Related Research Articles
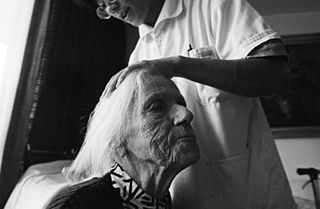
Home care is supportive care provided in the home. Care may be provided by licensed healthcare professionals who provide medical treatment needs or by professional caregivers who provide daily assistance to ensure the activities of daily living (ADLs) are met. In-home medical care is often and more accurately referred to as home health care or formal care. Home health care is different non-medical care, custodial care, or private-duty care which refers to assistance and services provided by persons who are not nurses, doctors, or other licensed medical personnel. For patients recovering from surgery or illness, home care may include rehabilitative therapies. For terminally ill patients, home care may include hospice care.

Elderly care, or simply eldercare, serves the needs of old adults. It encompasses assisted living, adult daycare, long-term care, nursing homes, hospice care, and home care.
Allied health professions (AHPs) are a category of health professionals that provide a range of diagnostic, preventive, therapeutic, and rehabilitative services in connection with health care. While there is no international standard for defining the diversity of allied health professions, they are typically considered those which are distinct from the fields of medicine, nursing and dentistry.

Long-term care (LTC) is a variety of services which help meet both the medical and non-medical needs of people with a chronic illness or disability who cannot care for themselves for long periods. Long-term care is focused on individualized and coordinated services that promote independence, maximize patients' quality of life, and meet patients' needs over a period of time.

The American Health Care Association (AHCA) is a non-profit federation of affiliated state health organizations that represents more than 14,000 non-profit and for-profit nursing homes, assisted living communities, and facilities for individuals with disabilities. Clifton J. Porter, II became CEO on 14 October 2024.
Supported living or supportive living refers to a range of services and community living arrangements (CLAs) designed with individuals with disabilities and their families to support citizens with disabilities to attain or retain their independence or interdependence in their local communities. Supported living is recorded in the history of the NASDDDS, celebrating its 50th anniversary. Community Supported Living Arrangements (CSLA) was a landmark federal multi-state demonstration to illustrate the federal role in community living in the US. Supported living is considered a core service or program of community living programs funded through federal-state-local partnerships.
The term sheltered workshop refers to an organization or environment that employs people with disabilities separately from others, usually with exemptions from labor standards, including but not limited to the absence of minimum wage requirements.
Direct Support Professionals (DSPs) are professionals who work directly with people with intellectual and developmental disabilities, with the aim of assisting the individual to become integrated into their community or the least restrictive environment.
A mental health professional is a health care practitioner or social and human services provider who offers services for the purpose of improving an individual's mental health or to treat mental disorders. This broad category was developed as a name for community personnel who worked in the new community mental health agencies begun in the 1970s to assist individuals moving from state hospitals, to prevent admissions, and to provide support in homes, jobs, education, and community. These individuals were the forefront brigade to develop the community programs, which today may be referred to by names such as supported housing, psychiatric rehabilitation, supported or transitional employment, sheltered workshops, supported education, daily living skills, affirmative industries, dual diagnosis treatment, individual and family psychoeducation, adult day care, foster care, family services and mental health counseling.
A group home, congregate living facility, care home, adult family home, etc., is a structured and supervised residence model that provides assisted living and medical care for those with complex health needs. Traditionally, the model has been used for children or young people who cannot live with their families or afford their own homes, people with chronic disabilities who may be adults or seniors, or people with dementia and related aged illnesses. Typically, there are no more than six residents, and there is at least one trained caregiver there 24 hours a day. In some early "model programs", a house manager, night manager, weekend activity coordinator, and four part-time skill teachers were reported. Originally, the term group home referred to homes of 8 to 16 individuals, which was a state-mandated size during deinstitutionalization. Residential nursing facilities, also included in this article, may be as large as 100 individuals in 2015, which is no longer the case in fields such as intellectual and developmental disabilities. Depending on the severity of the condition requiring one to need to live in a group home, some clients are able to attend day programs and most clients are able to live normal lifestyles.
Patient advocacy is a process in health care concerned with advocacy for patients, survivors, and caregivers. The patient advocate may be an individual or an organization, concerned with healthcare standards or with one specific group of disorders. The terms patient advocate and patient advocacy can refer both to individual advocates providing services that organizations also provide, and to organizations whose functions extend to individual patients. Some patient advocates are independent and some work for the organizations that are directly responsible for the patient's care.

