
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several weeks after infection; the incubation period between exposure and being able to infect others is thought to be on the order of two to six weeks. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination. Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy.

Safe sex is sexual activity using methods or contraceptive devices to reduce the risk of transmitting or acquiring sexually transmitted infections (STIs), especially HIV. "Safe sex" is also sometimes referred to as safer sex or protected sex to indicate that some safe sex practices do not eliminate STI risks. It is also sometimes used colloquially to describe methods aimed at preventing pregnancy that may or may not also lower STI risks.

Cervicitis is inflammation of the uterine cervix. Cervicitis in women has many features in common with urethritis in men and many cases are caused by sexually transmitted infections. Non-infectious causes of cervicitis can include intrauterine devices, contraceptive diaphragms, and allergic reactions to spermicides or latex condoms. Cervicitis affects over half of all women during their adult life.

Chancroid is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection characterized by painful sores on the genitalia. Chancroid is known to spread from one individual to another solely through sexual contact. However, there have been reports of accidental infection through the hand.
Men who have sex with men (MSM) are male persons who engage in sexual activity with members of the same sex. The term was created in the 1990s by epidemiologists to study the spread of disease among all men who have sex with men, regardless of sexual identity, to include, for example, male prostitutes. The term is often used in medical literature and social research to describe such men as a group for research studies. It does not describe any specific sexual activity, and which activities are covered by the term depends on context.
Post-exposure prophylaxis, also known as post-exposure prevention (PEP), is any preventive medical treatment started after exposure to a pathogen in order to prevent the infection from occurring.
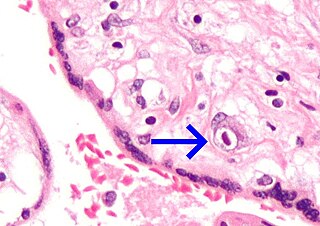
A vertically transmitted infection is an infection caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses that use mother-to-child transmission, that is, transmission directly from the mother to an embryo, fetus, or baby during pregnancy or childbirth. It can occur when the mother has a pre-existing disease or becomes infected during pregnancy. Nutritional deficiencies may exacerbate the risks of perinatal infections. Vertical transmission is important for the mathematical modelling of infectious diseases, especially for diseases of animals with large litter sizes, as it causes a wave of new infectious individuals.

Sexual health clinics specialize in the prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted infections.
Serosorting, also known as serodiscrimination, is the practice of using HIV status as a decision-making point in choosing sexual behavior. The term is used to describe the behavior of a person who chooses a sexual partner assumed to be of the same HIV serostatus in order to engage in unprotected sex with them for a reduced risk of acquiring or transmitting HIV/AIDS.

The Berkeley Free Clinic is a non-profit community clinic located in Berkeley, California, US. It is operated as a worker-run collective by more than 100 volunteers. It has provided free medical care since opening in 1969.
Venereology is a branch of medicine that is concerned with the study and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). The name derives from Roman goddess Venus, associated with love, beauty and fertility. A physician specializing in venereology is called a venereologist. In many areas of the world, the specialty is usually combined with dermatology.
Women who have sex with women (WSW) are women who engage in sexual activities with other women, whether they identify themselves as lesbian, bisexual, or heterosexual, or dispense with sexual identification altogether. The term WSW is often used in medical literature to describe such women as a group for clinical study, without needing to consider sexual self-identity.

Ass to mouth is a slang term associated with the porn industry describing anal sex immediately followed by oral sex. The term is primarily used to describe a sexual practice whereby an erect penis is removed from a receptive partner's anus and then directly put into their mouth, or possibly the mouth of another.
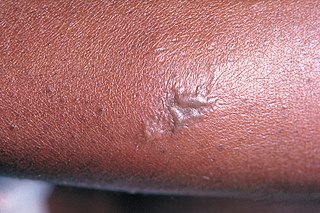
Gonorrhoea or gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Infected men may experience pain or burning with urination, discharge from the penis, or testicular pain. Infected women may experience burning with urination, vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods, or pelvic pain. Complications in women include pelvic inflammatory disease and in men include inflammation of the epididymis. Many of those infected, however, have no symptoms. If untreated, gonorrhea can spread to joints or heart valves.

Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of passing the infection on to others. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some STIs can cause infertility.

Syphilis is a bacterial infection transmitted by sexual contact and is believed to have infected 12 million people in 1999 with greater than 90% of cases in the developing world. It affects between 700,000 and 1.6 million pregnancies a year, resulting in spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, and congenital syphilis. In Sub-Saharan Africa syphilis contributes to approximately 20% of perinatal deaths.
Infectious diseases within American correctional settings are a concern within the public health sector. The corrections population is susceptible to infectious diseases through exposure to blood and other bodily fluids, drug injection, poor health care, prison overcrowding, demographics, security issues, lack of community support for rehabilitation programs, and high-risk behaviors. The spread of infectious diseases, such as HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases, hepatitis C (HCV), hepatitis B (HBV), and tuberculosis, result largely from needle-sharing, drug use, and consensual and non-consensual sex among prisoners. HIV and hepatitis C need specific attention because of the specific public health concerns and issues they raise.
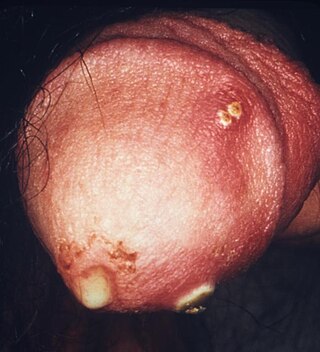
Penile discharge is fluid that comes from the urethra at the end of the penis that is not urine, precum or semen.
Mutual monogamy is a form of monogamy that exists when two partners agree to be sexually active with only one another. Being in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship reduces the risk of acquiring a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is one of the most reliable ways to avoid STIs. Those who choose mutual monogamy can be tested before the sexual relationship to be certain they are not infected. This strategy for the prevention of acquiring a sexually transmitted infection requires that each partner remain faithful and does not engage in sexual activity with another partner.
Human sexual promiscuity is the practice of having many different sexual partners. In the case of men, this behavior of sexual nondiscrimination and hypersexuality is referred to as satyriasis, while in the case of women, this behavior is conventionally known as nymphomania. Both conditions are regarded as possibly compulsive and pathological qualities, closely related to hyper-sexuality. The results of, or costs associated with, these behaviors are the effects of human sexual promiscuity.











