
Afroasiatic (Afro-Asiatic), also known as Afrasian and in older sources as Hamito-Semitic (Chamito-Semitic) or Semito-Hamitic, is a large language family of about 300 languages. It includes languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa and parts of the Sahel.

The Chadic languages form a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken in parts of the Sahel. They include 150 languages spoken across northern Nigeria, southern Niger, southern Chad, Central African Republic and northern Cameroon. The most widely spoken Chadic language is Hausa, a lingua franca of much of inland Eastern West Africa.

The Khoisan languages are a group of African languages originally classified together by Joseph Greenberg. Khoisan languages share click consonants and do not belong to other African language families. For much of the 20th century, they were thought to be genealogically related to each other, but this is no longer accepted. They are now held to comprise three distinct language families and two language isolates.

The Niger–Congo languages constitute one of the world's major language families and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area, number of speakers, and number of distinct languages. It is generally considered to be the world's largest language family in terms of distinct languages, ahead of Austronesian, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger–Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540. It is the third-largest language family in the world by number of native speakers, comprising around 700 million people as of 2015. Within Niger–Congo, the Bantu languages alone account for 350 million people (2015), or half the total Niger–Congo speaking population.
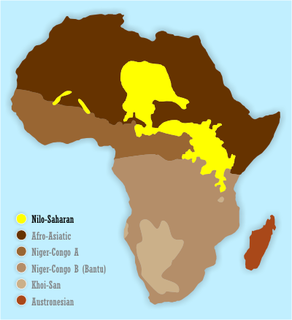
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. The languages extend through 17 nations in the northern half of Africa: from Algeria to Benin in the west; from Libya to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the centre; and from Egypt to Tanzania in the east.
The Nilotic peoples are peoples indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages, which constitute a large sub-group of the Nilo-Saharan languages spoken in South Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, and northern Tanzania. In a more general sense, the Nilotic peoples include all descendants of the original Nilo-Saharan speakers. Among these are the Luo, Sara, Maasai, Kalenjin, Dinka, Nuer, Shilluk, Ateker, and the Maa-speaking peoples, each of which is a cluster of several ethnic groups. Some ethnic groups in West Africa such as the Serer people of Senegal, the Gambia and Mauritania have been reported as being of Nilotic origin.
The Nubian languages are a group of related languages spoken by the Nubians. They form a branch of the Eastern Sudanic languages, which is part of the wider Nilo-Saharan phylum. Initially, Nubian languages were spoken throughout much of Sudan, but as a result of arabization they are today mostly limited to the Nile Valley between Aswan and Al Dabbah as well as a few villages in the Nuba mountains and Darfur.

The Bantu expansion is a major series of migrations of the original proto-Bantu language speaking group, who spread from an original nucleus around West Africa-Central Africa across much of sub-Saharan Africa. In the process, the Proto-Bantu-speaking settlers displaced or absorbed pre-existing hunter-gatherer and pastoralist groups that they encountered.
In historical linguistics, an Urheimat is the area of origin of the speakers of a proto-language, the parent language of a group of languages assumed to be genetically related.
The Eastern Nilotic languages are one of the three primary branches of the Nilotic languages, themselves belonging to the Eastern Sudanic subfamily of Nilo-Saharan; they are believed to have begun to diverge about 3,000 years ago, and have spread southwards from an original home in Equatoria in South Sudan. They are spoken across a large area in East Africa, ranging from Equatoria to the highlands of Tanzania. Their speakers are mostly cattle herders living in semi-arid or arid plains.

In most classifications, the Eastern Sudanic languages are a group of nine families of languages that may constitute a branch of the Nilo-Saharan language family. Eastern Sudanic languages are spoken from southern Egypt to northern Tanzania.

The Languages of Africa is a 1963 book of essays by Joseph Greenberg, in which the author sets forth a genetic classification of African languages that, with some changes, continues to be the most commonly used one today. It is an expanded and extensively revised version of his 1955 work Studies in African Linguistic Classification, which was itself a compilation of eight articles which Greenberg had published in the Southwestern Journal of Anthropology between 1949 and 1954. It was first published in 1963 as Part II of the International Journal of American Linguistics, Vol. 29, No. 1; however, its second edition of 1966, in which it was published as an independent work, is more commonly cited.

In early 20th century classification of African languages, Sudanic was a generic term for languages spoken in the Sahel belt, from Ethiopia in the east to Senegal in the west.

Charles Gabriel Seligman FRS was a British physician and ethnologist. His main ethnographic work described the culture of the Vedda people of Sri Lanka and the Shilluk people of the Sudan. He was a Professor at London School of Economics and was highly influential as the teacher of such notable anthropologists as Bronisław Malinowski, E. E. Evans-Pritchard and Meyer Fortes all of whose work overshadowed his own. He was a proponent of the Hamitic hypothesis, according to which, some civilizations of Africa were thought to have been founded by Caucasoid Hamitic peoples.

The Southern Romance languages make up a sub-group of the family of Romance languages proposed by Ethnologue and Glottolog. According to Ethnologue and Glottolog, the family would include Sardinian and Corsican. However, the classification of Corsican and Sardinian into the same linguistic group has received little support among other linguists.
The Khoe languages are the largest of the non-Bantu language families indigenous to southern Africa. They were once considered to be a branch of a Khoisan language family, and were known as Central Khoisan in that scenario. Though Khoisan is now rejected as a family, the name is retained as a term of convenience.
The South Omotic, Somotic, or Aroid languages belong to the Afro-Asiatic family and are spoken in Ethiopia. There are four languages:
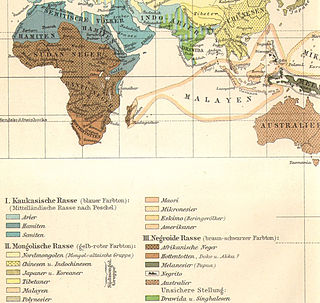
Hamites is a historical term in 19th and early 20th century ethnology and linguistics for a division of the Caucasian race and the group of related languages these populations spoke. The appellation Hamitic was applied to the Berber, Cushitic, and Egyptian branches of the Afroasiatic language family, which, together with the Semitic branch, was thus formerly labelled "Hamito-Semitic". However, since the three Hamitic branches have not been shown to form an exclusive (monophyletic) phylogenetic unit of their own, separate from other Afroasiatic languages, linguists no longer use the term in this sense. Each of these branches is instead now regarded as an independent subgroup of the larger Afroasiatic family.














