Description
The bomb consisted of a block of explosive, into which was inserted a metal tube of about 7 cm containing an OTO Mod. 35 hand grenade (known to the British as the "Red Devil") to serve as a detonator. The whole assembly was then covered with a canvas bag fitted with a transport hook.
Built in two variants of 1 kg and 2 kg, they required a good physical strength for the launch because of the weight but they were only effective if launched precisely on the engine compartment, in which case they were able to destroy any armored vehicle. For this reason the soldier who wanted to use it necessarily had to approach the objective avoiding being hit by machine-gun fire on board or by the infantry who followed the tanks during their advance. [1]
In 1942 samples of "Pazzaglia" Bombs were sent to be studied in Italy by the military engineering but they never were mass-produced in homeland factory. [2]
Operative use
For an effective launch the bomb must be handled with the right hand on the handle and using the left hand to withdraw the safe. To be properly launched it had to be thrown by standing up with a circular path from 'top down and possibly at least 20/25 mt.
Normally Italian soldiers, when they judged the distance of their objective, jumped out of their defensive positions (trenches or holes) and rushed to approach the tank. Other times crawling in between the moving carts and, to avoid being crushed by the tracks, even leaving that these would pass over them and then get up and launch their weapons after the tank had passed.
Besides the risk of being hit by enemy weapons or being crushed by the tracks, the same use of the bomb was dangerous because high flames immediately blazed with its explosion of the engine compartment, also hot hydraulic fluid squirted in all directions and ammunition inside the tank could explode.
Seeing in action the Italian Bersaglieri with their Passaglia, Erwin Rommel wrote in his commentary: «The German soldiers have impressed the world but the Italian bersaglieri have impressed the German soldiers».

A rocket-propelled grenade (RPG) is a shoulder-fired rocket weapon that launches rockets equipped with an explosive warhead. Most RPGs can be carried by an individual soldier, and are frequently used as anti-tank weapons. These warheads are affixed to a rocket motor which propels the RPG towards the target and they are stabilized in flight with fins. Some types of RPG are reloadable with new rocket-propelled grenades, while others are single-use. RPGs are generally loaded from the front.

The BMP-1 is a Soviet amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle that has been in service from 1966 to the present. BMP stands for Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty 1, meaning "infantry fighting vehicle, 1st serial model". The BMP-1 was the first mass-produced infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) of the Soviet Union. It was called the M-1967, BMP and BMP-76PB by NATO before its correct designation was known.

The Projector, Infantry, Anti Tank (PIAT) Mk I was a British man-portable anti-tank weapon developed during the Second World War. The PIAT was designed in 1942 in response to the British Army's need for a more effective infantry anti-tank weapon and entered service in 1943.

A bazooka is a man-portable recoilless anti-tank rocket launcher weapon, widely deployed by the United States Army, especially during World War II. Also referred to as the "stovepipe", the innovative bazooka was among the first generation of rocket-propelled anti-tank weapons used in infantry combat. Featuring a solid-propellant rocket for propulsion, it allowed for high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) shaped charge warheads to be delivered against armored vehicles, machine gun nests, and fortified bunkers at ranges beyond that of a standard thrown grenade or mine. The universally applied nickname arose from the M1 variant's vague resemblance to the musical instrument called a bazooka invented and popularized by 1930s American comedian Bob Burns.

Anti-tank warfare originated during World War I from the desire to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks. After the Allies deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire introduced the first anti-tank weapons. The first developed anti-tank weapon was a scaled-up bolt-action rifle, the Mauser 1918 T-Gewehr, that fired a 13.2 mm cartridge with a solid bullet that could penetrate the thin armor used by tanks at that time and destroy the engine or ricochet inside, killing occupants. Because tanks represent an enemy's strong force projection on land, military strategists have incorporated anti-tank warfare into the doctrine of nearly every combat service since. The most predominant anti-tank weapons at the start of World War II in 1939 included the tank-mounted gun, anti-tank guns and anti-tank grenades used by the infantry, and ground-attack aircraft.

