
Costume is the distinctive style of dress and/or makeup of an individual or group that reflects class, gender, occupation, ethnicity, nationality, activity or epoch—in short, culture.

Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with a sewing needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic era. Before the invention of spinning yarn or weaving fabric, archaeologists believe Stone Age people across Europe and Asia sewed fur and leather clothing using bone, antler or ivory sewing-needles and "thread" made of various animal body parts including sinew, catgut, and veins.

A T-shirt is a style of fabric shirt named after the T shape of its body and sleeves. Traditionally, it has short sleeves and a round neckline, known as a crew neck, which lacks a collar. T-shirts are generally made of stretchy, light, and inexpensive fabric and are easy to clean. The T-shirt evolved from undergarments used in the 19th century and, in the mid-20th century, transitioned from undergarments to general-use casual clothing.

Machine embroidery is an embroidery process whereby a sewing machine or embroidery machine is used to create patterns on textiles. It is used commercially in product branding, corporate advertising, and uniform adornment. It is also used in the fashion industry to decorate garments and apparel. Machine embroidery is used by hobbyists and crafters to decorate gifts, clothing, and home decor. Examples include designs on quilts, pillows, and wall hangings.

Pattern grading is the process of turning base size or sample size patterns into additional sizes using a size specification sheet or grading increments. This can be done manually or digitally using computerized pattern drafting software.

Costume design is the creation of clothing for the overall appearance of a character or performer. Costume may refer to the style of dress particular to a nation, a social class, or a period. In many cases, it may contribute to the fullness of the artistic, visual world which is unique to a particular theatrical or cinematic production. The most basic designs are produced to denote status, provide protection or modesty, or provide visual interest to a character. Costumes may be for a theater, cinema, musical performance, cosplay, parties, or other events. Costume design should not be confused with costume coordination which merely involves altering existing clothing, although both create stage clothes.

A dressmaker, also known as a seamstress, is a person who makes clothing for women, such as dresses, blouses, and evening gowns. Dressmakers were historically known as mantua-makers, and are also known as a modiste or fabrician.
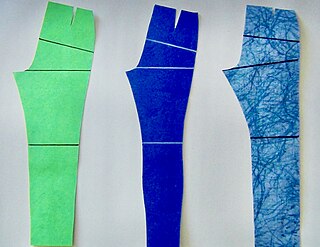
In sewing and fashion design, a pattern is the template from which the parts of a garment are traced onto woven or knitted fabrics before being cut out and assembled. Patterns are usually made of paper, and are sometimes made of sturdier materials like paperboard or cardboard if they need to be more robust to withstand repeated use. The process of making or cutting patterns is sometimes compounded to the one-word patternmaking, but it can also be written pattern(-)making or pattern cutting.

Bespoke tailoring or custom tailoring is clothing made to an individual buyer's specifications by a tailor. Bespoke garments are completely unique and created without the use of a pre-existing pattern, while made to measure uses a standard-sized pattern altered to fit the customer.

Designer clothing is clothing designed by a particular fashion designer or licensed by a person or brand. It is often luxury clothing proven to be high quality and haute couture for the general public, made by, or carrying the label of, a well-known designer. Licensing of designer names has been a common practice within the fashion industry since about the 1970s. Designer clothing comprises numerous types of apparel, including designer jeans that often cost several hundreds of dollars.
Shirin Guild is an Iranian-born British fashion designer. Her fashion label was established in London, in 1991. Her clothing design is minimalist and she has reworked Iranian clothing traditions through a "reductionist aesthetic". Her design work has been described as "trans-cultural".

A wrap dress is generic term for a dress with a front closure formed by wrapping one side across the other, and is fastened at the side or tied at the back. This forms a V-shaped neckline. A faux wrap dress resembles this design, except that it comes already fastened together with no opening in front, but instead is slipped on over the head. A wrap top is a top cut and constructed in the same way as a wrap dress, but without a skirt. The design of wrap-style closure in European garments was the results of the heavy influences of Orientalism which was popular in the 19th century.

In casting, a pattern is a replica of the object to be cast, used to form the sand mould cavity into which molten metal is poured during the casting process. Once the pattern has been used to form the sand mould cavity, the pattern is then removed, Molten metal is then poured into the sand mould cavity to produce the casting. The pattern is non consumable and can be reused to produce further sand moulds almost indefinitely.

Fashion design is the art of applying design, aesthetics, clothing construction and natural beauty to clothing and its accessories. It is influenced by culture and different trends, and has varied over time and place. "A fashion designer creates clothing, including dresses, suits, pants, and skirts, and accessories like shoes and handbags, for consumers. He or she can specialize in clothing, accessory, or jewelry design, or may work in more than one of these areas."
Advanced Fashion Design and Technology is a fashion-related manufacturing process that integrates new technologies.

Darts are folds sewn into fabric to take in ease and provide shape to a garment, especially for a woman's bust. They are used frequently in all sorts of clothing to tailor the garment to the wearer's shape, or to make an innovative shape in the garment. Fabric may be thought of as flat, and a dart has the effect of removing a wedge shaped piece and pulling the edges of that wedge together to create a shallow cone. This effect can be seen quite easily with a paper pattern by pulling together the edges of a dart intake as it would be sewn. Since fabric is generally more flexible than paper, the fabric will shift around the apex of the cone and form a softer, but still curved, shape. In a garment, a dart ends in a point at a full area of the body.
Zero-waste fashion refers to a fashion design strategy, that generates little or no textile waste during the production process, particularly focusing on the pattern making and cutting stages. It is a reaction to the high amount of discarded clothing items going into landfills around the world.
In sewing and patternmaking, ease is the amount of room a garment allows the wearer beyond the measurements of their body. For example, if a man has a 40-inch chest measurement, a jacket with a 40-inch chest would be very tight and would constrict movement. An ease of 3 or 4 inches might be added to the pattern, or more to enhance comfort or style. Ease is not generally included in sizing measurements. To use the example again, a man with a 40-inch chest will likely buy a jacket advertised as size 40, but the actual measurements of the garment will almost always be somewhat larger.

Manus x Machina: Fashion in an Age of Technology was an exhibition at the Metropolitan Museum of Art that showcased the dichotomy between Manus, also known as haute couture, and Machina, also known as prêt-à-porter. The Metropolitan Museum of Art debuted this exhibition during the 2016 Met Gala and ran it from May 5, 2016 to September 5, 2016. It included over 120 pieces from designers like Chanel and Christian Dior, varying from the 20th Century to present day.
The Portland Fashion Institute (PFI) is a private, nonprofit nationally accredited career institute of higher learning located in Portland, Oregon. It focuses on design, technology and business connected to the fashion industry. It was founded in 2010. It is Oregon's only accredited fashion design school.














