Related Research Articles

Mato Grosso is one of the states of Brazil, the third largest by area, located in the Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP.

Mato Grosso do Sul is one of the Midwestern states of Brazil. Neighboring Brazilian states are Mato Grosso, Goiás, Minas Gerais, São Paulo and Paraná. It also borders the countries of Paraguay, to the southwest, and Bolivia, to the west. The economy of the state is largely based on agriculture and cattle-raising. Crossed in the south by the Tropic of Capricorn, Mato Grosso do Sul generally has a warm, sometimes hot, and humid climate, and is crossed by numerous tributaries of the Paraná River. The state has 1.3% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.5% of the Brazilian GDP.

Cáceres is a municipality in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso. It covers an area of 24,000km2 and as of 2020 had an estimated population of 94,861.
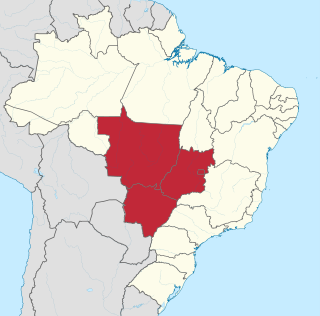
The Central-West or Center-West Region of Brazil is composed of the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul; along with Distrito Federal, where Brazil's national capital, Brasília, is situated. The region comprises 18.86% of the national territory.

The Federal University of Mato Grosso is a public university in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Responsible for serving the entire state, its main campus is in the capital city of Cuiabá. Smaller campuses are located in Barra do Garças, Pontal do Araguaia, Sinop, and Várzea Grande, while the former campus at Rondonópolis is now the Federal University of Rondonópolis, split off in 2018.

Miranda is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, named for its location on the river by the same name. Its population was 28,220 in 2020 and its area is 5,479 km².
The Aporé River is a river forming the border between Goiás and Mato Grosso do Sul states in central Brazil. It is a tributary of the Paranaíba River, which it enters in the reservoir created by Ilha Solteira Dam on the Paraná River.
The Ferro River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil. It flows northeast, receives the Steinen River from the south, enters the Xingu Indigenous Park, receives the combined Ronuro and Jatoba rivers from the south and joins the Xingu River which flows north into the Amazon.
The Paranaíta River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil.
The Sumidouro Grande River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil.
The São João da Barra River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil. It is a tributary of the Juruena River.
The São Venceslau River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil.

The Aquidauana River is a river of Mato Grosso do Sul state in southwestern Brazil. It is a tributary of the Miranda River, itself a part of the Paraguay River basin.
The Nioaque River is a river of Mato Grosso do Sul state in southwestern Brazil.

The Piripucu River is a river of Mato Grosso do Sul state in southwestern Brazil.
The Salobra River is a river of Mato Grosso do Sul state in Midwest Brazil.

Tapurah is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil.
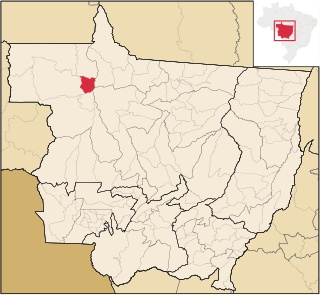
Juruena is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil.

Alto Garças is a municipality) in the south-east of the Brazilian State of Mato Grosso with a population of about 12,000 on an area of 3672 km. The distance to the state capital Cuiabá is approximately 350 km². In 1933 Alto Garças became a district of the municipality of Santa Rita do Araguaia and on 10 December 1953 it was separated as an independent entity. Alto Garças is part of the micro-region Alto Araguaia.
References
Coordinates: 12°58′S56°44′W / 12.967°S 56.733°W