
Joseph Oswald Mauborgne co-invented the one-time pad with Gilbert Vernam of Bell Labs. In 1914 he published the first recorded solution of the Playfair cipher. Mauborgne became a Major General in the United States Army, and from October 1937 to his retirement in 1941 was the Army's 12th Chief Signal Officer, in command of the Signal Corps.

The SCR-270 was one of the first operational early-warning radars. It was the U.S. Army's primary long-distance radar throughout World War II and was deployed around the world. Its also known as the Pearl Harbor Radar, since it was an SCR-270 set that detected the incoming raid about 45 minutes before the December 7, 1941, attack on Pearl Harbor commenced.

The history of radar started with experiments by Heinrich Hertz in the late 19th century that showed that radio waves were reflected by metallic objects. This possibility was suggested in James Clerk Maxwell's seminal work on electromagnetism. However, it was not until the early 20th century that systems able to use these principles were becoming widely available, and it was German inventor Christian Hülsmeyer who first used them to build a simple ship detection device intended to help avoid collisions in fog. True radar, such as the British ‘Chain Home’ early warning system provided directional information to objects over short ranges, were developed over the next two decades.

The United States Army Signal Corps (USASC) is a branch of the United States Army that creates and manages communications and information systems for the command and control of combined arms forces. It was established in 1860, the brainchild of Major Albert J. Myer, and had an important role in the American Civil War. Over its history, it had the initial responsibility for portfolios and new technologies that were eventually transferred to other U.S. government entities. Such responsibilities included military intelligence, weather forecasting, and aviation.
Northrop Grumman Electronic Systems (NGES) was a sector of Northrop Grumman from 1996 to 2015 until a reorganization on January 1, 2016 merged other Northrop Grumman businesses into NGES to form a new sector called Mission Systems. NGES had originally been created by Northrop Grumman's acquisition of Westinghouse Electronic Systems Group in 1996. The Electronic Systems sector was a leading designer, developer, and manufacturer of a wide variety of advanced defense electronics and systems. The division had 120 locations worldwide, including 72 international offices, and approximately 24,000 employees. Accounting for 20% of company sales in 2005, it was the single largest sector in the corporation.

Camp Evans Historic District is an area of the Camp Evans Formerly Used Defense Site in Wall Township, New Jersey. The site of the military installation is noted for a 1914 transatlantic radio receiver and various World War II/Cold War laboratories of the United States Army. It was designated a National Historic Landmark District in 2012, in recognition of the site's long role in the development of modern civilian and military electronic communications.

The SCR-268 was the United States Army's first radar system. Introduced in 1940, it was developed to provide accurate aiming information for antiaircraft artillery and was also used for gun laying systems and directing searchlights against aircraft. The radar was widely utilized by both Army and Marine Corps air defense and early warning units during World War II. By the end of World War II the system was already considered out of date, having been replaced by the much smaller and more accurate SCR-584 microwave-based system.

The CXAM radar system was the first production radar system deployed on United States Navy ships, operating in the mid-high VHF frequency band of 200 MHz. It followed several earlier prototype systems, such as the NRL radar installed in April 1937 on the destroyer Leary; its successor, the XAF, installed in December 1938 on the battleship New York; and the first RCA-designed system, the CXZ, installed in December 1938 or January 1939 on the battleship Texas. Based on testing in January 1939, where the XAF was more reliable, the US Navy ordered RCA to build six XAF-based units for deployment and then shortly thereafter ordered 14 more.

The SCR-584 was an automatic-tracking microwave radar developed by the MIT Radiation Laboratory during World War II. It was one of the most advanced ground-based radars of its era, and became one of the primary gun laying radars used worldwide well into the 1950s. A trailer-mounted mobile version was the SCR-784.

The Opana Radar Site is a National Historic Landmark and IEEE Milestone that commemorates the first operational use of radar by the United States in wartime, during the attack on Pearl Harbor. It is located off the Kamehameha Highway just inland from the north shore of Oahu, Hawaii, south of Kawela Bay. It is not open to the public.

