Related Research Articles

Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.
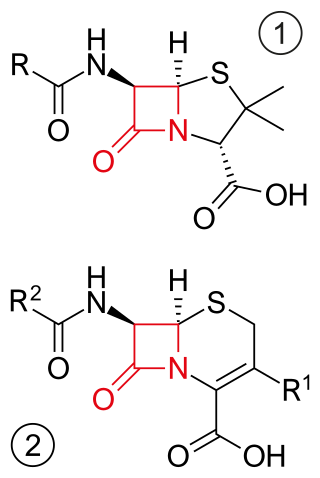
β-lactam antibiotics are antibiotics that contain a beta-lactam ring in their chemical structure. This includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins and cephamycins (cephems), monobactams, carbapenems and carbacephems. Most β-lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis in the bacterial organism and are the most widely used group of antibiotics. Until 2003, when measured by sales, more than half of all commercially available antibiotics in use were β-lactam compounds. The first β-lactam antibiotic discovered, penicillin, was isolated from a strain of Penicillium rubens.
This is the timeline of modern antimicrobial (anti-infective) therapy. The years show when a given drug was released onto the pharmaceutical market. This is not a timeline of the development of the antibiotics themselves.

Ertapenem, sold under the brand name Invanz, is a carbapenem antibiotic medication used for the treatment of infections of the abdomen, the lungs, the upper part of the female reproductive system, and the diabetic foot.

Klebsiella pneumoniae is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose-fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar.

The cephalosporins are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus Acremonium, which was previously known as Cephalosporium.
Esomeprazole, sold under the brand name Nexium [or Neksium] among others, is a medication which reduces stomach acid. It is used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. Its effectiveness is similar to that of other proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein.
Meropenem, sold under the brand name Merrem among others, is an intravenous β-lactam antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Some of these include meningitis, intra-abdominal infection, pneumonia, sepsis, and anthrax.

Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Similar to penicillins and cephalosporins, carbapenems are members of the beta-lactam antibiotics drug class, which kill bacteria by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, thus inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, these agents individually exhibit a broader spectrum of activity compared to most cephalosporins and penicillins. Furthermore, carbapenems are typically unaffected by emerging antibiotic resistance, even to other beta-lactams.

Doripenem is an antibiotic drug in the carbapenem class. It is a beta-lactam antibiotic drug able to kill Pseudomonas aeruginosa.

Beta-lactamases are a family of enzymes involved in bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. In bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, the bacteria have beta-lactamase which degrade the beta-lactam rings, rendering the antibiotic ineffective. However, with beta-lactamase inhibitors, these enzymes on the bacteria are inhibited, thus allowing the antibiotic to take effect. Strategies for combating this form of resistance have included the development of new beta-lactam antibiotics that are more resistant to cleavage and the development of the class of enzyme inhibitors called beta-lactamase inhibitors. Although β-lactamase inhibitors have little antibiotic activity of their own, they prevent bacterial degradation of beta-lactam antibiotics and thus extend the range of bacteria the drugs are effective against.
Panipenem (INN) is a carbapenem antibiotic used in combination with betamipron. It is not used in the United States.
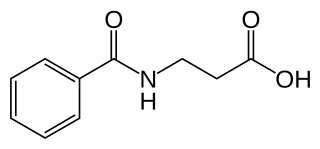
Betamipron (INN) or N-benzoyl-β-alanine is a chemical compound which is used together with panipenem to inhibit panipenem uptake into the renal tubule and prevent nephrotoxicity.

Helicobacter cinaedi is a bacterium in the family Helicobacteraceae, Campylobacterales order, Helicobacteraceae family, Helicobacter genus. It was formerly known as Campylobacter cinaedi until molecular analysis published in 1991 led to a major revision of the genus Campylobacter. H. cinaedi is a curved, spiral, or fusiform rod with flagellum at both of its ends which it uses to dart around. The bacterium is a pathogen.
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) or carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) are Gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to the carbapenem class of antibiotics, considered the drugs of last resort for such infections. They are resistant because they produce an enzyme called a carbapenemase that disables the drug molecule. The resistance can vary from moderate to severe. Enterobacteriaceae are common commensals and infectious agents. Experts fear CRE as the new "superbug". The bacteria can kill up to half of patients who get bloodstream infections. Tom Frieden, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has referred to CRE as "nightmare bacteria". Examples of enzymes found in certain types of CRE are KPC and NDM. KPC and NDM are enzymes that break down carbapenems and make them ineffective. Both of these enzymes, as well as the enzyme VIM have also been reported in Pseudomonas.

Tebipenem is a broad-spectrum orally-administered antibiotic, from the carbapenem subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics. It was developed as a replacement drug to combat bacteria that had acquired antibiotic resistance to commonly used antibiotics. Tebipenem is formulated as the ester tebipenem pivoxil due to the better absorption and improved bioavailability of this form. It has performed well in clinical trials for ear infection and looks likely to be further developed in future. It is only marketed in Japan. Tebipenem is the first carbapenem whose prodrug form, the pivalyl ester, is orally available.

Teneligliptin is a pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. It belongs to the class of anti-diabetic drugs known as dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors or "gliptins".

Ceftazidime/avibactam, sold under the brand name Avycaz among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication composed of ceftazidime, a cephalosporin antibiotic, and avibactam, a β-lactamase inhibitor. It is used to treat complicated intra-abdominal infections, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia. It is only recommended when other options are not appropriate. It is given by injection into a vein.
Cefiderocol, sold under the brand name Fetroja among others, is an antibiotic used to treat complicated urinary tract infections when no other options are available. It is indicated for the treatment of multi-drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It is given by injection into a vein.
References
- ↑ Hikida M, Terashima S, Sato Y, Okamoato R, Inoue M (November 2001). "[Comparative antibacterial activity of carbapenems against P. aeruginosa (1)]". The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics. 54 (11): 571–9. doi:10.11553/antibiotics1968b.54.571. PMID 11828603.
- ↑ "Sankyo Launch". The Pharmaletter. 1994-01-24.
- ↑ International Drug Names : Carbenin.
- ↑ Finch RG (2003). Antibiotic and chemotherapy: anti-infective agents and their use in therapy. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 269ff. ISBN 978-0-443-07129-4 . Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ↑ Goa KL, Noble S (2003). "Panipenem/betamipron". Drugs. 63 (9): 913–25, discussion 926. doi:10.2165/00003495-200363090-00005. PMID 12678575. S2CID 263994230.