Technology during World War I (1914–1918) reflected a trend toward industrialism and the application of mass-production methods to weapons and to the technology of warfare in general. This trend began at least fifty years prior to World War I during the American Civil War of 1861–1865, and continued through many smaller conflicts in which soldiers and strategists tested new weapons.

Team Fortress Classic is a first-person shooter game developed by Valve and published by Sierra Studios. It was originally released in April 1999 for Windows, and is based on Team Fortress, a mod for the 1996 game Quake. The game puts two teams against each other in online multiplayer matches; each member plays as one of nine classes, each with different skills. The scenarios include capture the flag, territorial control, and escorting a "VIP" player.

An anti-materiel rifle (AMR) is a rifle designed for use against military equipment, structures, and other hardware (materiel) targets. Anti-materiel rifles are chambered in significantly larger calibers than conventional rifles and are employed to eliminate equipment such as engines and unarmored or lightly armored targets. While modern armored vehicles are resistant to anti-materiel rifles, the extended range and penetration still has many modern applications. Although not intended for use against human targets, the bullet weight and velocity of anti-materiel rifles gives them exceptional long-range capability even when compared with designated sniper rifles. Anti-materiel rifles are made in both bolt-action as well as semi-automatic designs.

Arditi was the name adopted by a Royal Italian Army elite special force of World War I. They and the opposing German Stormtroopers were the first modern shock troops, and they have been called "the most feared corps by opposing armies".

The C1 Ariete is a 3rd generation main battle tank of the Italian Army, developed by Consorzio Iveco Oto Melara (CIO), a consortium formed by IVECO and OTO Melara. The chassis and engine were produced by Iveco, while the turret and fire-control system were supplied by OTO Melara. The vehicle carries the latest optical and digital-imaging and fire-control systems, enabling it to fight day and night and to fire on the move. Six prototypes were developed by 1988, which were subject to intensive testing. The following year the vehicles travelled a combined 16,000 km. Deliveries were first planned for 1993, and took place in 1994 due to delays. Final delivery occurred 7 years later in August 2002.

The Dardo is an infantry fighting vehicle designed for the Italian Army as a replacement for the M113 APC. It is designed and built by the Iveco Fiat Oto Melara Syndicated Company based in Rome. Iveco is responsible for the hull and propulsion systems, while Oto Melara is responsible for the weapons and fire control systems.
RPG-76 Komar is a disposable one-shot anti-tank grenade launcher that fires an unguided anti-tank rocket-propelled grenade. The weapon was designed as a smaller and lighter alternative to the RPG-7, especially for use by airborne troops. Thanks to jet nozzles located between the warhead and the fuel compartment, it can be fired from inside of a building or a vehicle.
An anti-tank grenade is a specialized hand-thrown grenade used to defeat armored targets. Although their inherently short range limits the usefulness of grenades, troops can lie in ambush or maneuver under cover to exploit the limited outward visibility of the crew in a target vehicle. Hand launched anti-tank grenades became redundant with the introduction of standoff rocket propelled grenades and man-portable anti-tank systems.

The Breda Mod. 35 is a hand grenade issued to the Royal Italian Army during World War II.

The Breda Mod. 42 was an anti-tank grenade, developed by Breda, supplied to the Royal Italian Army during World War II.

The OTO Mod. 35 was a hand grenade issued to the Regio Esercito during World War II.
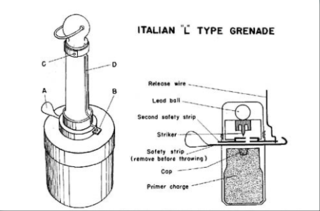
The Type L is an anti-tank hand grenade provided to the Royal Italian Army during World War II.

The OTO Mod. 42 is an incendiary anti-tank hand grenade supplied to the Royal Italian Army during World War II.
