A nursing shortage occurs when the demand for nursing professionals, such as Registered Nurses (RNs), exceeds the supply locally—within a healthcare facility—nationally or globally. It can be measured, for instance, when the nurse-to-patient ratio, the nurse-to-population ratio, the number of job openings necessitates a higher number of nurses than currently available, or the current number of nurses is above a certain age where retirement becomes an option and plays a factor in staffing making the workforce in a higher need of nurses. The nursing shortage is global according to 2022 World Health Organization fact sheet.

The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 29 U.S.C. § 203 (FLSA) is a United States labor law that creates the right to a minimum wage, and "time-and-a-half" overtime pay when people work over forty hours a week. It also prohibits employment of minors in "oppressive child labor". It applies to employees engaged in interstate commerce or employed by an enterprise engaged in commerce or in the production of goods for commerce, unless the employer can claim an exemption from coverage. The Act was enacted by the 75th Congress and signed into law by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1938.

Unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are paraprofessionals who assist individuals with physical disabilities, mental impairments, and other health care needs with their activities of daily living (ADLs). UAPs also provide bedside care—including basic nursing procedures—all under the supervision of a registered nurse, licensed practical nurse or other health care professional. UAPs must demonstrate their ability and competence before gaining any expanded responsibilities in a clinical setting. While providing this care, UAPs offer compassion and patience and are part of the patient's healthcare support system. Communication between UAPs and registered nurses (RNs) is key as they are working together in their patients' best interests. The scope of care UAPs are responsible for is delegated by RNs or other clinical licensed professionals.

Founded in 1893 by nursing pioneer Lillian D. Wald and Mary M. Brewster, VNS Health is one of the largest not-for-profit home- and community-based health care organizations in the United States, serving the five boroughs of New York City; Nassau, Suffolk, and Westchester Counties; and parts of upstate New York.
The companionship exemption refers to federal labor regulations in the United States that exclude workers providing companionship services to the elderly or disabled from the federal minimum wage and overtime protections that apply to most other American workers.
The Eldercare Workforce Alliance (EWA), a project of the Tides Center, is a coalition of 35 US national organizations that came together to focus on short- and long-term healthcare workforce issues relating to older adults. The Alliance helped pass the 2018 Raise Family Caregivers Act, supports ongoing funding for the Title VII Geriatrics Workforce Enhancement Program, and advocates for including elder care in government and professional policies, including related questions of educating and maintaining the labor force such care requires.
The John A. Hartford Foundation is a private United States–based philanthropy whose current mission is to improve the care of older adults. For many years, it made grants for research and education in geriatric medicine, nursing and social work. It now focuses on three priority areas: creating age-friendly health systems, supporting family caregivers and improving serious illness, and end-of-life care.
As of 2017, approximately 1.4 million Americans live in a nursing home, two-thirds of whom rely on Medicaid to pay for their care. Residential nursing facilities receive Medicaid federal funding and approvals through a state health department. These facilities may be overseen by various types of state agency.
The Bureau of Health Workforce is a part of the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA), of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. HRSA programs train health care professionals and place them where they are needed most. Grants support scholarship and loan repayment programs at colleges and universities to meet critical workforce shortages and promote diversity within the health professions.
References
- ↑ Leland, John (April 24, 2010). “A Graying Population, A Graying Workforce.” New York Times. Retrieved October 7, 2010.
- ↑ The New York Times New Old Age blog July 27, 2010. Dale Russakoff. “One Way to Judge a Nursing Home.”
- ↑ Span, Paula (May 10, 2009). “Marilyn Daniel’s Reward.” Washington Post. Retrieved October 7, 2010.
- ↑ Jones, Diana Nelson (May 23, 2010). “National Movement Focuses on Choice, Independence for elderly.” Pittsburgh Post-Gazette.
- ↑ Scott, Jason (December 28, 2009). “Reporter’s Notebook: Legislator Participates in Come Care with Me Day.” The Sentinel.
- ↑ Higgins, Kaileigh (September 30, 2010). “Jehlen Rolls Up Her Sleeves at 102-Year-Old’s House.” Boston.com
- ↑ "Home Care Workers Deserve Minimum Wage & Overtime".