Related Research Articles
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending. This may be triggered by various events, such as a financial crisis, an external trade shock, an adverse supply shock, the bursting of an economic bubble, or a large-scale natural or anthropogenic disaster. In the United States, it is defined as "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the market, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales". In the United Kingdom, it is defined as a negative economic growth for two consecutive quarters.

Paul Robin Krugman is an American economist who is the Distinguished Professor of Economics at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York, and a columnist for The New York Times. In 2008, Krugman was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to New Trade Theory and New Economic Geography. The Prize Committee cited Krugman's work explaining the patterns of international trade and the geographic distribution of economic activity, by examining the effects of economies of scale and of consumer preferences for diverse goods and services.

Zero interest-rate policy (ZIRP) is a macroeconomic concept describing conditions with a very low nominal interest rate, such as those in contemporary Japan and December 2008 through December 2015 in the United States. It has begun again in the United States since March 15, 2020; the Federal Reserve cut the Fed Funds rate to nearly zero due to the COVID-19 pandemic and weakening economy. ZIRP is considered to be an unconventional monetary policy instrument and can be associated with slow economic growth, deflation, and deleverage.
A liquidity trap is a situation, described in Keynesian economics, in which, "after the rate of interest has fallen to a certain level, liquidity preference may become virtually absolute in the sense that almost everyone prefers holding cash rather than holding a debt which yields so low a rate of interest."
Austerity is a set of political-economic policies that aim to reduce government budget deficits through spending cuts, tax increases, or a combination of both. Austerity measures are often used by governments that find it difficult to borrow or meet their existing obligations to pay back loans. The measures are meant to reduce the budget deficit by bringing government revenues closer to expenditures. This reduces the amount of borrowing required and may also demonstrate a government's fiscal discipline to creditors and credit rating agencies and make borrowing easier or cheaper as a result.
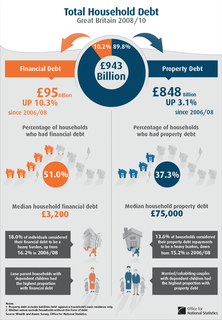
Household debt is defined as the combined debt of all people in a household. It includes consumer debt and mortgage loans. A significant rise in the level of this debt coincides historically with many severe economic crises and was a cause of the U.S. and subsequent European economic crises of 2007–2012. Several economists have argued that lowering this debt is essential to economic recovery in the U.S. and selected Eurozone countries.
In economics, the Pigou effect is the stimulation of output and employment caused by increasing consumption due to a rise in real balances of wealth, particularly during deflation. The term was named after Arthur Cecil Pigou by Don Patinkin in 1948.
The paradox of thrift is a paradox of economics. The paradox states that an increase in autonomous saving leads to a decrease in aggregate demand and thus a decrease in gross output which will in turn lower total saving. The paradox is, narrowly speaking, that total saving may fall because of individuals' attempts to increase their saving, and, broadly speaking, that increase in saving may be harmful to an economy. Both the narrow and broad claims are paradoxical within the assumption underlying the fallacy of composition, namely that which is true of the parts must be true of the whole. The narrow claim transparently contradicts this assumption, and the broad one does so by implication, because while individual thrift is generally averred to be good for the economy, the paradox of thrift holds that collective thrift may be bad for the economy.
In macroeconomic theory, liquidity preference is the demand for money, considered as liquidity. The concept was first developed by John Maynard Keynes in his book The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (1936) to explain determination of the interest rate by the supply and demand for money. The demand for money as an asset was theorized to depend on the interest foregone by not holding bonds. Interest rates, he argues, cannot be a reward for saving as such because, if a person hoards his savings in cash, keeping it under his mattress say, he will receive no interest, although he has nevertheless refrained from consuming all his current income. Instead of a reward for saving, interest, in the Keynesian analysis, is a reward for parting with liquidity. According to Keynes, money is the most liquid asset. Liquidity is an attribute to an asset. The more quickly an asset is converted into money the more liquid it is said to be.
At the micro-economic level, deleveraging refers to the reduction of the leverage ratio, or the percentage of debt in the balance sheet of a single economic entity, such as a household or a firm. It is the opposite of leveraging, which is the practice of borrowing money to acquire assets and multiply gains and losses.
Debt deflation is a theory that recessions and depressions are due to the overall level of debt rising in real value because of deflation, causing people to default on their consumer loans and mortgages. Bank assets fall because of the defaults and because the value of their collateral falls, leading to a surge in bank insolvencies, a reduction in lending and by extension, a reduction in spending.
Paul Allen McCulley is an American economist and former managing director at PIMCO. He coined the terms "Minsky moment" and "shadow banking system", which became famous during the Financial crisis of 2007–2009. He is currently a senior fellow at Cornell Law School.

The Lost Decade or the Lost 10 Years was a period of economic stagnation in Japan from about 1991 to 2001, caused by the Japanese asset price bubble's collapse in late 1991. From 1991 to 2003, the Japanese economy, as measured by GDP, grew only 1.14% annually, well below that of other industrialized nations.

Fiat money is a currency established as money, often by government regulation, but that has no intrinsic value. Fiat money does not have use value, and has value only because a government maintains its value, or because parties engaging in exchange agree on its value. It was introduced as an alternative to commodity money and representative money. Representative money is similar to fiat money, but it represents a claim on a commodity.

The Capitol Hill Babysitting Cooperative (CHBC) is a cooperative located in Washington, D.C., whose purpose is to fairly distribute the responsibility of babysitting between its members. The co-op is often used as an allegory for a demand-oriented model of an economy. The allegory illustrates several economic concepts, including the paradox of thrift and the importance of the money supply to an economy's well being. The allegory has received continuing attention, particularly in the wake of the late-2000s recession.
The paradox of toil is the economic hypothesis that total employment will shrink if everybody wants to work more when "the short-term nominal interest rate is zero and there are deflationary pressures and output contraction". When wages are pushed down by the simultaneous efforts of everyone in the labor force to work more even at lower wages, with interest rates against the zero bound, demand must fall because the only source of added demand would be added credit to compensate for those lower wages, credit which cannot be made available on any looser terms; this loss of demand leads to loss of jobs.
The Wallace neutrality, is an economics proposition asserting that in certain environment, holding fiscal policy constant, alternative paths of the government financial policies have no effect on the sequences for the price level and for real allocations in the economy. The proposition rests upon a no arbitrage argument similar to that of the Modigliani–Miller theorem. Policy implication is that, whenever Wallace neutrality applies, conventional open-market purchases of securities by the central bank won't be an effective monetary policy.
The Zero Lower Bound (ZLB) or Zero Nominal Lower Bound (ZNLB) is a macroeconomic problem that occurs when the short-term nominal interest rate is at or near zero, causing a liquidity trap and limiting the capacity that the central bank has to stimulate economic growth.
A balance sheet recession is a type of economic recession that occurs when high levels of private sector debt cause individuals or companies to collectively focus on saving by paying down debt rather than spending or investing, causing economic growth to slow or decline. The term is attributed to economist Richard Koo and is related to the debt deflation concept described by economist Irving Fisher. Recent examples include Japan's recession that began in 1990 and the U.S. recession of 2007-2009.
Gauti Bergþóruson Eggertsson is a professor of economics at Brown University.
References
- ↑ Eggertsson, Gauti B.; Krugman, Paul (14 February 2011), Debt, Deleveraging, and the Liquidity Trap: A Fisher-Minsky-Koo Approach (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on 3 October 2011, retrieved 15 December 2011
- ↑ Eggertsson, Gauti (Feb 2010). "The Paradox of Toil" (PDF). NY Fed Staff Report. New York, NY: Federal Reserve Bank of New York (433). Retrieved 2011-12-15.
| This article related to macroeconomics is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |