diseases including kidney cancer. It is also done to remove a normal healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor, which is part of a kidney transplant procedure.

Hydronephrosis describes hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dilation of the entire upper urinary tract.
Horseshoe kidney, also known as ren arcuatus, renal fusion or super kidney, is a congenital disorder affecting about 1 in 500 people that is more common in men, often asymptomatic, and usually diagnosed incidentally. In this disorder, the patient's kidneys fuse to form a horseshoe-shape during development in the womb. The fused part is the isthmus of the horseshoe kidney. The abnormal anatomy can affect kidney drainage resulting in increased frequency of kidney stones and urinary tract infections as well as increase risk of certain renal cancers.

Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), also known as vesicoureteric reflux, is a condition in which urine flows retrograde, or backward, from the bladder into one or both ureters and then to the renal calyx or kidneys. Urine normally travels in one direction from the kidneys to the bladder via the ureters, with a one-way valve at the vesicoureteral (ureteral-bladder) junction preventing backflow. The valve is formed by oblique tunneling of the distal ureter through the wall of the bladder, creating a short length of ureter (1–2 cm) that can be compressed as the bladder fills. Reflux occurs if the ureter enters the bladder without sufficient tunneling, i.e., too "end-on".

A ureteral stent, or ureteric stent, is a thin tube inserted into the ureter to prevent or treat obstruction of the urine flow from the kidney. The length of the stents used in adult patients varies between 24 and 30 cm. Additionally, stents come in differing diameters or gauges, to fit different size ureters. The stent is usually inserted with the aid of a cystoscope. One or both ends of the stent may be coiled to prevent it from moving out of place; this is called a JJ stent, double J stent or pig-tail stent.
Pyelogram is a form of imaging of the renal pelvis and ureter.

Papillorenal syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder marked by underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the kidney and colobomas of the optic nerve.
Ovarian vein syndrome is a rare condition in which a dilated ovarian vein compresses the ureter. This causes chronic or colicky abdominal pain, back pain and/or pelvic pain. The pain can worsen on lying down or between ovulation and menstruation. There can also be an increased tendency towards urinary tract infection or pyelonephritis. The right ovarian vein is most commonly involved, although the disease can be left-sided or affect both sides. It is currently classified as a form of pelvic congestion syndrome.
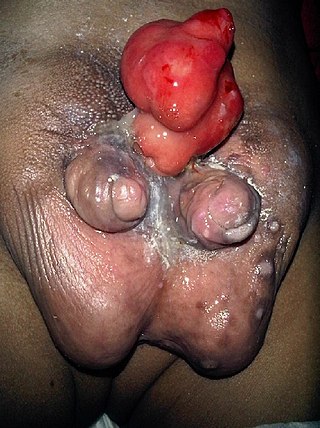
Diphallia, penile duplication (PD), diphallic terata, or diphallasparatus is an extremely rare developmental abnormality in which a male is born with two penises. The first reported case was by Johannes Jacob Wecker in 1609. Its occurrence is 1 in 5.5 million boys in the United States.
Bladder outlet obstruction occurs when urine is unable to flow from the kidneys through the ureters and out of the bladder through the urethra. Decreased flow of urine leads to swelling of the urinary tract, called hydronephrosis. This process of decreased flow of urine through the urinary tract can begin as early as during intrauterine life and it prevents normal development of fetal kidneys and fetal urine. Low levels of fetal urine leads to low amniotic fluid levels and incomplete lung maturation. Older children and adults can also experience bladder outlet obstruction; however, this process is usually reversible and isn't associated with as many poor outcomes as in infants with congenital bladder outlet obstruction.

Fryns syndrome is an autosomal recessive multiple congenital anomaly syndrome that is usually lethal in the neonatal period. Fryns (1987) reviewed the syndrome.
Crossed dystopia is a rare form of renal ectopia where both kidneys are on the same side of the spine. In many cases, the two kidneys are fused together, yet retain their own vessels and ureters. The ureter of the lower kidney crosses the midline to enter the bladder on the contralateral side. Both renal pelves can lie one above each other medial to the renal parenchyma or the pelvis of the crossed kidney faces laterally. Urogram is diagnostic.
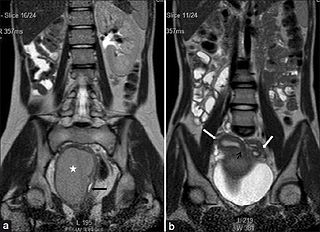
Herlyn–Werner–Wunderlich syndrome, also known as OHVIRA is an extremely rare syndrome characterized by a congenital birth defect of the lower abdominal and pelvic organs. It is a type of abnormality of the Müllerian ducts.

Strømme syndrome is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic condition characterised by intestinal atresia, eye abnormalities and microcephaly. The intestinal atresia is of the "apple-peel" type, in which the remaining intestine is twisted around its main artery. The front third of the eye is typically underdeveloped, and there is usually moderate developmental delay. Less common features include an atrial septal defect, increased muscle tone or skeletal abnormalities. Physical features may include short stature, large, low-set ears, a small jaw, a large mouth, epicanthic folds, or fine, sparse hair.

17q12 microdeletion syndrome, also known as 17q12 deletion syndrome, is a rare chromosomal anomaly caused by the deletion of a small amount of material from a region in the long arm of chromosome 17. It is typified by deletion of the HNF1B gene, resulting in kidney abnormalities and renal cysts and diabetes syndrome. It also has neurocognitive effects, and has been implicated as a genetic factor for autism and schizophrenia.
References
- 1 2 3 González Reimers, E; Santolaria Fernández, F; Pestana Pestana, M; Jorge Hernández, JA; Batista Lopez, N; Abreu González, J; Hernández Nieto, L (November 1985). "[Clinical and prognostic value of quantified fibrosis in alcoholic hepatic cirrhosis]". Revista espanola de las enfermedades del aparato digestivo. 68 (5): 413–9. PMID 4081266.
- ↑ Chaker, Kays; Sellami, Ahmed; Ben Chehida, Mohamed Ali; Ben Rhouma, Sami; Nouira, Yassine (1 March 2019). "Pancake kidney: A case report". Urology Case Reports. 23: 19–20. doi:10.1016/j.eucr.2018.11.014. ISSN 2214-4420. PMC 6260232 . Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ↑ Charachon, R; Eyraud, S; Guenoun, A; Egal, F (1984). "[Surgical treatment of cholesteatoma in children]". Revue de laryngologie - otologie - rhinologie. 105 (5): 465–74. PMID 6531527.