The Communications-Electronics Command (CECOM) is a Life Cycle Management Command (LCMC) of the United States Army based at Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland, United States. It is one of four such commands under the Army Materiel Command (AMC), and is the Army's provider and maintainer of Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Cyber, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (C5ISR) capabilities.
Signal Corps Laboratories (SCL) was formed on June 30, 1930, as part of the U.S. Army Signal Corps at Fort Monmouth, New Jersey. Through the years, the SCL had a number of changes in name, but remained the operation providing research and development services for the Signal Corps.
Harold Adelbert Zahl was an American physicist who had a 35-year career with the U.S. Army Signal Corps Laboratories, where he served as the Director of Research at Fort Monmouth and made major contributions to radar development. He is perhaps most famous for inventing the GA-4 Transmitter-Receiver Tube and the VT-158, which became known as the Zahl tube.

William Richards Blair was an American scientist and United States Army officer, who worked on the development of the radar from the 1930s onward. He led the U.S. Army's Signal Corps Laboratories during its formative years and is often called the "Father of American Radar".

Highlands Air Force Station was a military installation in Middletown Township near the borough of Highlands, New Jersey. The station provided ground-controlled interception radar coverage as part of the Lashup Radar Network and the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment network, as well as providing radar coverage for the Highlands Army Air Defense Site. The site's 240 acres (97 ha) is now the Rocky Point section in Hartshorne Woods Park of the Monmouth County Parks System.
John William Marchetti was a radar pioneer who had an outstanding career combining government and industrial activities. He was born of immigrant parents in Boston, Massachusetts, and entered Columbia College and Columbia School of Engineering and Applied Science in 1925. In a six-year program combining liberal arts and engineering, he earned both A.B. and B.S. degrees, followed by the graduate E.E. degree in 1931. He was employed by New York Edison as a power engineer for several years, during which time he also participated in the U.S. Naval Reserve as an Ensign.
Radar in World War II greatly influenced many important aspects of the conflict. This revolutionary new technology of radio-based detection and tracking was used by both the Allies and Axis powers in World War II, which had evolved independently in a number of nations during the mid 1930s. At the outbreak of war in September 1939, both Great Britain and Germany had functioning radar systems. In Great Britain, it was called RDF, Range and Direction Finding, while in Germany the name Funkmeß (radio-measuring) was used, with apparatuses called Funkmessgerät . By the time of the Battle of Britain in mid-1940, the Royal Air Force (RAF) had fully integrated RDF as part of the national air defence.

The Aircraft Warning Corps (AWC) was a World War II United States Army Air Force organization for Continental United States air defense. The corps' information centers networked an area's "Army Radar Stations" which communicated radar tracks by telephone, and the information centers also integrated visual reports processed by Ground Observer Corps filter centers. The AWC notified air defense command posts of the First Air Force, Second Air Force, Third Air Force, and Fourth Air Force. These command posts would deploy interceptors which used command guidance to achieve ground-controlled interception.

The VT-158, also known as the Zahl tube, was a vacuum tube invented by American physicist Harold A. Zahl in the 1930s and used during World War II and the Korean War. It allowed the radar technology at the time to detect low-flying planes by generating enough power to produce ultrahigh frequency energy.
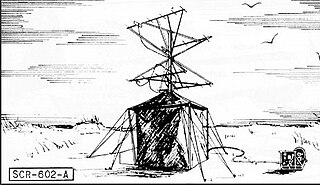
The SCR-602 also known as the AN/TPS-3, was a mobile, lightweight, medium-range, early-warning radar utilized by the United States and its allies during World War II. The radar was originally designed for use during the initial stages of an amphibious assault or military operation where its lightweight relative to other radar systems was a distinct advantage. Once larger radars such as the SCR-270 or AN/TPS-1 came online the SCR-602 could also be used to fill in gaps in radar coverage.