Papuans may refer to:
- Indonesian Papuans – the Native Indonesians of Papua-origin
- Papua New Guineans – the nationals of Papua New Guinea
- Indigenous people of New Guinea
Papuans may refer to:

Papua is a province of Indonesia, comprising the northern coast of Western New Guinea together with island groups in Cenderawasih Bay to the west. It roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Tabi Saireri. It is bordered by nation of Papua New Guinea to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the north, Cenderawasih Bay to the west, and the provinces of Central Papua and Highland Papua to the south. The province also shares maritime boundaries with Palau in the Pacific. Following the splitting off of twenty regencies to create the three new provinces of Central Papua, Highland Papua, and South Papua on 30 June 2022, the residual province is now restricted to the northern part of that territory and to the islands in Cenderawasah Bay, and is divided into eight regencies and one city (kota), the latter being the provincial capital of Jayapura. The province has a large potential in natural resources, such as gold, nickel, petroleum, etc. Papua, along with five other Papuan provinces, has a higher degree of autonomy level compared to other Indonesian provinces.

Dutch New Guinea or Netherlands New Guinea was the western half of the island of New Guinea that was a part of the Dutch East Indies until 1949, later an overseas territory of the Kingdom of the Netherlands from 1949 to 1962. It contained what are now Indonesia's six easternmost provinces, Central Papua, Highland Papua, Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua, which were administered as a single province prior to 2003 under the name Irian Jaya, and now comprise the Papua region of the country.
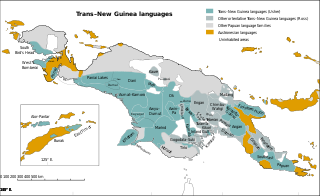
Trans–New Guinea (TNG) is an extensive family of Papuan languages spoken on the island of New Guinea and neighboring islands, a region corresponding to the country Papua New Guinea as well as parts of Indonesia.

Jayapura is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of 940.0 km2 (362.9 sq mi). The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sudarso Bay to the north, the country of Papua New Guinea to the east, Keerom Regency to the south, and Jayapura Regency to the west.
Guinea or Guinea-Conakry is a republic in West Africa, independent since 1958.

The Free Papua Movement or Free Papua Organization is a name given to a separatist movement that aims to separate West Papua from Indonesia and establish an independent state in the region. The territory is currently divided into six Indonesian provinces of Central Papua, Highland Papua, Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua, also formerly known as Papua, Irian Jaya and West Irian.

West Papua, formerly Irian Jaya Barat, is an Indonesian province located in Indonesia Papua. It covers most of the two western peninsulas of the island of New Guinea: the eastern half of the Bird's Head Peninsula and the whole of the Bomberai Peninsula, along with nearby smaller islands. The province is bordered to the north by the Pacific Ocean, to the west by Southwest Papua Province, the Halmahera Sea and the Ceram Sea, to the south by the Banda Sea, and to the east by the province of Central Papua and the Cenderawasih Bay. Manokwari is the province's capital and largest city. With an estimated population of 569,570 in mid-2023, West Papua is the least populous province in Indonesia after South Papua, following the separation off in 2022 of the western half of the Bird's Head Peninsula to create the new province of Southwest Papua, containing 52% of what had been West Papua's population. Its population density is similar to Russia.
Papua may refer to:

The indigenous peoples of Western New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Archipelago perhaps 50,000 years ago when New Guinea and Australia were a single landmass called Sahul and, much later, a wave of Austronesian people from the north who introduced Austronesian languages and pigs about 3,500 years ago. They also left a small but significant genetic trace in many coastal Papuan peoples.

A crow is a bird of the genus Corvus, or more broadly, a synonym for all of Corvus. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not linked scientifically to any certain trait but is rather a general grouping for larger-sized species of Corvus.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, and Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the island of New Guinea, formerly Dutch and granted to Indonesia in 1962. Given the island is alternatively named Papua, the region is also called West Papua.
West Papua may refer to:
Isirawa is a Papuan language spoken by about two thousand people on the north coast of Papua province, Indonesia. It's a local trade language, and use is vigorous. Stephen Wurm (1975) linked it to the Kwerba languages within the Trans–New Guinea family, and it does share about 20% of its vocabulary with neighboring Kwerba languages. However, based on its pronouns, Malcolm Ross (2005) felt he could not substantiate such a link, and left it as a language isolate. The pronouns are not, however, dissimilar from those of Orya–Tor, which Ross links to Kwerba, and Donahue (2002) accept it as a Greater Kwerba language.
Karo may refer to:

Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 839 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages ."

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the African region of Guinea.

The Papua conflict is an ongoing conflict in Western New Guinea (Papua) between Indonesia and the Free Papua Movement. Subsequent to the withdrawal of the Dutch administration from the Netherlands New Guinea in 1962 and implementation of Indonesian administration in 1963, the Free Papua Movement has conducted a low-intensity guerrilla war against Indonesia by targeting its military and police, along with ordinary Indonesian civilians.

Indonesia–Papua New Guinea relations are foreign relations between Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, two bordering countries north of Australia.

The North Halmahera (NH) languages are a family of languages spoken in the northern and eastern parts of the island of Halmahera and some neighboring islands in Indonesia. The southwestern part of the island is occupied by the unrelated South Halmahera languages, which are a subgroup of Austronesian. They may be most closely related to the languages of the Bird's Head region of West Papua, but this is not well-established.
Ende may refer to the following languages: