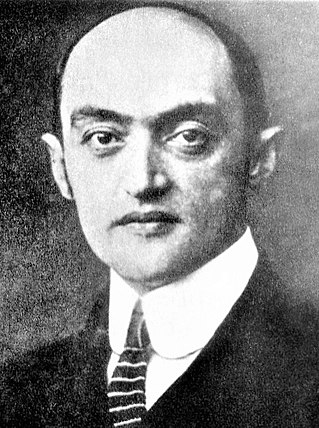In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any other external authority. Proponents of the free market as a normative ideal contrast it with a regulated market, in which a government intervenes in supply and demand by means of various methods such as taxes or regulations. In an idealized free market economy, prices for goods and services are set solely by the bids and offers of the participants.
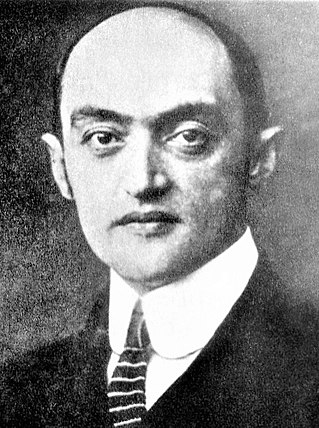
Joseph Alois Schumpeter was an Austrian political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at Harvard University, where he remained until the end of his career, and in 1939 obtained American citizenship.

Economic history is the study of history using methodological tools from economics or with a special attention to economic phenomena. Research is conducted using a combination of historical methods, statistical methods and the application of economic theory to historical situations and institutions. The field can encompass a wide variety of topics, including equality, finance, technology, labour, and business. It emphasizes historicizing the economy itself, analyzing it as a dynamic entity and attempting to provide insights into the way it is structured and conceived.
Creative destruction is a concept in economics that describes a process in which new innovations replace and make obsolete older innovations.

In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and objectives.
The concept of late capitalism was first used by the German social scientist Werner Sombart (1863-1941) in 1928, to describe the new capitalist order emerging at that time - with the claim, that it was the beginning of a new stage in the history of capitalism. As a young man, Sombart was a socialist who associated with Marxist intellectuals and the German social-democratic party. As a mature academic who became well-known for his own sociological writings, Sombart had a sympathetically critical attitude to the ideas of Karl Marx. Sombart's texts and lectures helped to make "capitalism" a household word in Europe, as the name of a socio-economic system with a specific structure and dynamic, a history, a mentality, a dominant morality and a culture.
Business cycles are intervals of general expansion followed by recession in economic performance. The changes in economic activity that characterize business cycles have important implications for the welfare of the general population, government institutions, and private sector firms.
The German historical school of economics. was an approach to academic economics and to public administration that emerged in the 19th century in Germany, and held sway there until well into the 20th century. The professors involved compiled massive economic histories of Germany and Europe. Numerous Americans were their students. The school was opposed by theoretical economists. Prominent leaders included Gustav von Schmoller (1838–1917), and Max Weber (1864–1920) in Germany, and Joseph Schumpeter (1883–1950) in Austria and the United States.

An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making processes, and patterns of consumption that comprise the economic structure of a given community.
In Marxian economics and preceding theories, the problem of primitive accumulation of capital concerns the origin of capital and therefore how class distinctions between possessors and non-possessors came to be.

Imperialism: A Study (1902), by John A. Hobson, is a politico-economic discourse about the negative financial, economic, and moral aspects of imperialism as a nationalistic business enterprise. Hobson argues that capitalist business activity brought about imperialism.
Gu Zhun was a Chinese intellectual, economist and pioneer of post-Marxist Chinese liberalism. A victim of "anti-Rightist" purges, he spent his later life in prisons and reeducation centres.

Giovanni Arrighi was an Italian economist, sociologist and world-systems analyst, from 1998 a Professor of Sociology at Johns Hopkins University. His work has been translated into over fifteen languages.
An economic ideology is a set of views forming the basis of an ideology on how the economy should run. It differentiates itself from economic theory in being normative rather than just explanatory in its approach, whereas the aim of economic theories is to create accurate explanatory models to describe how an economy currently functions. However, the two are closely interrelated, as underlying economic ideology influences the methodology and theory employed in analysis. The diverse ideology and methodology of the 74 Nobel laureates in economics speaks to such interrelation.

Capitalism, Socialism, and Democracy is a book on economics, sociology, and history by Joseph Schumpeter, arguably his most famous, controversial, and important work. It is also one of the most famous, controversial, and important books on social theory, social sciences, and economics—in which Schumpeter deals with capitalism, socialism, and creative destruction. It is the third most cited book in the social sciences published before 1950, behind Marx's Capital and The Wealth of Nations by Adam Smith.

Sustainability measurement is a set of frameworks or indicators used to measure how sustainable something is. This includes processes, products, services and businesses. Sustainability is to quantify. It may even be impossible to measure as there is no fixed definition. To measure sustainability, frameworks and indicators consider environmental, social and economic domains. The metrics vary by use case and are still evolving. They include indicators, benchmarks and audits. They include sustainability standards and certification systems like Fairtrade and Organic. They also involve indices and accounting. They can include assessment, appraisal and other reporting systems. The metrics are used over a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. For organizations, sustainability measures include corporate sustainability reporting and Triple Bottom Line accounting. For countries, they include estimates of the quality of sustainability governance or quality of life measures, or environmental assessments like the Environmental Sustainability Index and Environmental Performance Index. Some methods let us track sustainable development. These include the UN Human Development Index and ecological footprints.
Throughout modern history, a variety of perspectives on capitalism have evolved based on different schools of thought.
Lars Jörgen Pålsson Syll is a Swedish economist who is a Professor of Social Studies and Associate professor of Economic History at Malmö University College. Pålsson Syll has been a prominent contributor to the economic debate in Sweden over the 2007–2008 financial crisis.
Democratic socialism is a left-wing economic and political philosophy that supports political democracy and some form of a socially owned economy, with a particular emphasis on economic democracy, workplace democracy, and workers' self-management within a market socialist, decentralised planned, or democratic centrally planned socialist economy. Democratic socialists argue that capitalism is inherently incompatible with the values of freedom, equality, and solidarity and that these ideals can only be achieved through the realisation of a socialist society. Although most democratic socialists seek a gradual transition to socialism, democratic socialism can support revolutionary or reformist politics to establish socialism. Democratic socialism was popularised by socialists who opposed the backsliding towards a one-party state in the Soviet Union and other countries during the 20th century.
Crisis theory, concerning the causes and consequences of the tendency for the rate of profit to fall in a capitalist system, is associated with Marxian critique of political economy, and was further popularised through Marxist economics.