
Medicare is a federal health insurance program in the United States for people age 65 or older and younger people with disabilities, including those with end stage renal disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It was begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration and is now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS).

The healthcare industry is an aggregation and integration of sectors within the economic system that provides goods and services to treat patients with curative, preventive, rehabilitative, and palliative care. It encompasses the creation and commercialization of products and services conducive to the preservation and restoration of well-being. The contemporary healthcare sector comprises three fundamental facets, namely services, products, and finance. It can be further subdivided into numerous sectors and categories and relies on interdisciplinary teams of highly skilled professionals and paraprofessionals to address the healthcare requirements of both individuals and communities.
Prescription drug list prices in the United States continually are among the highest in the world. The high cost of prescription drugs became a major topic of discussion in the 21st century, leading up to the American health care reform debate of 2009, and received renewed attention in 2015. One major reason for high prescription drug prices in the United States relative to other countries is the inability of government-granted monopolies in the American health care sector to use their bargaining power to negotiate lower prices, and the American payer ends up subsidizing the world's R&D spending on drugs.

The Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act, also called the Medicare Modernization Act or MMA, is a federal law of the United States, enacted in 2003. It produced the largest overhaul of Medicare in the public health program's 38-year history.

The Cigna Group is an American multinational managed healthcare and insurance company based in Bloomfield, Connecticut. Its insurance subsidiaries are major providers of medical, dental, disability, life and accident insurance and related products and services, the majority of which are offered through employers and other groups. Cigna is incorporated in Delaware.
Humana Inc. is a for-profit American health insurance company based in Louisville, Kentucky. In 2023, the company ranked 42 on the Fortune 500 list, which made it the highest ranked company based in Kentucky. It is the fourth largest health insurance provider in the U.S.
Single-payer healthcare is a type of universal healthcare, in which the costs of essential healthcare for all residents are covered by a single public system. Single-payer systems may contract for healthcare services from private organizations or may own and employ healthcare resources and personnel. "Single-payer" describes the mechanism by which healthcare is paid for by a single public authority, not a private authority, nor a mix of both.
The term managed care or managed healthcare is used in the United States to describe a group of activities intended to reduce the cost of providing health care and providing American health insurance while improving the quality of that care. It has become the predominant system of delivering and receiving American health care since its implementation in the early 1980s, and has been largely unaffected by the Affordable Care Act of 2010.
...intended to reduce unnecessary health care costs through a variety of mechanisms, including: economic incentives for physicians and patients to select less costly forms of care; programs for reviewing the medical necessity of specific services; increased beneficiary cost sharing; controls on inpatient admissions and lengths of stay; the establishment of cost-sharing incentives for outpatient surgery; selective contracting with health care providers; and the intensive management of high-cost health care cases. The programs may be provided in a variety of settings, such as Health Maintenance Organizations and Preferred Provider Organizations.
Families USA is a nonprofit, nonpartisan consumer health advocacy and policy organization.
AHIP is an American political advocacy and trade association of health insurance companies that offer coverage through the employer-provided, Medicare Advantage, Medicaid managed care, and individual markets.

The Medicare for All Act, also known as the Expanded and Improved Medicare for All Act or United States National Health Care Act, is a bill first introduced in the United States House of Representatives by Representative John Conyers (D-MI) in 2003, with 38 co-sponsors. In 2019, the original 16-year-old proposal was renumbered, and Pramila Jayapal (D-WA) introduced a broadly similar, but more detailed, bill, HR 1384, in the 116th Congress. As of November 3, 2019, it had 116 co-sponsors still in the House at the time, or 49.8% of House Democrats.
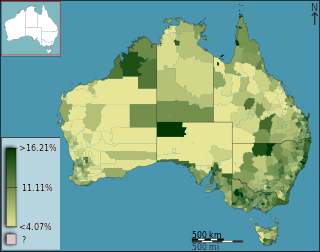
Health care in Australia operates under a shared public-private model underpinned by the Medicare system, the national single-payer funding model. State and territory governments operate public health facilities where eligible patients receive care free of charge. Primary health services, such as GP clinics, are privately owned in most situations, but attract Medicare rebates. Australian citizens, permanent residents, and some visitors and visa holders are eligible for health services under the Medicare system. Individuals are encouraged through tax surcharges to purchase health insurance to cover services offered in the private sector, and further fund health care.
In the United States, health insurance helps pay for medical expenses through privately purchased insurance, social insurance, or a social welfare program funded by the government. Synonyms for this usage include "health coverage", "health care coverage", and "health benefits". In a more technical sense, the term "health insurance" is used to describe any form of insurance providing protection against the costs of medical services. This usage includes both private insurance programs and social insurance programs such as Medicare, which pools resources and spreads the financial risk associated with major medical expenses across the entire population to protect everyone, as well as social welfare programs like Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program, which both provide assistance to people who cannot afford health coverage.
Healthcare reform in the United States has had a long history. Reforms have often been proposed but have rarely been accomplished. In 2010, landmark reform was passed through two federal statutes: the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), signed March 23, 2010, and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010, which amended the PPACA and became law on March 30, 2010.

The American Hospital Association (AHA) is a health care industry trade group. It includes nearly 5,000 hospitals and health care providers.

Wendell Potter is an American advocate for health insurance payment reform, New York Times bestselling author, and former health insurance industry communications director. A critic of HMOs and the tactics used by health insurers, Potter is also a leading national advocate for major reforms of the health insurance industry, including Medicare for All and universal health care.
Healthcare Leadership Council is an organization of Chief Executive Officers from several companies and organizations associated with the health care field in the United States. Membership includes heads of health insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers, pharmacy chains, hospitals, and others. The organization's website describes it as "a coalition of chief executives from all disciplines within American healthcare" and a "forum ... to jointly develop policies, plans, and programs to achieve their vision of a 21st century system that makes affordable, high-quality care accessible to all Americans."

Healthcare in the United States is largely provided by private sector healthcare facilities, and paid for by a combination of public programs, private insurance, and out-of-pocket payments. The U.S. is the only developed country without a system of universal healthcare, and a significant proportion of its population lacks health insurance. The United States spends more on healthcare than any other country, both in absolute terms and as a percentage of GDP; however, this expenditure does not necessarily translate into better overall health outcomes compared to other developed nations. Coverage varies widely across the population, with certain groups, such as the elderly and low-income individuals, receiving more comprehensive care through government programs such as Medicaid and Medicare.
Stephen A. Huffman is a Republican member of the Ohio Senate, representing the 5th district since 2019. Previously, Huffman served two terms in the Ohio House of Representatives.
Center Forward is an American political action committee advocating selected policies in the United States government. The group has been heavily funded with dark money donations from the pharmaceutical industry's lobbying group.








