
Parental leave, or family leave, is an employee benefit available in almost all countries. The term "parental leave" may include maternity, paternity, and adoption leave; or may be used distinctively from "maternity leave" and "paternity leave" to describe separate family leave available to either parent to care for small children. In some countries and jurisdictions, "family leave" also includes leave provided to care for ill family members. Often, the minimum benefits and eligibility requirements are stipulated by law.

The Children Act 1989 is a United Kingdom Act of Parliament which allocates duties to local authorities, courts, parents, and other agencies in the United Kingdom, to ensure children are safeguarded and their welfare is promoted. It centres on the idea that children are best cared for within their own families; however, it also makes provisions for instances when parents and families do not co-operate with statutory bodies.
Emancipation of minors is a legal mechanism by which a child before attaining the age of majority is freed from control by their parents or guardians, and the parents or guardians are freed from any and all responsibility toward the child. Children before that age are normally considered legally incompetent to enter into contracts and to handle their own affairs. Emancipation overrides that presumption and allows emancipated children legally to make certain decisions on their own behalf.

A children's hearing is part of the legal and welfare systems in Scotland; it aims to combine justice and welfare for children and young people. As of 31 March 2013, 1.4% (12,514) of Scotland's children were subject to a supervision requirement.
In the United Kingdom and the nations of the European Union, parental responsibility refers to the rights and privileges which underpin the relationship between the children and the children's parents and those adults who are granted parental responsibility by either signing a 'parental responsibility agreement' with the mother or getting a 'parental responsibility order' from a court. The terminology for this area of law now includes matters dealt with as contact and residence in some states.
In Canada and the United States, the term parental responsibility refers to the potential or actual liability that may be incurred by parents for the behavior of their children.
H. L. v. Matheson, 450 U.S. 398 (1981), was a United States Supreme Court abortion rights case, according to which a state may require a doctor to inform a teenaged girl's parents before performing an abortion or face criminal penalty.

Child protection is the safeguarding of children from violence, exploitation, abuse, and neglect. Article 19 of the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child provides for the protection of children in and out of the home. One of the ways to ensure this is by giving them quality education, the fourth of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, in addition to other child protection systems.
In family law, contact, visitation and access are synonym terms that denotes the time that a child spends with the noncustodial parent, according to an agreed or court specified parenting schedule. The visitation term is not used in a shared parenting arrangement where the mother and father have joint physical custody.
Residence may refer to various parts of English law including taxation, immigration, and family law. This article deals exclusively with English family law. See residence in English law for disambiguation.

The Family Law Act 1975, referred to as the FLA by legal practitioners, is an Act of the Australian Parliament. It has 15 parts and is the main Australian legislation dealing with divorce, parenting arrangements between separated parents, property separation, and financial maintenance involving children or divorced or separated de facto partners. It came into effect on 1 January 1976, repealing the Matrimonial Causes Act 1961, which had been largely based on fault.
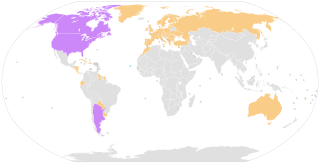
The Hague Convention on parental responsibility and protection of children, or Hague Convention 1996, officially Convention of 19 October 1996 on Jurisdiction, Applicable Law, Recognition, Enforcement and Co-operation in respect of Parental Responsibility and Measures for the Protection of Children or Hague Convention 1996 is a convention of the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It covers civil measures of protection concerning children, ranging from orders concerning parental responsibility and contact to public measures of protection or care, and from matters of representation to the protection of children's property. It is therefore much broader in scope than two earlier conventions of the HCCH on the subject.

The tender years doctrine is a legal principle in family law since the late 19th century. In common law, it presumes that during a child's "tender" years, the mother should have custody of the child. The doctrine often arises in divorce proceedings.

Scots family law is the body of laws in Scotland which regulate certain aspects of adult relationships and the rights and obligations in respect of children.
A gatekeeper parent is a term sometimes utilized in the legal arena to refer to a parent who appoints themself the power to decide what relationship is acceptable between the other parent and the child(ren). The term is broad and may refer to power dynamics within a marriage or may describe the behaviors of divorced or never married parents.
The Parental Rights Amendment to the United States Constitution is a proposed change to the United States Constitution. The amendment's advocates say that it will allow parents' rights to direct the upbringing of their children, protected from federal interference, and the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child. The Amendment was first proposed during the 110th Congress as House Joint Resolution 97 in July 2008, but no action was taken during that Congress. The Amendment has been described as a "wedge issue" and part of the culture wars.

Brussels II Regulation (EC) No 2201/2003, also called Brussels IIA or II bis is a European Union Regulation on conflict of law issues in family law between member states; in particular those related to divorce, child custody and international child abduction. It replaces Convention Council Regulation (EC) No 1347/2000 of 29 May 2000 on the jurisdiction, recognition and enforcement of judgments in matrimonial matters and in matters of parental responsibility for joint children. The regulation applies to all EU member states except Denmark.
Parental child abduction is the hiding, taking, or keeping hold of a child by his/her parent while defying the rights of the child's other parent or another member of the family.

The Children and Adoption Act 2006 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.

A referendum on one of the country's opt-outs from the European Union was held in Denmark on 3 December 2015. Specifically, the referendum was on whether to convert Denmark's current full opt-out on home and justice matters into an opt-out with case-by-case opt-in similar to that currently held by Ireland and the United Kingdom. Approval of the referendum was needed for Denmark to remain in Europol under the new rules. However, it was rejected by 53% of voters.








