Related Research Articles

Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. It is the world's third largest island country with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

The Prime Minister of Papua New Guinea is Papua New Guinea's head of government, consequent on being the leader of the party or coalition with majority support in the National Parliament. The Prime Minister serves as the head of his party, the head of the coalition government, and the chairman of the National Executive Council. The office of Prime Minister was preceded by the Chief Ministry.

The Territory of Papua comprised the southeastern quarter of the island of New Guinea from 1883 to 1975. In 1883, the Government of Queensland annexed this territory for the British Empire. The United Kingdom Government refused to ratify the annexation but in 1884 a Protectorate was proclaimed over the territory, then called "British New Guinea". There is a certain ambiguity about the exact date on which the entire territory was annexed by the British. The Papua Act 1905 recites that this happened "on or about" 4 September 1888. On 18 March 1902, the Territory was placed under the authority of the Commonwealth of Australia. Resolutions of acceptance were passed by the Commonwealth Parliament, who accepted the territory under the name of Papua.

Morobe Province is a province on the northern coast of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital and largest city is Lae. The province covers 33,705 km², with a population of 674,810, and since the division of Southern Highlands Province in May 2012 it is the most populous province. It includes the Huon Peninsula, the Markham River, and delta, and coastal territories along the Huon Gulf. The province has nine administrative districts. At least 101 languages are spoken, including Kâte and Yabem language. English and Tok Pisin are common languages in the urban areas, and in some areas pidgin forms of German are mixed with the native language.
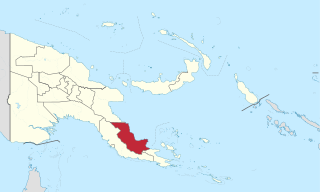
Oro Province, formerly Northern Province, is a coastal province of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital is Popondetta. The province covers 22,800 km2, and has 176,206 inhabitants. The province shares land borders with Morobe Province to the northwest, Central Province to the west and south, and Milne Bay Province to the southeast. The province is located within the Papuan Peninsula.

Southern Highlands is a province in Papua New Guinea. Its provincial capital is the town of Mendi. According to Papua New Guinea's national 2011 census, the total population of Southern Highlands is 515,511 spread across 15,089 square kilometers (5,826 sq mi).

The University of Papua New Guinea (UPNG) is a university located in Port Moresby, capital of Papua New Guinea. It was established by ordinance of the Australian administration in 1965. This followed the Currie Commission which had enquired into higher education in Papua New Guinea. The University of Papua New Guinea Act No. 18, 1983 bill repealing the old Ordinance was passed by the National Parliament in August 1983.

Manus Province is the smallest province in Papua New Guinea with a land area of 2,100 square kilometres (810 sq mi), but with more than 220,000 square kilometres (85,000 sq mi) of water. The provincial town of Manus is Lorengau and the total population is 60,485.

The law of Papua New Guinea consists of the Constitution, ordinary statutes enacted by Parliament or adopted at independence from overseas and judge-made law.

The Supreme Court of Papua New Guinea has been the highest court of Papua New Guinea since 16 September 1975, replacing the pre-Independence Supreme Court and the overseas appellate tribunals from 1902 to 1975 of the High Court of Australia and the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. Judges of the pre-Independence Supreme Court automatically became the justices of the National Court and accordingly among the pool of judges available to be empanelled as a Supreme Court bench.

The Territory of New Guinea was an Australian-administered territory on the island of New Guinea from 1914 until 1975. In 1949, the Territory and the Territory of Papua were established in an administrative union by the name of the Territory of Papua and New Guinea. That administrative union was renamed as Papua New Guinea in 1971. Notwithstanding that it was part of an administrative union, the Territory of New Guinea at all times retained a distinct legal status and identity until the advent of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.

The Territory of Papua and New Guinea was established by an administrative union between the Australian-administered territories of Papua and New Guinea in 1949. In December 1971, the name of the Territory changed to "Papua New Guinea" and in 1975 it became the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.
The Papua New Guinea Post-Courier is a newspaper based in Konedobu, Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Papua New Guinea:

The monarchy of Papua New Guinea is a system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of Papua New Guinea. The current monarch, since 16 September 1975, is Queen Elizabeth II. Although the person of the sovereign is equally shared with 15 other independent countries within the Commonwealth of Nations, each country's monarchy is separate and legally distinct. As a result, the current monarch is officially titled the Queen of Papua New Guinea and, in this capacity, she and other members of the Royal Family undertake public and private functions domestically and abroad as representatives of the Papua New Guinean state. However, the Queen is the only member of the Royal Family with any constitutional role. The Queen lives predominantly in the United Kingdom and, while several powers are the sovereign's alone, most of the royal governmental and ceremonial duties in Papua New Guinea are carried out by the Queen's representative, the governor-general.
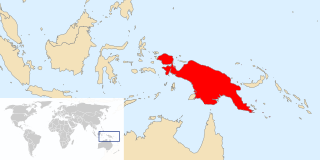
New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, and with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi), the largest island in the Southern Hemisphere. Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, it is separated by the 150 km wide Torres Strait from Australia. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea or West Papua, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua and West Papua.
Asmat is a Papuan language cluster of West New Guinea.
In Papua New Guinea (PNG), also officially known as the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, capital punishment is a legal form of punishment. Despite its legality, capital punishment has not been imposed in PNG in over sixty years. The last known execution took place under the colonial administration of Australia. The last execution is understood to have been done by way of hanging and took place in the capital city of PNG, Port Moresby, in November 1954.
Sinasian Sign Language (SSSL) is a village sign language of the Sinasina valley in Chimbu Province, Papua New Guinea. This language is used by approximately 3 deaf and 50 hearing individuals, including members of the Kere community. SSSL was first encountered and reported by linguists in 2016. Documentation efforts are ongoing.
Papua New Guinean nationality law is regulated by the 1975 Constitution of Papua New Guinea, as amended; the Citizenship Act 1975, and its revisions; and international agreements entered into by the Papua New Guinean government. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Papua New Guinea. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Papua New Guinean nationality is typically obtained either on the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in Papua New Guinea or under the rules of jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth abroad to parents with Papua New Guinean nationality. It can be granted to persons who have lived in the country for a specific period of time, who have contributed to the country's development, or who have an affiliation to the country through naturalization.
References
- ↑ "Papua New Guinea Law Society" . Retrieved 2 April 2017.